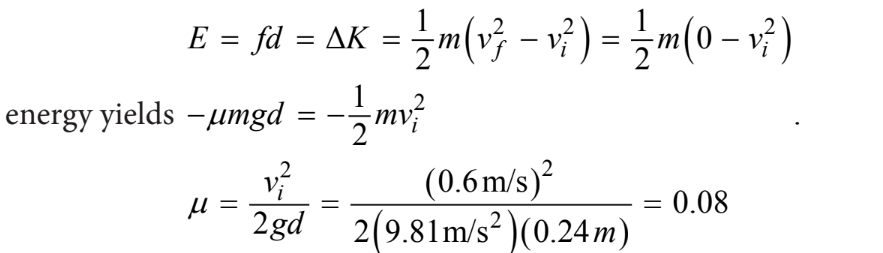Question(a)-(b)are based on the following information.
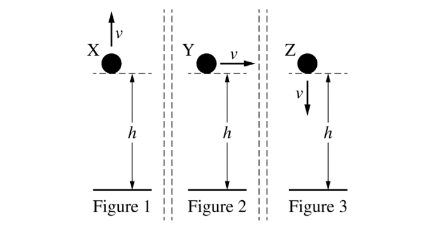
Three identical spheres are thrown from the same height above the ground. Sphere X is thrown vertically up, sphere Y is thrown horizontally, and sphere Z is thrown vertically down, as shown in
figures 1, 2, and 3 above, respectively. All three spheres are thrown with the same speed. Air resistance is negligible.
Question(a)
Which sphere or spheres initially collide with the ground with the greatest speed?
(A) Sphere X only
(B) Sphere Y only
(C) Sphere Z only
(D) Spheres X and Z only
(E) All three spheres collide with the same speed.
Answer/Explanation
Question(b)
Assume the spheres collide elastically with the ground. Which of the following ranks the spheres based on the rebound height after they collide with the ground?
(A) X>Y>Z
(B) Y> (X => Z)
(C) Z>Y>X
(D) ( X =Y ) >Z
(E) (X= Z) >= Y
Answer/Explanation
Question
A ball of mass m is dropped from rest at a height h and collides elastically with the floor, rebounding to its original height. What is the magnitude of the net impulse on the ball during the collision with the floor?
(A) Zero
(B)\(m\sqrt{gh}\)
(C)\(m\sqrt{2gh}\)
(D)\(m\sqrt{4gh}\)
(E)\m\sqrt{8gh}\)
Answer/Explanation
Ans:E
The net impulse is the change in momentum of the ball during its collision with the floor. First, substituting into the conservation of energy equation to calculate the speed of the ball \(K_i=U_{gf}\)
when it reaches the floor yields \(\frac{1}{2}mv^2_i=mgh\) .The ball returns to \(v=\sqrt{2gh}\) .
the same height when it leaves the floor; thus, the final speed for the ball during the collision with the floor is the same as the speed when the ball reaches the floor, but it will be moving in the opposite direction. Therefore, one of the velocities must be negative. Then, substituting into the equation for change in momentum yields 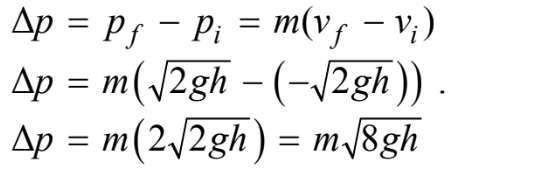
Questions (a)-(b)
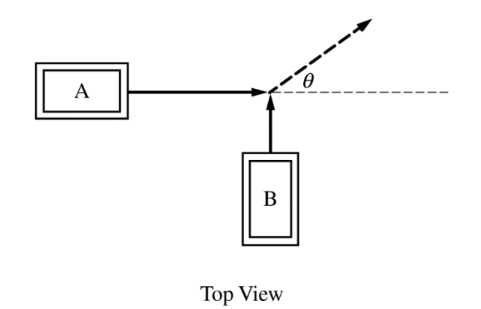
Cart A is traveling east when it collides with cart B, which is traveling north. Cart A has a mass of 3.05 kg, and cart B has a mass of 2.10 kg. The two carts travel together as a single object on a
horizontal surface at an angle θ relative to due east, as shown above.
Question(a)
In one trial, the initial speed of cart A is 2.5 m s and the initial speed of cart B is 1.5 m s. The angle θ relative to east that the carts travel after the collision is most nearly
(A) \(22^{\circ}\)
(B) \(36^{\circ}\)
(C) \(45^{\circ}\)
(D) \(54^{\circ}\)
(E) \(62^{\circ}\)
Answer/Explanation
Ans:A
During the collision, momentum is conserved. Momentum is a vector; thus, the horizontal and vertical directions can be analyzed independently. Substituting into conservation of momentum in the horizontal direction yields
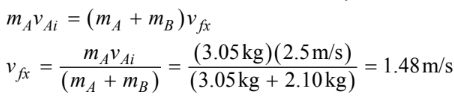 and in the vertical direction yields
and in the vertical direction yields
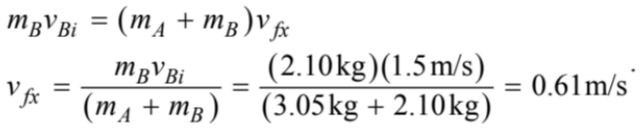 Substituting into the trigonometric function for tangent yields
Substituting into the trigonometric function for tangent yields
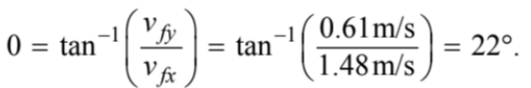
Question(b)
In another trial, the speed of the carts immediately after the collision is 0.60 m s, and the carts slide 0.24 m on the horizontal surface before coming to rest. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the sliding carts and the surface is most nearly
(A) 0.08
(B) 0.13
(C) 0.19
(D) 0.25
(E) 0.75
Answer/Explanation
Ans:A
Setting the energy dissipated equal to the change in kinetic