Question
Rock X is released from rest at the top of a cliff that is on Earth. A short time later, Rock Y is released from rest from the same location as Rock X . Both rocks fall for several seconds before landing on the ground directly below the cliff. Frictional forces are considered to be negligible.
After Rock Y is released from rest several seconds after Rock X is released from rest, what happens to the separation distance S between the rocks as they fall but before they reach the ground, and why? Take the positive direction to be downward.
A S is constant because at the moment Rock Y is released, the only difference between the rocks is their difference in height above the ground.
B S is constant because the difference in speed between the two rocks stays constant as they fall.
C S increases because the difference in speed between the two rocks increases as they fall.
D S increases because at all times Rock X falls with a greater speed than Rock Y .
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:D
Rock X and Rock Y accelerate downward from the cliff toward Earth at the same rate, which means that both rocks gain their respective downward speeds at the same rate. This means that the numerical difference between their speeds remains the same as they fall toward Earth. However, at all times, Rock X will have a greater downward speed than Rock Y since Rock X has fallen for a greater interval of time. Therefore, between the time Rock Y is released and when it hits the ground, Rock X will have fallen a greater distance than Rock Y. Therefore, the separation distance between the rocks increases as they fall.
Question
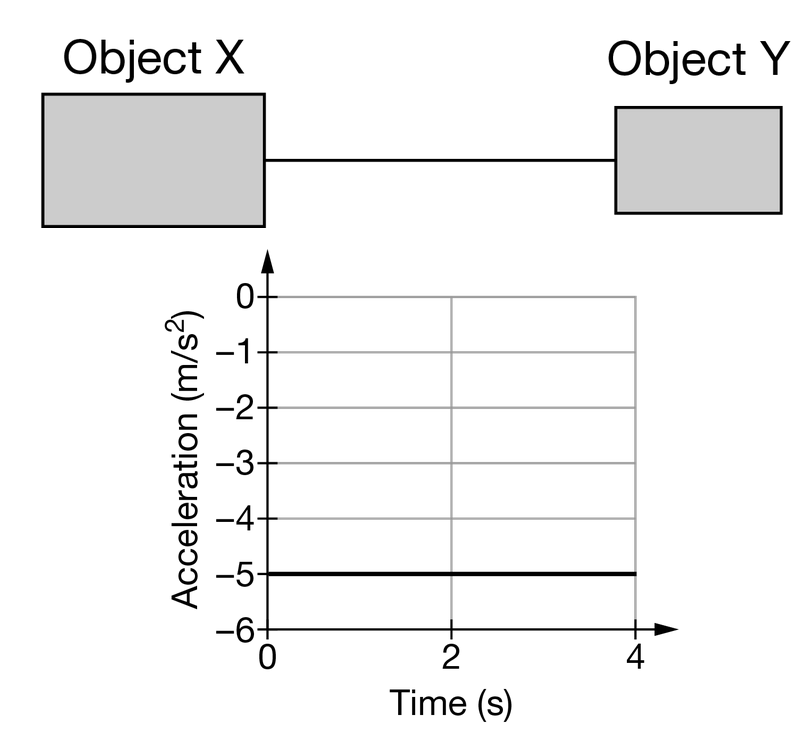
Two objects, object X and object Y, are held together by a light string and are released from rest near a planet’s surface in the orientation that is shown in the figure. Object X has a greater mass than object Y. A graph of the acceleration as a function of time for the system’s center of mass is shown for the 4s. The positive direction is considered to be upward. How does the speed of object X \(v_x\) compare to that of the system’s speed vs after the objects have fallen for 4s ?
A \(v_x=vs\)
B \(v_x>vs\)
C \(v_x<vs\)
D The answer cannot be determined without knowing the relative masses of object X and object Y .
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:A
The acceleration of object X due to gravity is the same for that of object Y . Therefore, the acceleration of the system due to gravity of the system is the same as that for the two objects.
Question
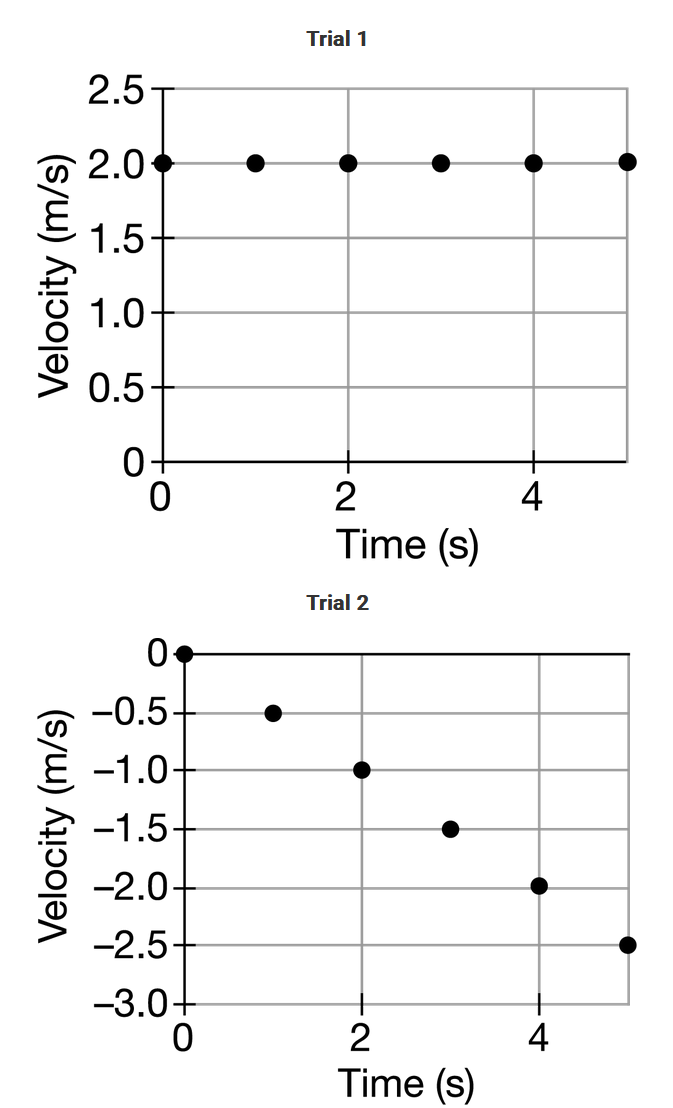
A student uses a motion sensor to collect data of the velocity of an object as a function of time during two experimental trials, as shown. In which trial does the object have the greatest magnitude of acceleration, and in which trial does the object travel the greatest distance?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:D
