Question
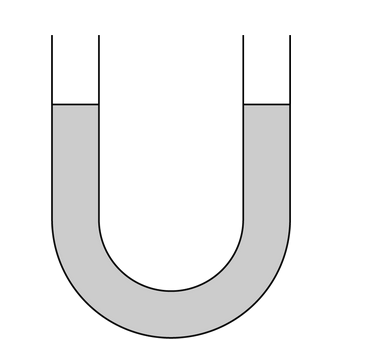
Water is poured into a U-shaped tube and allowed to come to rest, as shown in the figure. Which of the following can help explain why the water in the left and right sides of the tube reaches the same height? Select two answers.
A The force exerted by the atmosphere on the surface of the water is the same on both sides.
B The average speed of the water molecules on both sides is the same.
C The surface tension of the water on both sides is the same.
D The weight of water in the left and right halves of the tube is the same.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: A , D
The equilibrium water levels occurs when the net force is the same for both halves of the tube. Determining the net force includes accounting for the force exerted by the atmosphere. Since both ends of the tube are open to the air, the atmospheric force is the same on both of them. The other factor is the weight of liquid in each half of the tube. Since the atmospheric force is the same, the weight of liquid in each half must be the same. With only one liquid, this occurs when the same amount of liquid is in each half.
The equilibrium water levels occurs when the net force is the same on both sides. Determining the net force includes accounting for the weight of fluid in each half of the tube. Since both ends of the tube are open to the air, the atmospheric force is the same on both of them. Since the atmospheric force is the same, the weight of liquid in each half must be the same. With only one liquid, this occurs when the same amount of liquid is in each half
Question
A wooden cube is floating at rest on the surface of a liquid. Which of the following is an action-reaction pair of forces that can explain why the force exerted by the liquid on the bottom of the container is greater with the floating cube than without it?
A Earth exerts a gravitational force on the cube, and the liquid exerts a net upward force on the cube.
B The liquid exerts a net upward force on the cube, and the cube exerts a contact force on the liquid.
C Earth exerts a gravitational force on the cube, and the cube exerts a gravitational force on Earth.
D Earth exerts a gravitational force on the liquid, and the liquid exerts a net upward force on the cube.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:B
The force the cube exerts on the liquid is equivalent to increasing the force the air exerts on the liquid. The result is an increase in the force exerted by the liquid.
Question
A cube submerged in a rectangular tank of liquid is at rest. Which of the following is a Newton’s third law pair of forces in this situation?
A The force that the liquid exerts on a side of the tank and the force the liquid exerts on a side of the cube
B The force that the liquid exerts on a side of the tank and the force the side of the tank exerts on the liquid
C The force that the liquid exerts on the top of the cube and the force the liquid exerts on the bottom of the cube
D The force that the bottom of the cube exerts on the liquid and the force the liquid exerts on the bottom of the tank
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:B
An interacting force pair involves the forces that two objects exert on each other.
Question
A block of weight W is floating in water, and one-third of the block is above the surface of the water. Which of the following correctly describes the magnitude F of the force that the block exerts on the water and explains why F has that value?
A \(F=\frac{2}{3}W\) . Only two-thirds of the block is in contact with the water, so it will exert a force on the water equal to two-thirds of the block’s weight.
B \(F=\frac{2}{3}W\) . The water exerts a force on the block equal to the weight of the part of the block that is underwater. The block then exerts a force of equal magnitude on the water.
C \(F=W\) . The block is at rest, so the net force on it must be zero. The water must exert an upward force of magnitude F on the block to make this so. The block then exerts a force of equal magnitude on the water.
D \(F=W\) . Any object will always exert a force on the surface beneath it that is equal to the weight of the object.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:C
By Newton’s second law, the net force on the stationary block must be zero. So the water must be exerting a force equal to the block’s weight on the block. By Newton’s third law, the block must be exerting a force of magnitude W
on the water.
Question
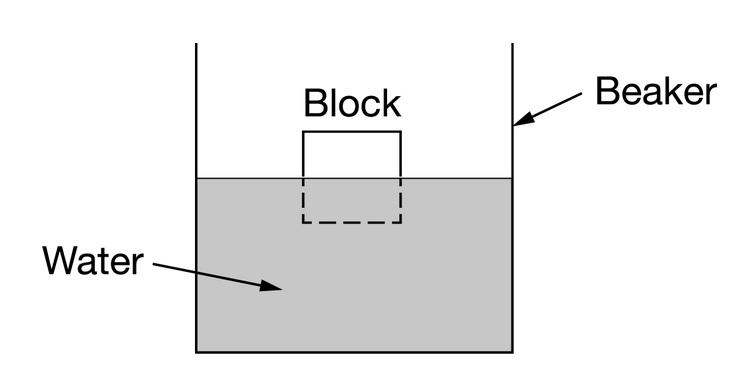
The figure shows a block of wood floating in a beaker of water. Which of the following is true of the force exerted by the wood on the water?
A The wood exerts a downward force on the water that is equal in magnitude to the upward force exerted by the beaker on the water.
B The wood exerts a downward force on the water that is equal in magnitude to the weight of the wood.
C The wood exerts an upward force on the water that is equal in magnitude to the weight of the displaced water.
D The wood does not exert a force on the water.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:B
Since the block is not moving, the water must be exerting an upward force on it that equals its weight. By Newton’s third law, the block must be exerting a force of equal magnitude on the water in the opposite direction.
