Question
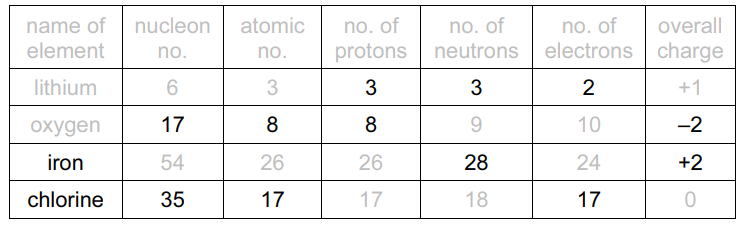
(a) Complete the table to show the composition and identity of some atoms and ions
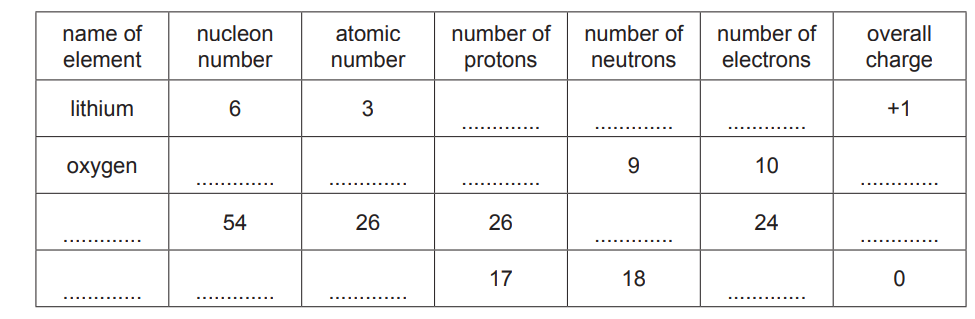
(b) Beams of protons, neutrons and electrons behave differently in an electric field due to their differing properties.
The diagram shows the path of a beam of electrons in an electric field.
Add and label lines to represent the paths of beams of protons and neutrons in the same field.
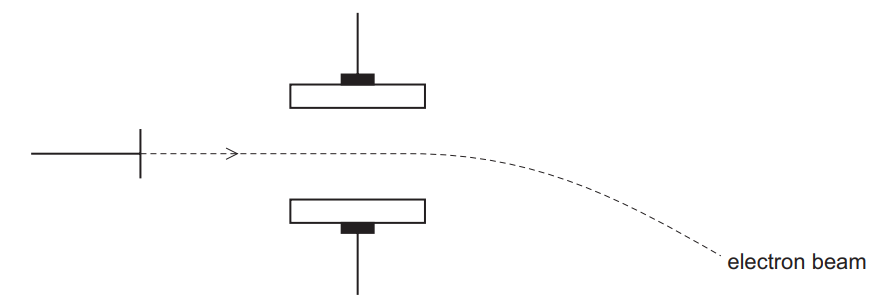
(c) The fifth to eighth ionisation energies of three elements in the third period of the Periodic Table are given. The symbols used for reference are not the actual symbols of the elements.
(i) State and explain the group number of element Y.
group number ………………………….
explanation ………………………………………………………………………………………………………….[1]
(ii) State and explain the general trend in first ionisation energies across the third period………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. [2]
(iii) Explain why the first ionisation energy of element Y is less than that of element X………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. [2]
(iv) Complete the electronic configuration of element Z.
$1s^{2}$ ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… [1]
(d) A sample of strontium exists as a mixture of four isotopes. Information about three of these isotopes is given in the table.
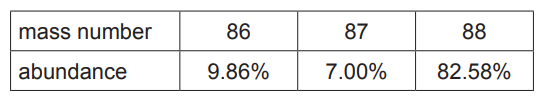
abundance 9.86% 7.00% 82.58%
(i) Calculate the abundance of the fourth isotope
abundance = ……………………….. % [1]
(ii) The relative atomic mass of this sample of strontium is 87.71.
Calculate the mass number of the fourth isotope.
mass number = ……………………….. [2] [Total: 16]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
1 (a)
(b) line straight on labelled ‘neutrons’
line (curving) up labelled ‘protons’
proton line clearly shows less (overall) deflection than electron curve
(c) (i) Group 16/6/VI
AND
Big (owtte) increase/big difference/ big gap/ big jump/ jump in increase/ jump in difference after 6th IE
(ii) increases (across period) due to increasing attraction (of nucleus for electrons)
due to increasing nuclear charge/ atomic / proton number AND
constant/similar shielding/ same (outer/ number of) shell/ energy level
(iii) electron (pair) repulsion
(Y has a) pair of electrons in a (3)p orbital/ a (3)p orbital is full ORA
(iv) $\quad\left(1 s^2\right) 2 s^2 2 p^6 3 s^2 3 p^5$
(d) (i) 0.56(%)
(ii)
$
\begin{aligned}
& \frac{(A \times 0.56)+(86 \times 9.86)+(87 \times 7.00)+(88 \times 82.58)}{100}=87.71 \\
& A=84
\end{aligned}
$
Question
(a) The table shows information about some of the elements in the third period.
