Question
For time t ≥ 0, a particle moves in the xy-plane with position (x(t), y(t)) , and velocity vector \(\left \langle (t-1)^{e^{t^{2}}}, sin \left ( t^{1.25} \right ) \right \rangle.\) At time t = 0 , the position of the particle is (−2, 5) .
(a) Find the speed of the particle at time t = 1.2. Find the acceleration vector of the particle at time t = 1.2.
(b) Find the total distance traveled by the particle over the time interval 0 ≤ t ≤ 1.2.
(c) Find the coordinates of the point at which the particle is farthest to the left for t ≥ 0. Explain why there is no point at which the particle is farthest to the right for t ≥ 0.
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a)
\(Speed = \sqrt{(x'(t))^{2}+(y'(t))^{2}}\)
\(\sqrt{\left ( (1.2-1)e^{(1.2)^{2}} \right )^{2}+\left ( sin((1.2)^{1.25}) \right )^{2}}\)
Speed = 1.271 \(accel: \left \langle (t-1)(2+e^{t2})+(1)(e^{t2}),cos (t^{1.25}\cdot 1.25t^{.25}) \right \rangle\)
of t = 1.2
accel = < 6.247, .405>
(b)
\(\int_{0}^{1.2}\sqrt{\left ( (t-1)e^{t2} \right )^{2}+\left ( sin(t^{1.25}) \right )^{2}}dt\)
= 1.010
(c)
x'(t) is negative on (0, 1) and is positive on (1, 0). x'(1) = 0 Since x'(t) goes from negative to positive at t = 1 and x'(1) = 0, x(t) has a rel. minimum at t=1, since x(t) decreases until t=1 and always increases afterwards, x(1) is on abs. min / that is the location of further to the left, \(-2+\int_{0}^{1}(t-1)e^{t2}dt = x(1)\)
x(1) = -2.604
\(5+\int_{0}^{0}(sin (e^{1.25}))dt = y(1)\)
y (1) = 5.410
(-2.604, 5.410)
There is no point furthest to the right because x'(t) increases towards infinity on +20, meaning there is no abs max of x(t) (sint x(t) will thus be increasing towards ∝ on t > 1). This means the particle will continue to the right for t > 1, creating no furthest right point.
Question
There are two vectors 〈1, -4〉 and 〈2, k〉 where k is an unknown quantity.
(A) Find a value of k such that the vectors are orthogonal.
(B) Find a value of k such that the vectors are parallel.
(C) If k = 6, find the angle between the two vectors. Round to the nearest tenth of a degree.
Answer/Explanation
(A) If vectors are orthogonal, the angle between them is \(\frac{\pi }{2}\) so that their dot product is defined by \(r_{1}r_{2}\cos \Theta =0\) Then \(r_{1}r_{2}=x_{1}x_{2}+y_{1}y_{2}=\left \langle 1,-4 \right \rangle.\left \langle 2,k \right \rangle=1(2)+(-4)(k)=0\).Then \(-4k=-2\Rightarrow k=\frac{1}{2}\)
(B)If vectors are parallel, the angle between them is 0, where cos(0) = 1. You know that, in the case of parallel vectors,\(r_2=Cr_1\) , where C is a constant. In this case, the horizontal component of \(r_{2}\) differs from \(r_{1}\) by a factor of 2. Multiplying the y-component by the same factor, you get k = -8. You can get the same result by applying the equation \(\cos \Theta =\frac{r_{1}.r_{2}}{\left \| r_{1} \right \|\left \| r_{2} \right \|}=-1\). You find that \(\frac{2-4k}{(\sqrt{17})\sqrt{4+k^{2}}}=-1\). If you multiply through by the denominator and then square both sides, you find that
\(4-16k+16k^{2}=17(4+k^{2})\) and, combining terms, you get \(k^{2}+16k+64=0\). You can then factor to find that (k + 8)(k + 8) = 0 or k = -8.
(C) Find the angle between two vectors by applying the equation \(\Theta =\cos ^{-1}\frac{r_1.r_2}{\left \| r_{1} \right \|\left \| r_{2} \right \|}.\)Here,\(r_{1}.r_{2}=1(2)-4(6)=-22,\left \| r_{1} \right \|=\sqrt{1^{2}+4^{2}}=\sqrt{17}\) and \( \left \| r_{2} \right \|=\sqrt{2^{2}+6^{2}}=\sqrt{40}=2\sqrt{10}.\)Substituting, we find that \(\Theta =-\frac{22}{2\sqrt{170}}\approx 147.5^{\circ}\)
Question
A force of 2 newtons is applied to the right side of an object. A force of 4 newtons is applied from below. A force of 8 newtons is applied to the left side of the object at an angle of \(\frac{\pi }{3}\) above the horizontal.
(A) Find the resultant force vector being applied to the object.
(B) Find an approximation (to the nearest hundredth) of the magnitude of the total force on the object.
(C) What additional force vector would need to be applied to keep the object from moving?
