Question
The addition of 0.100M \(AgNO_3\) (aq) to a beaker containing 0.100 M NaCl (aq) results in the
formation of a precipitate.
a. What is the identity of the precipitate?
b. Write the net ionic equation showing this precipitate’s formation.
c. A concentrated solution of NH3 (aq) was added to the beaker containing the precipitate. As a result, the precipitate dissolved. Write equations showing the chemical reaction which takes place when the ammonia solution is added to the beaker.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Answer:

Question
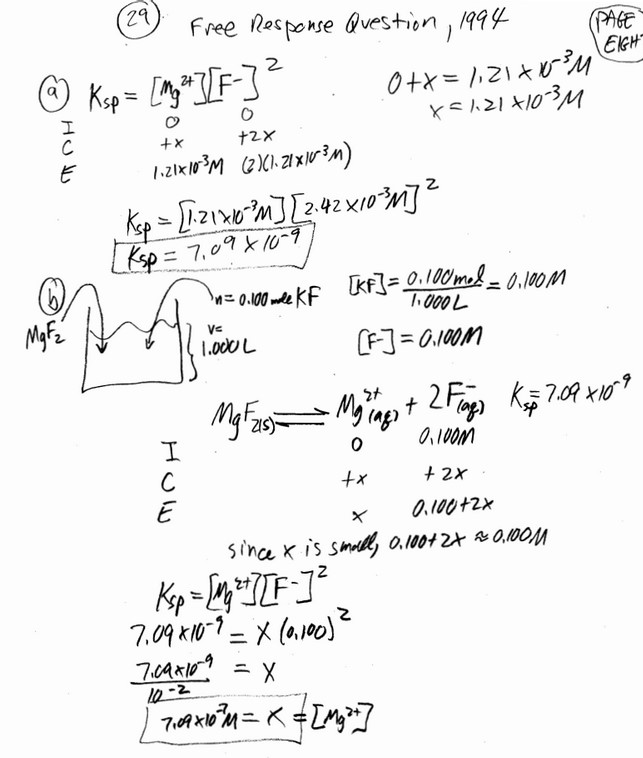
\(MgF_2(s) \Leftrightarrow Mg^{2+}(aq) + 2 F^{ -}(aq)\)
In a saturated solution of \(MgF_2\) at 18° C, the concentration of \(Mg^{2+}\) is \(1.21 x 10^ {-3}\) molar. The equilibrium is represented by the equation above.
(a) Write the expression for the solubility-product constant, \(K_{sp}\), and calculate its value at 18° C.
(b) Calculate the equilibrium concentration of \(Mg^{2+}\) in 1.000 liter of saturated \(MgF_2\) solution at 18°C to which 0.100 mole of solid KF has been added. The KF dissolves completely. Assume the volume change is negligible.
(c) Predict whether a precipitate of \(MgF_2\) will form when 100.0 milliliters of a \(3.00 \times 10 ^{-3}\) molar \(Mg(NO_3)_2\) solution is mixed with 200.0 milliliters of a \(2.00 \times 10 ^{-3}\) molar NaF solution at 18°C.
Calculations to support your prediction must be shown.
(d) At 27°C the concentration of \(Mg^{2+}\) in a saturated solution of \(MgF_2\) is \(1.17 \times 10 ^{-3}\) molar. Is the dissolving of \(MgF_2\) in water an endothermic or an exothermic process? Give an explanation to support your conclusion.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Answer: