Question
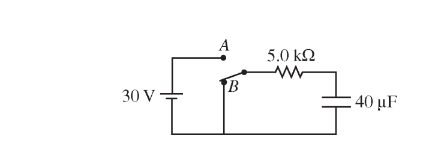
The capacitor in the circuit represented above is uncharged when the switch is at position B. The switch is then moved to position A. What is the energy stored by the capacitor when the current in
the circuit is 2.0 mA?
(A) 0.8 mJ
(B) 1.2 mJ
(C) 8.0 mJ
(D) 16 mJ
(E) 18 mJ</
Answer/Explanation
Question
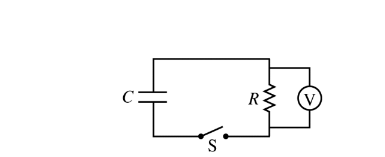
A charged capacitor C, resistor R, and switch S are connected in series. Voltmeter V is connected in parallel with the resistor, as shown in the figure above. At time t = 0, the switch is then closed. Which of the following shows the potential difference ΔV reading on the voltmeter as a function of time t after the switch is closed?
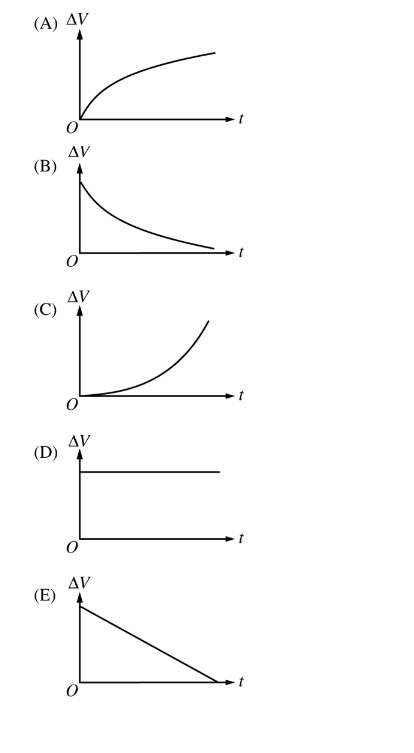
Answer/Explanation
Question
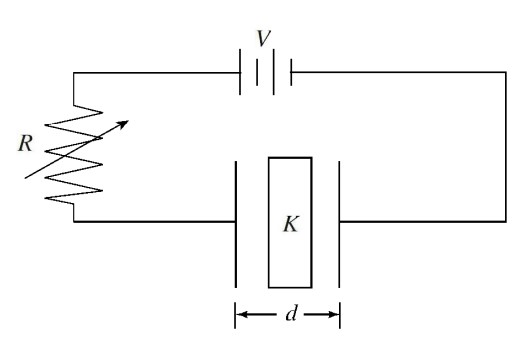
A parallel plate capacitor has a dielectric material between the plates with a constant K. The capacitor is connected to a variable resistor R and a power supply of potential difference V. Each plate of the capacitor has a cross-sectional area A and the plates are separated by a distance d. Which of the following changes could increase the capacitance and decrease the amount of charge stored on the capacitor?
(A) Increase R and increase A
(B) Decrease V and decreased
(C) Decrease R and increase d
(D) Increase K and increase V
(E) Increase K and increase R
Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question
What is the value of the following product?
\(2oµF x 500 Ω\)
(A) 0.01 henry
(B) 0.01 ampere per coulomb
(C) 0.01 weber
(D) 0.01 second
(E) 0.01 volt per ampere
Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Note that all answers have the same number, so for this problem, don’t even worry about multiplying the numbers just focus on the units.
Because the time constant for an RC circuit is equal to the product of resistance and capacitance, T = RC, this product has the dimensions of time. If you don’t know that off the top of your head, just be sure to carefully break the farad and ohm into their subunits, simplifying where possible:
Question
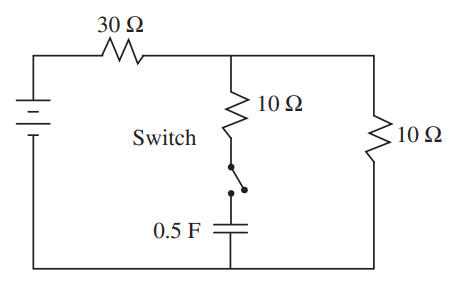
In the circuit shown above, the 0.5-F capacitor is initially uncharged. The switch is closed at time t = 0. What is the time constant (the time for the capacitor to charge to 63% of its maximum charge) for the charging of this capacitor?
(A) 5 s
(B) 10 s
(C) 20 s
(D) 30 s
(E) 40 s
Answer/Explanation
Ans:C
