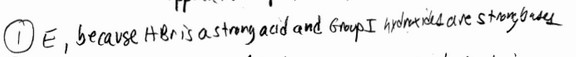Question
\(CH_3CH_2COOH(aq)+H_2O(l)\)⇄\(H_3O+(aq)+CH_3CH_2COO^−(aq)\) \(K_a=1.4\times 10^{−5} \)at 25°C
\(CH_3CH_2COO^−(aq)+H_2O(l)\)⇄\(CH_3CH_2COOH(aq)+OH^−(aq)\) \(K_b=7.4\times 10^{−10 }\)at 25°C
The acid equilibrium for \(CH_3CH_2COOH\) and the base equilibrium for \(CH_3CH_2COO^−\) are represented above. One liter of a buffer solution with pH=4.85 is made by mixing 0.100M \(CH_3CH_2COOH\) and 0.100M \(NaCH_3CH_2COO\). If 10.0mL of 0.500M \(NaOH\) is added to the buffer, which of the following is most likely the resulting pH, and why?
A The pH will be much less than 4.85, because the buffer will respond to the addition of NaOH by producing more \(CH_3CH_2COOH\) .
B The pH will be much greater than 4.85, because there is a large increase in the concentration of the weak base, \(CH_3CH_2COO^-\).
C The pH will be slightly less than 4.85, because the addition of \(NaOH\) reduces the autoionization of \(H_2O\).
D The pH will be slightly greater than 4.85, because some \(CH_3CH_2COOH\) will react with the added base, resulting in a slight decrease in \([H_3O^+]\).
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:D
The addition of a very small amount of a strong base to the buffer solution results in a very small increase in the pH because the added base would be partially consumed by the \(CH_3CH_2COOH\) present in the solution.
Question
A buffer solution that is 0.100M in both \(HCOOH\) and \(HCOOK\) has a pH=3.75. A student says that if a very small amount of 0.100M \(HCl\) is added to the buffer, the pH will decrease by a very small amount. Which of the following best supports the student’s claim?
A \(HCOO^−\) will accept a proton from\(HCl\) to produce more \(HCOOH\) and \(H_2O\).
B \(HCOOH\) will accept a proton from \(HCl\) to produce more \(HCOO^−\) and \(H_2O\) .
C \(HCOO^−\)will donate a proton to \(HCl\) to produce more \(HCOOH\) and \(H_2O\).
D \(HCOOH\) will donate a proton to \(HCl\) to produce more HCOO− and \(H_2O\).
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:A
\(HCOO^−\) accepts a proton (or hydronium ion) from \(HCl\) to produce \(HCOOH\) according to the equation \(HCOO^−(aq)+H_3O^+(aq)\)⇄\(HCOOH(aq)+H_2O(l)\). Thus, the pH of the solution is decreased only slightly when \(HCl\) is added, as the majority of \(H_3O^+\) ions from the strong acid are converted into other substances, and the \([H_3O^+]\) increases only slightly.
Question
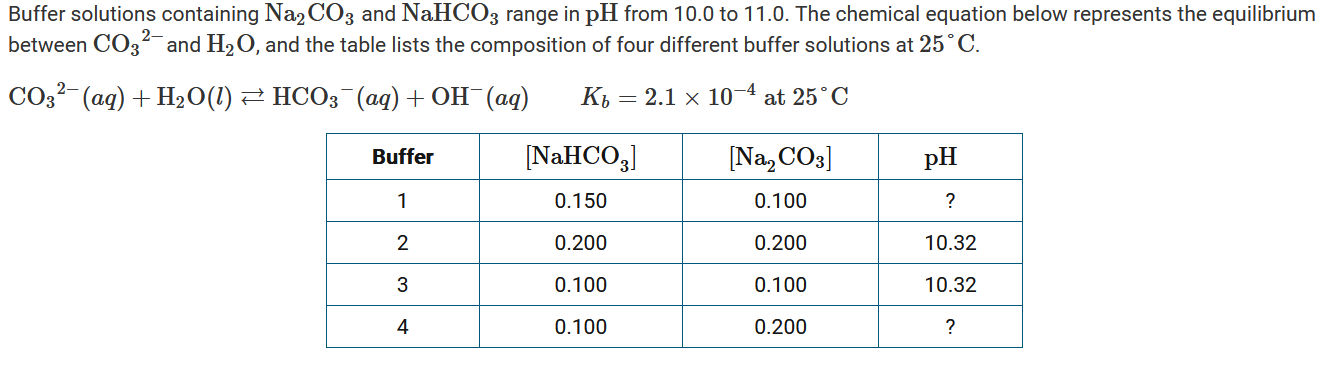
Which of the following chemical equilibrium equations best shows what happens in the buffer solutions to minimize the change in pH when a small amount of a strong base is added?
A \(H_3O^+(aq)+OH^−(aq)\rightleftharpoons 2H_2O(l)\)
B \(HCO_3^−(aq)+OH^−(aq)\rightleftharpoons CO_3^{2−}(aq)+H_2O(l)\)
C \(CO_3^{2−}(aq)+H_3O^+(aq)\rightleftharpoons HCO_3^−(aq)+H_2O(l)\)
D \(CO_3^{2−}(aq)+H_2O(l)\rightleftharpoons HCO_3^{−}(aq)+OH^{−}(aq)\)
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:B
The species \(HCO_3^−\) partially consumes the added \(OH^−\). Therefore, \(HCO_3^−(aq)+OH^−(aq)\rightleftharpoons CO_3^{2−}(aq)+H_2O(l)\) is the chemical equilibrium equation that best shows how the buffer minimizes change in pH when base is added.
Question
Which one of the following pairs cannot be mixed together to form a buffer solution?
A) \(NH_3, NH_4Cl\)
B) KOH, HF
C) \(H_3PO_4, KH_2PO_4\)
D) \(NaC_2H_3O_2\), HCl (\(C_2H_3O_2^-\) =acetate)
E) RbOH, HBr
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: E