Question
A device that takes mechanical energy and converts it into electrical energy is
(A) a solenoid
(B) an electric motor
(C) a transformer
(D) a generator
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:(D)
A generator creates electrical power by harnessing mechanical energy. An electric motor does the opposite. A solenoid creates a magnet from current. A transformer transforms AC voltage into a higher or lower voltage.
Question
Which of the following transformations could a transformer accomplish? Select two answers.
(A) Increasing input AC voltage
(B) Increasing input AC current
(C) Increasing input DC voltage
(D) Increasing input DC current
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:(A) and (B)
As long as the input is alternating (not direct) in nature, a transformer can either step up the voltage (stepping down the current) or step down the voltage (stepping up the current).
Question
Which of the following are synonyms for voltage? Select two answers.
(A) Electromotive force
(B) Electrical potential energy
(C) Potential difference
(D) amp · hr
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:(A) and (C)
Electromotive force (emf) is voltage, as is potential, electric potential, and potential difference. Electric potential energy is the actual energy present (measured in joules, not volts!) when charge is present in the field.
Question
Lenz’s law is an electrical restatement of which conservation law?
(A) Linear momentum
(B) Angular momentum
(C) Charge
(D) Energy
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:(D)
Conservation of energy is the underlying principle. By opposing the change in flux, Lenz’s law is trying to keep the field energy constant.
Question
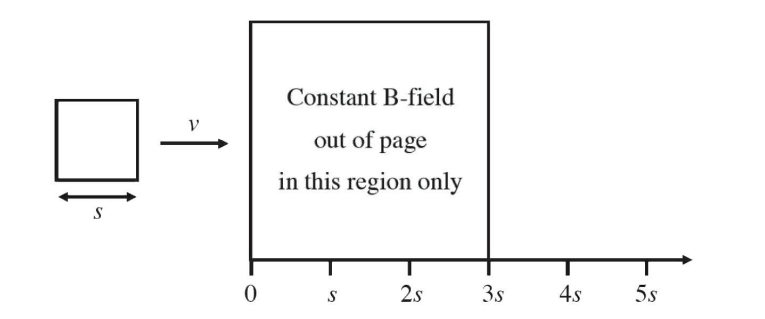
A square loop of conducting wire with sides is moved at a constant rate v to the right into a region where there is a constant magnetic field directed out of the page. Which of the following graphs shows the flux through the loop as a function of distance?
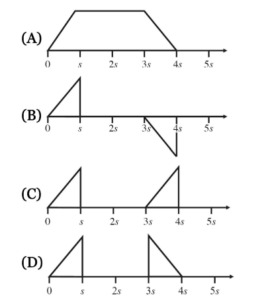
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:A
Flux is the product of the area enclosed by the loop of wire and the field strength. The flux will increase linearly up to a maximum value when the wire is completely within the field, and will begin to decrease once the wire begins to leaves the region within the field.