Answer/Explanation
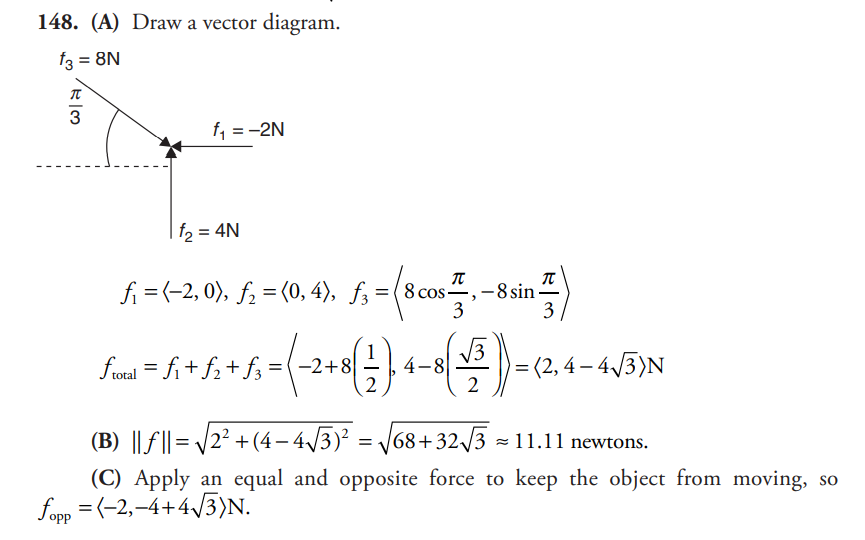
Question
An object is moving on a path defined by the vector-valued function \(r(t)=\left \langle 2\cos t,2\sin t \right \rangle\).Find the following functions at time \(t=\frac{\pi }{4}\).
(A) the velocity vector
(B) the acceleration vector
(C) the tangent vector
(D) the normal vector.
Answer/Explanation
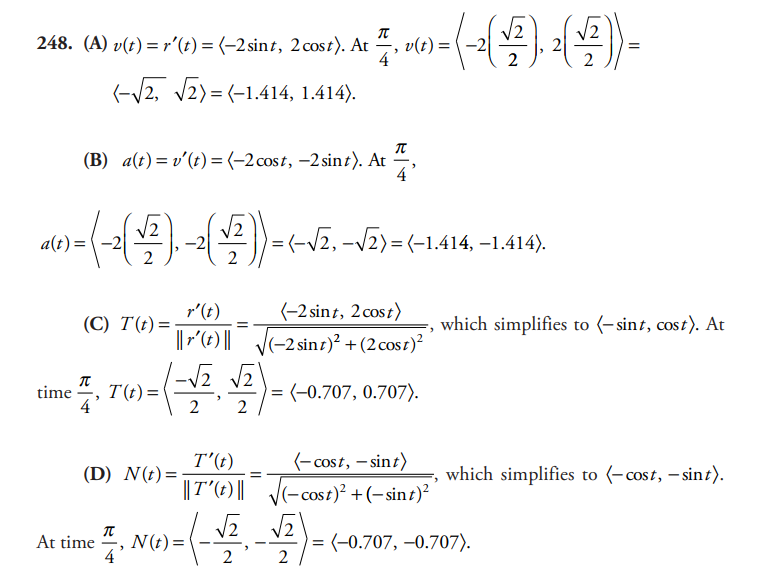
Question
A curve is defined by parametric equations \( x(t)=t^{3}-2t+1\) and \(y(t)=t^{2}-5t\).
(A) Find an equation for the tangent line corresponding to t = 1.
(B) For what value(s) of t is the tangent line horizontal?
(C) For what value(s) of t is the tangent line vertical?
Answer/Explanation
(A) The slope of the tangent line equals\(\frac{\mathrm{d} y}{\mathrm{d} x}=\frac{\frac{\mathrm{d} y}{\mathrm{d} t}}{\frac{\mathrm{d} x}{\mathrm{d} t}}=\frac{2t-5}{3t^{2}-2}-3\) at t=-1 Substituting t = 1 into the parametric equations gives us the coordinates (0, -4). Thus, the equation for the tangent line is y+4=-3(x-0)or,solving fory,y=-3x-4.
(B) The tangent line is horizontal if \(\frac{\mathrm{d} y}{\mathrm{d} t}=0\).Thus 2t-5=0 and \(t=\frac{5}{2}\)
(C) The tangent line is vertical if \(\frac{\mathrm{d} x}{\mathrm{d} t}=9.\)Thus \(3t^{2}-2=0\) and \(t=\pm \sqrt{\frac{2}{3}}\)
Question
A curve is defined by parametric equations \( x(t)=t^{3}-2t+1\) and \(y(t)=t^{2}-5t\).
(A) Find an equation for the tangent line corresponding to t = 1.
(B) For what value(s) of t is the tangent line horizontal?
(C) For what value(s) of t is the tangent line vertical?
Answer/Explanation
(A) The slope of the tangent line equals\(\frac{\mathrm{d} y}{\mathrm{d} x}=\frac{\frac{\mathrm{d} y}{\mathrm{d} t}}{\frac{\mathrm{d} x}{\mathrm{d} t}}=\frac{2t-5}{3t^{2}-2}-3\) at t=-1 Substituting t = 1 into the parametric equations gives us the coordinates (0, -4). Thus, the equation for the tangent line is y+4=-3(x-0)or,solving fory,y=-3x-4.
(B) The tangent line is horizontal if \(\frac{\mathrm{d} y}{\mathrm{d} t}=0\).Thus 2t-5=0 and \(t=\frac{5}{2}\)
(C) The tangent line is vertical if \(\frac{\mathrm{d} x}{\mathrm{d} t}=9.\)Thus \(3t^{2}-2=0\) and \(t=\pm \sqrt{\frac{2}{3}}\)
