Question.
Certain human conditions result from changes in the DNA sequence. The following is a segment of the template strand of an open reading frame of a functional gene.
3′ . . . GTT CAT CTA ACC CCT GAG GAG . . . 5′
(a) Using the segment shown above, determine the sequence of the corresponding mRNA sequence. Indicate the 5′ and 3′ ends.
(b) Using the table provided, determine the amino acid sequence of the polypeptide fragment.
(c) The mutation results in the following sequence:
3′ . . . GTT CAT CTA ACC CCT GTG GAG . . . 5′
Determine the change in the primary structure of the protein due to this mutation, and explain how this change may lead to a change in the function of the protein.
(d) Describe ONE common human genetic condition that is caused by this type of mutation, including the effect of the change in protein function on the health of the affected individual.
(e) Describe TWO techniques that can be used to identify the presence of this type of genetic change.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Certain human conditions result from changes in the DNA sequence. The following is a segment of the template strand of an open reading frame of a functional gene.
3′ . . . GTT CAT CTA ACC CCT GAG GAG . . . 5′
(a) Using the segment shown above, determine the sequence of the corresponding mRNA sequence. Indicate the 5′ and 3′ ends. (2 points maximum: 1 point for correct sequence with a maximum of one error; 1 point for proper orientation of the 5′ and 3′ ends)
5′ . . . CAA GUA GAU UGG GGA CUC CUC . . . 3′
(b) Using the table provided, determine the amino acid sequence of the polypeptide fragment. (2 points for
correct sequence; only 1 point if sequence contains an error)
gln – val – asp – trp – gly – his – leu
Changed AA may lead to a change in the structure of the protein. Possible elaboration points:
• Change is in the folding into the tertiary or quaternary structure.
• Some AA side groups are more important than others, e.g., cysteine forms disulfide bridges.
• Some AA can be interchanged with no effect on the structure due to lack of interactive side groups.
• Change to enzyme’s active or allosteric site is especially damaging.
• Others as appropriate.
(d)
Common conditions include:
• Tay-sachs
• Sickle-cell anemia
• Increased cancer risk (P53 gene)
• Cystic fibrosis
• Hemophilia
• Others as appropriate
(e)
