Question
Wild guppies (Poecilia reticulata) live in ponds on the island of Trinidad. Male guppies have great variation in the number and colors of spots, leading to a wide variety of color patterns among male guppies. Female guppies do not express these spots and are drably colored. Female guppies will more often choose to mate with males who possess bright color patterns. However, males with brighter color patterns are more visible to predators. An experiment was performed to measure the effect of the presence of a guppy predator (Cichlidae alta) on the number of spots in male guppies. Guppies were placed into two different environments: one with no predators and the other in which C. alta was present. Guppies were allowed to reproduce in both environments for 20 generations. After 20 generations, the number of spots on each male guppy was counted. The mean number of spots on male guppies is shown in the table.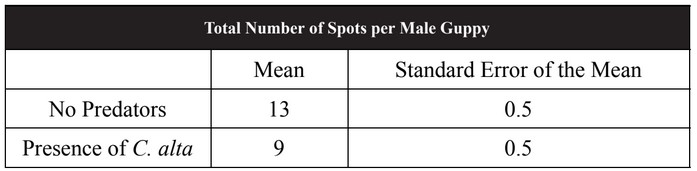
(a) Describe the type of selection (directional, stabilizing, or disruptive) that is caused by the presence of C. alta.
(b) On the axes provided, construct a graph of the mean number of spots per male guppy for each group. Include 95% confidence intervals on your graph.
(c) Use the graph you constructed in part (b) to make a claim about the mean number of spots per male guppy in the no-predator environment as compared to the mean number of spots per male guppy in the environment with C. alta. Support your claim with evidence from the graph.
(d) As a follow-up experiment, some of the guppies in the environment with C. alta were removed and placed in an environment with no predators. They were allowed to reproduce for 20 generations. Predict what you would expect to happen to the mean number of spots per male guppy in this new predator- free environment after the guppies were allowed to reproduce for 20 generations. Justify your prediction.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a) This is an example of directional selection because in the presence
of the predator C. alta, the mean number of spots per male guppy
decreases.
(b)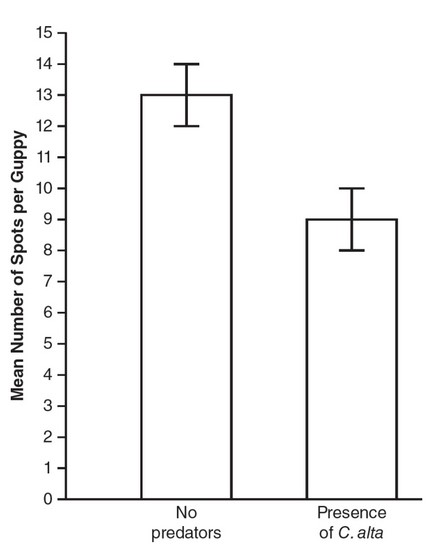
(c) There is a statistically significant difference between the mean
number of spots per guppy in the environments without predators
and in the environment with C. alta. This claim is supported by the
data because the 95% confidence intervals of the two groups do not
overlap.
(d) If the guppies were moved out of the environment that had the
predator C. alta and were placed into an environment without
predators, over time, it would be expected that the mean number of
spots per male guppy would increase. This is because there would
no longer be a disadvantage to having spots, and spots would attract mates, increasing the likelihood that the guppies with spots
would reproduce.
Question
Viruses are not considered alive, yet they can evolve. Explain how a nonliving entity can evolve by natural selection. State the minimum requirements for natural selection to occur in a biological entity.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
Darwinian selection can occur in nonliving things as long as there are
three essential ingredients (necessary and sufficient): reproduction,
heritable variation, and selection. Viruses can reproduce within cells.
They are obligate cellular parasites. They contain genetic information in the
form of RNA and/or DNA, so when they are replicated, variation can be
produced, usually by mutation. They are subject to selection because only
those viruses that have the ability to find, enter, and manipulate host cells
into replicating them will produce new viral particles.
Question
The ability to learn is adaptive for animals, particularly those that can move. Give an example of animal learning that is adaptive and explain how natural selection could act on that behavior.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
Learning is a change in behavior due to experience. Instincts and
fixed action patterns, which are not learned and therefore cannot be
unlearned or changed, do not require learning to occur. This allows some
animals to respond to specific triggers in their environment without learning
and in a mostly fixed way. Learning is particularly important in animals
because most animals move and therefore must be able to navigate their
environment and respond to changes relatively quickly.
Learning is a necessary part of being able to fly, run, or walk. The ability
to learn would be an advantage to animals that hunt other animals because
they could associate their prey with a particular time and place, for
example, so they are more likely to find their prey for a given amount of
hunting energy. Animals learn when they get sick from eating something
toxic. An animal that learns to avoid harmful food is more likely to survive
because it will not expose itself repeatedly to a noxious substance. The
ability to learn is essential for most animals to survive and reproduce. It
is likely that only because animals can learn could they evolve and diversify
to the extent that they have. Once the program for learning evolved, the
ability to learn complex things became possible. Many birds and mammals
demonstrate complex social behaviors and innovation in acquiring skills
and making tools.