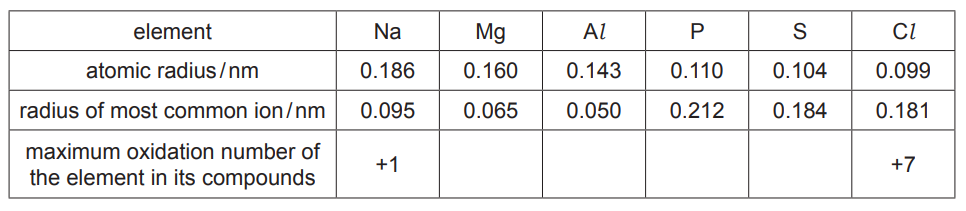
(i) Complete the table to show the maximum oxidation number of each element in its compounds.[1]
(ii) Explain why the atomic radius of elements in the third period decreases from $\mathrm{Na}$ to $\mathrm{Cl}$.[3]
(iii) The radius of the most common ion of $\mathrm{Mg}$ is much smaller than the radius of the most common ion of $\mathrm{S}$.
Identify both ions and explain the difference in their radii. [2]
(b) Phosphorus is a non-metal in the third period. It reacts vigorously with excess oxygen but slowly with chlorine.
Some reactions of phosphorus are shown
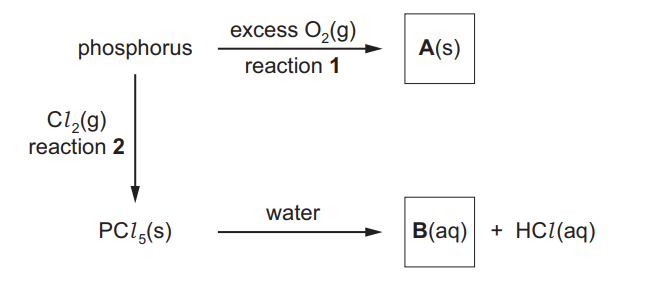
(i) Write an equation to represent reaction 1, the formation of compound A. ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… [1]
(ii) Give two observations you could make in reaction 2.
1. ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
2. ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..[2]
(iii) Name compound B………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. [1]
(c) Cerium is a lanthanoid metal that shows similar chemical reactions to some elements in the third period. Most of cerium’s compounds contain $\mathrm{Ce}^{3+}$ or $\mathrm{Ce}^{4+}$ ions.
(i) Cerium shows the same structure and bonding as a typical metal.Draw a labelled diagram to show the structure and bonding in cerium.[2]
(ii) Cerium(IV) oxide, $\mathrm{CeO}_2$, is a ceramic.
Suggest two physical properties of cerium(IV) oxide.
1.
5.[2]
(iii) A naturally occurring sample of cerium contains only four isotopes. Data for three of the isotopes are shown in the table.
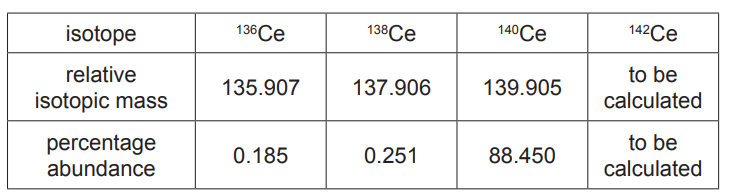
The $A_{\mathrm{r}}$ of the sample is 140.116 .
Use these data to calculate the relative isotopic mass of the fourth isotope in this sample of cerium.
Give your answer to three decimal places.relative isotopic mass $=$[3] [Total: 17]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a)(i)
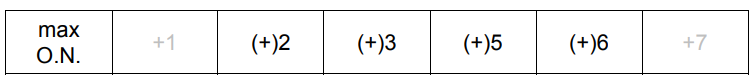
(a)(ii) (from Na to Cl) nuclear charge increases 1
electrons are in the same shell / have same shielding 1
greater/ stronger attraction (of electrons to nucleus)
(a)(iii) $\quad \mathrm{Mg}^{2+}$ AND $\mathrm{S}^{2-}$
(a)(iii) $\quad \mathrm{Mg}^{2+}$ AND $\mathrm{S}^{2-}$
ion of $\mathrm{Mg} / \mathrm{Mg}^{2+}$ has one fewer shell (than ion of $S / \mathrm{S}^{2-}$ )
(b)(i)
$\mathrm{P}_4+5 \mathrm{O}_2 \rightarrow \mathrm{P}_4 \mathrm{O}_{10} / 2 \mathrm{P}_2 \mathrm{O}_5$
(b)(ii) any 2 from:
• yellow/ green colour (of chlorine gas) disappears
• white flame
• white solid
• solid melts
(b)(iii) phosphoric(V) acid
(c)(i)
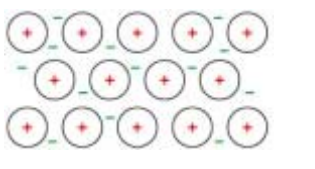
diagram showing regular arrangement of (positive) ions
surrounded by / sea of (delocalised) electrons
(c)(ii) any 2 from:
• high melting / boiling / sublimation point
• electrical /thermal insulator
• hard /rigid
• retains strength at high temperature / pressure
(c)(iii) M1
% abundance of fourth isotope
= 100 – (0.185 + 0.251 + 88.450) = 11.114
$\begin{aligned} & \text { M2 } \\ & \frac{(0.185 \times 135.907)+(0.251 \times 137.906)+(88.450 \times 139.905)+(11.114 \times \mathrm{RIM})}{100} \\ & =140.116 \\ & \therefore(140.116 \times 100)-12434.35=1577.246=11.114 \times \mathrm{RIM}\end{aligned}$
M3
$
\mathrm{RIM}=\frac{1577.246}{11.114}=141.915
$