Techniques include:
• Microarray assays to compare novel and mutant DNA
• DNA sequencing
• RFLP markers
• Presence of diagnostic phenotype
• Specific marker for mutated sequence
• Others as appropriate (Note: VNTR and Karyotyping are not appropriate techniques.)
Question
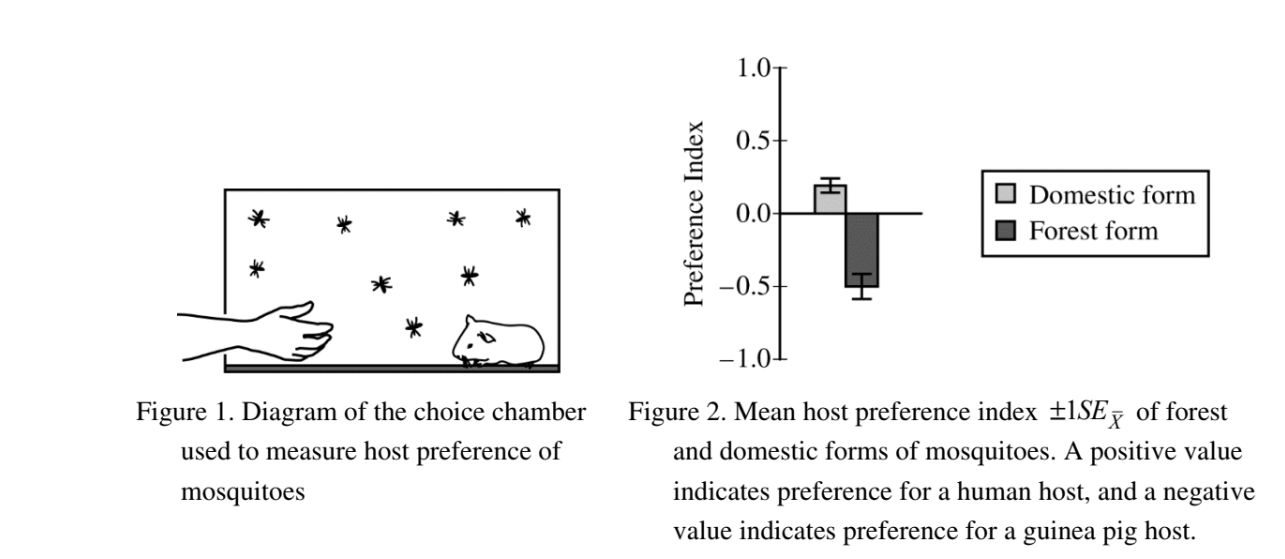
The yellow-fever mosquito (Aedes aegypti) is a major vector of human disease. In a particular location in Africa, there are two forms of the mosquito. The forest form of the mosquito is black and often lays its eggs in tree holes and pools of water in the forest. The domestic form of the mosquito is brown and prefers to lay its eggs in rainwater collected near human dwellings. Researchers used a choice chamber (Figure 1) to investigate the host preference of A. aegypti. The researchers recorded the number of forest-form and domestic-form mosquitoes that bit human or guinea pig hosts during several ten-minute trials. The researchers used these data to calculate a host-preference index for each form, as shown in Figure 2. Researchers also identified a gene in the mosquitoes, OR4, that encodes an olfactory receptor. A volatile odorant, sulcatone, binds to the OR4 receptor. Humans produce higher levels of sulcatone than do guinea pigs.
(a) Based on an analysis of the data, identify the preferred host of the forest form and of the domestic form of the mosquito.
(b) Propose a refinement to the initial experimental design that will rule out the possibility that preference is based on a visual cue. Propose a different refinement to the initial experiment to test whether sulcatone is the attractant for the human-preferring form.
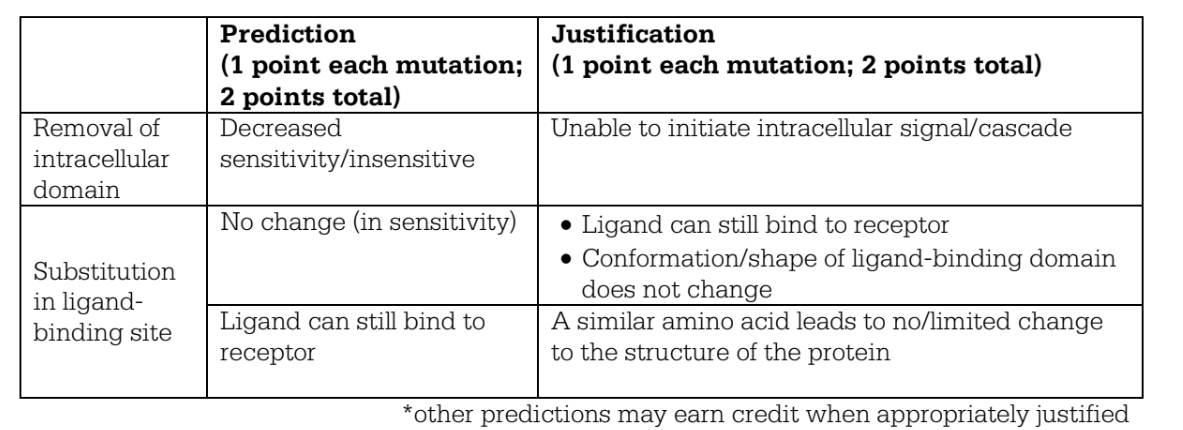
(c) Predict how each of the following mutations in the OR4 gene would most likely affect the sensitivity of mosquitoes to sulcatone. Justify each prediction. A mutation that results in the removal of the intracellular domain of the receptor protein A mutation that results in the substitution of a small hydrophobic amino acid for another small hydrophobic amino acid in the ligand-binding site of the receptor protein
(d) A researcher proposes that the two forms of mosquito are evolving into two different species. Identify ONE potential postzygotic isolating mechanism, and describe how the isolating mechanism would result in the evolution of the two forms into different species.