When provided with a graph of an object’s velocity as a function of time, the slope of the curve represents the change in velocity per unit of time between two instants in time. This quantity is also known as the average acceleration of the object between the two instants in time. In both trials, the slope of the curves are constant. Therefore, the acceleration of the object in both trials remains constant. The slope of the curve in trial 1 is zero, but the slope of the curve in trial 2 is nonzero. Therefore, the acceleration of the object in trial 2 is greater than the acceleration of the object in trial 1. When provided with a graph of an object’s velocity as a function of time, the area bound by the curve and the horizontal axis for a specific time interval represents the change in position of the object during the time interval. This quantity is also known as the displacement of the object between two instants in time. In both trials, the object does not change its direction. Therefore, the displacement of the object is equal to the distance traveled by the object. The area bound by the curve in trial 1 is greater than the area bound by the curve in trial 2. The object travels a greater distance in trial 1 than in trial 2.
Question
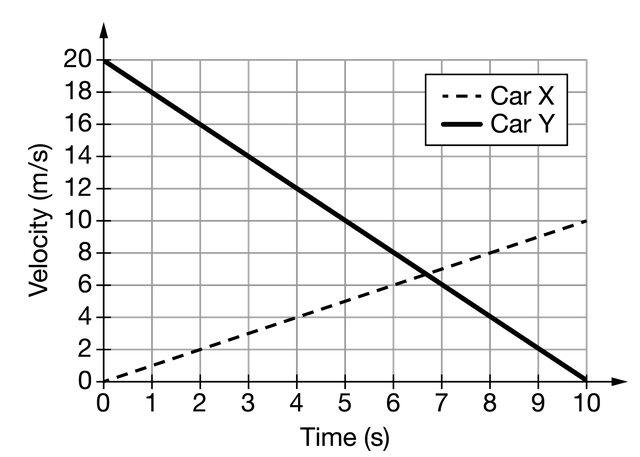
Car X and car Y travel on a horizontal surface along different parallel, straight paths. Each car’s velocity as a function of time is shown in the graph. Which of the following claims is correct about car X and car Y ?
A Both car X and car Y travel in the same direction.
B Between t=6 s and t=7 s, car X and car Y are at the same horizontal position.
C The change in car X ’s speed per unit of time increases as the time increases, and the change in car Y ’s speed per unit of time decreases as the time increases.
D The magnitude of the acceleration of car X is the same as the magnitude of the acceleration of car Y .
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:A
When a graph shows the velocity as a function of time for a moving object, the slope of the curve between two points in time represents the change in velocity per unit of time of the object. The change in velocity per unit of time for car X
is represented by a positive slope. The change in velocity per unit of time for car Y is represented by a negative slope. The sign of the slope for each curve indicates the direction of the acceleration for the respective cars. However, at all points in time in this particular situation, the velocity for each car is either zero or positive. Therefore, both cars, at any given time, are either at rest or travel in the positive direction.
Question
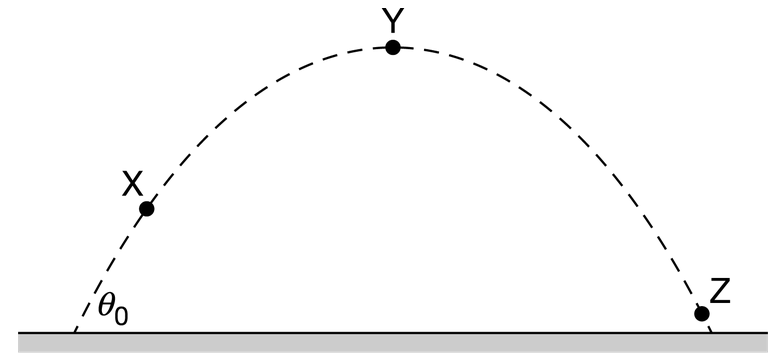
An object is launched upward at angle \(θ_0\) above the horizontal with a speed of v0. The trajectory and three positions of the object, X, Y, and Z, are shown in the figure. Position X is higher than position Z with respect to the ground, and position Y is at the object’s maximum vertical position. Which of the following claims is correct about the system that consists of only the object?
A The speed of the object at position X is greater than the speed of the object at position Z .
B The object’s speed at point Z is \(v_0\) .
C The object’s acceleration is the same at positions X , Y, and Z .
D The object is at rest at position Y .
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:C
At all points along the object’s trajectory, the object’s acceleration is the acceleration due to gravity that is always directed toward the center of Earth, or, in this case, toward the ground. The object does not accelerate in the horizontal direction at any point along the object’s trajectory. Therefore, the object’s acceleration remains the same at all points along the object’s trajectory.
