Question
Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (EDS) type IV is a result of a mutation in the COL3A1 gene, which results in the deletion of one of the exons in the
procollagen transcript.
(a) Describe the location in the cell where the splicing of exons occurs.
(b) Explain the difference between exons and introns.
(c) Predict the effect of the EDS mutation on the structure of the procollagen protein.
(d) Justify your prediction from part (c).
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a) The splicing of exons occurs in the nucleus.
(b) The codons in exons are expressed in the protein and code for
amino acids in the protein. Introns are noncoding sequences and do
not code for amino acids in the protein.
(c) The EDS mutation would result in a shorter, less functional
procollagen protein.
(d) If an exon was deleted, the resulting mRNA transcript would not
contain the complete code for the protein. So the translated protein
would be shorter and likely less functional.
Question
A mutation results in the deletion of the TATA box in the promoter of a eukaryotic gene.
(a) Describe the function of the promoter in gene expression.
(b) Explain why promoter sequences are highly conserved in living organisms.
(c) The figure that follows shows the gene and the DNA surrounding it. Draw an “X” on the most likely location of the promoter of the gene.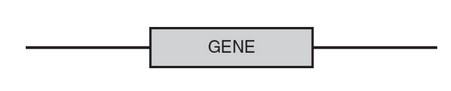
(d) Explain how the deletion of the TATA box in the promoter would most likely affect the levels of protein produced by the gene.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a) The promoter serves as a binding site for RNA polymerase at
which transcription begins.
(b) All living organisms use RNA polymerase, an enzyme that has a
consistent three-dimensional shape. All living organisms need
similar nucleotide sequences in their promoters that RNA
polymerase can recognize.
(c)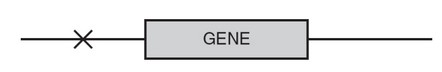
(Note that any “X” to the left of the gene is acceptable.)
(d) The deletion of the TATA box in the promoter would most likely
make it more difficult for RNA polymerase to recognize the
promoter. Less transcription would occur, and less protein would
be produced.
Question
Refer to the following information.
Antibodies are the one of the most abundant proteins in the blood (they make up about 20% of the plasma proteins). One of the five classes of
antibodies is shown as follows.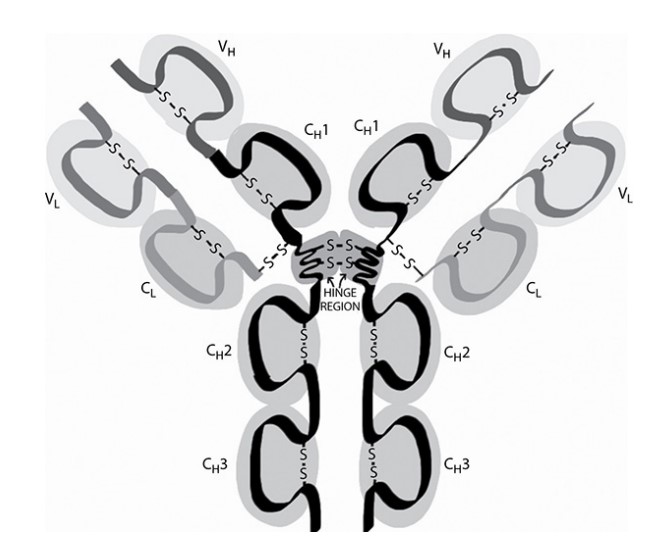
Each antibody contains four polypeptide chains: two identical heavy chains and two identical light chains. Each heavy chain has a 110 amino
acid variable region \((V_H)\) and a 330–440 amino acid constant region \((C_H1\), 2, and 3). Each light chain has a 110 amino acid variable \((V_L)\) region and a 110 amino acid constant region \((C_L )\). There are several disulfide bonds holding the structure together (indicated by S–S).
These antibodies are made by B-lymphocyte cells. During development of a B cell, the randomly chosen V gene is moved to lie next to a J gene
segment (3 in the diagram). The extra J segment (J is joining segment) and the intron are transcribed and then removed by splicing, and the V3 and J3 are joined together.
Explain why antibody diversity is an advantage to an organism.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
The greater the diversity of the antibody segments in an organism,
the greater the diversity of antibodies it can generate and the greater the
number of pathogens it can recognize. A pathogen’s surface usually has
more than one recognition site (antigenic determinant, epitope), so that with a broad diversity of antibodies there may be several kinds than can bind to one particular pathogen, increasing the effectiveness of the immune response.
Pathogens evolve and change to evade host immune systems, so the
greater the diversity of the host immune system, the less likely the evolution
of the pathogen will allow it to escape detection.