▶️Answer/Explanation
(a) Identification (2 points)
• Forest mosquitoes prefer guinea pig
• Domestic mosquitoes prefer human hosts
(b) Refinement: visual (1 point)
• Use a dark/no light box
• Cover the guinea pig/hand
• Use guinea pig/hand models
• Stop movement of guinea pig/hand
• Blind mosquitoes
Refinement: sulcatone (1 point)
• Use cotton ball/guinea pig/guinea-pig model soaked in sulcatone vs. control without sulcatone
• Use gloved/covered human hand that prevents odorant molecules from being released
•Remove or alter the \(OR_4 \) gene in mosquitoes
(c)
(d)Identification (1 point)
Hybrid inviability
Hybrid sterility
Reduced hybrid fitness/hybrid breakdown
Description (1 point)
Maintains reproductive isolation
Prevents gene flow
Question.
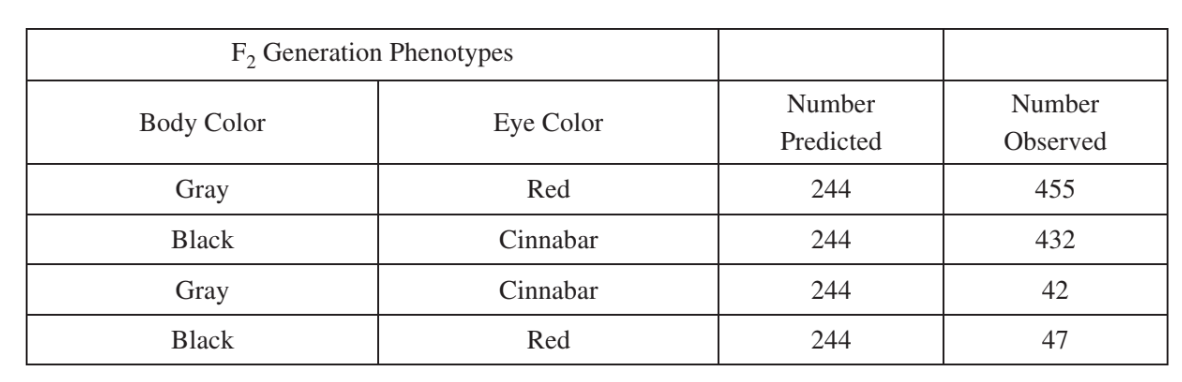
Fruit flies (Drosophila melanogaster) with a wild-type phenotype have gray bodies and red eyes. Certain mutations can cause changes to these traits. Mutant flies may have a black body and/or cinnabar eyes. To study the genetics of these traits, a researcher crossed a true-breeding wild-type male fly (with gray body and red eyes) with a true-breeding female fly with a black body and cinnabar eyes. All of the \(F_1\) progeny displayed a wild-type phenotype. Female flies from the\( F_1\) generation were crossed with true-breeding male flies with black bodies and cinnabar eyes. The table below represents the predicted outcome and the data obtained from the cross.
Explain the difference between the expected data and the actual numbers observed.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Student explanations include the following:
• Prediction of a 1:1:1:1 ratio with correct phenotypes based on independent assortment.
• Support for prediction with a diagram of the cross of BbEe x bbee.
• Correct application of chi-square analysis to show that observed results do not conform to expected Mendelian frequencies.
• Identification of body color and eye color as linked genes/loci.
• Use of ratios to show linkage and independent assortment of wing typeversus linked traits.
• Identification of the bottom two phenotypes as products of crossing over (recombinant chromosome).
• Mentioning that crossover rate is approximately 9–10 percent.