Question:
An anhydrous white salt, Z, is heated strongly for 30 minutes. A mixture of gases is given off. The solid remaining in the test-tube is then dissolved in a small volume of dilute hydrochloric acid. The addition of a few drops of dilute sulfuric acid to the test-tube causes a white precipitate to form. Which substance could be Z?
A barium carbonate
B barium nitrate
C magnesium carbonate
D magnesium nitrate
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:B
Question:
Which row correctly describes one property of barium and one property of barium oxide?

▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:D
Question
What are the trends in the stated properties as Group 2 is descended from magnesium to barium?
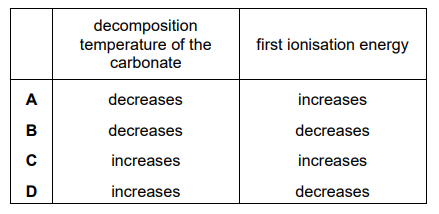
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:D
Question
This question is about two elements in Group 2, $Q$ and $R$.
Three of the statements shown are correct for metal Q.
The one remaining statement is correct for metal $R$.
Which statement applies to $\mathrm{R}$ ?
A A saturated solution of the hydroxide of this metal has the higher $\mathrm{pH}$ value.
B This metal has a carbonate that is used in agriculture to reduce the acidity of soil.
C This metal has the greater atomic radius.
D This metal reacts more quickly with cold water.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:B
Question
A student mixes pairs of chemicals together in separate test-tubes.
- excess calcium (s) + water (I)
- barium chloride $(a q)$ + strontium hydroxide $(a q)$
- calcium carbonate (s) + excess hydrochloric acid (aq)
- magnesium sulfate (aq) + barium nitrate (aq)
How many of the mixtures produce a white, solid product?
A 0
B 1
C 2
D 3
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:C
Question
A student mixes pairs of chemicals together in separate test-tubes.
- excess calcium (s) + water (I)
- barium chloride $(a q)$ + strontium hydroxide $(a q)$
- calcium carbonate (s) + excess hydrochloric acid (aq)
- magnesium sulfate (aq) + barium nitrate (aq)
How many of the mixtures produce a white, solid product?
A 0
B 1
C 2
D 3
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:C
Question
An excess of MgO is shaken with water. The resulting mixture is filtered into test-tube P.
An excess of BaO is shaken with water. The resulting mixture is filtered into test-tube Q.
Which oxide reacts more readily with water and which filtrate has the lower pH?

▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:A
Question
$ \mathrm{Z}$ is an anhydrous compound of a Group 2 element. When it is heated, $\mathbf{Z}$ undergoes thermal decomposition to produce two different gases. $\mathbf{Z}$ has relatively low thermal stability compared to other Group 2 compounds containing the same anion as $\mathbf{Z}$.
What is compound $\mathbf{Z}$ ?
A barium carbonate
B barium nitrate
C magnesium carbonate
D magnesium nitrate
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:D
Question
Why does barium react more rapidly with cold water than magnesium does?
A Barium atoms are larger and form ions more easily than magnesium atoms.
B Barium floats on the surface of the water but magnesium sinks in the water.
C Barium hydroxide is less soluble than magnesium hydroxide.
D The sum of the 1 st and 2 nd ionisation energies of barium is more than that for magnesium.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:A
Question
River water in a chalky agricultural area contains $\mathrm{Ca}^{2+}, \mathrm{Mg}^{2+}, \mathrm{CO}_3{ }^{2-}, \mathrm{HCO}_3^{-}, \mathrm{Cl}^{-}$and $\mathrm{NO}_3^{-}$ions. In a water treatment plant, such water is treated by adding a calculated quantity of calcium hydroxide.
What will be precipitated from the river water following the addition of calcium hydroxide?
A $\mathrm{CaCl}_2$
B $\mathrm{CaCO}_3$
C $\mathrm{Ca}\left(\mathrm{NO}_3\right)_2$
D $\mathrm{Mg}\left(\mathrm{NO}_3\right)_2$
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:B
Question
Which row gives correct comparisons between the solubilities of calcium hydroxide and barium hydroxide and the thermal stabilities of calcium carbonate and barium carbonate?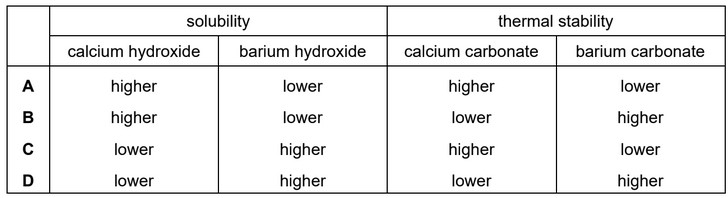
Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Question
Equal masses of \(CaCO_3\), \(Ca(NO_3)_2\), \(BaCO_3\) and \(Ba(NO_3)_2\) are thermally decomposed. The volume of gas produced in each experiment is measured under the same conditions.
Which compound will produce the greatest volume of gas?
A \(CaCO_3\) B \(Ca(NO_3)_2\) C \(BaCO_3\) D \(Ba(NO_3)_2\)
Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question
A mixture contains magnesium carbonate and barium carbonate only. A sample of the mixture is dissolved in nitric acid to produce a solution.
How could this solution be processed into a magnesium compound and a separate barium compound?
A Add HCl(aq), filter off the solid barium chloride.
B Add HCl(aq), filter off the solid magnesium chloride.
C Add \(H_2SO_4(aq)\), filter off the solid barium sulfate.
D Add \(H_2SO_4(aq)\), filter off the solid magnesium sulfate.
Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Question
A sample of magnesium nitrate is heated in the apparatus shown.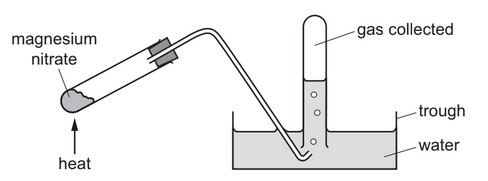
The pH of the solution in the trough is measured.
The gas collected is tested with a glowing splint.
What are the results?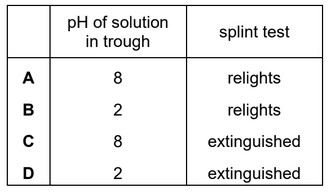
Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
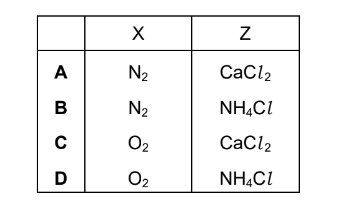
Question
The gaseous products of heating a mixture of Ca(OH)2 and NH4Cl are passed through solid CaO.
A single gaseous product, W, is collected.
A sample of W reacts with Cl2(g) to produce two gases, X and Y.
X is an element. Y is acidic.
Y reacts with W to produce Z.
What are X and Z?
Answer/Explanation
Answer: B
Question
Q is a mixture of a Group 2 oxide and a Group 2 sulfate. Q contains equal amounts of the two compounds.
Q is shaken with water and the resulting mixture filtered; a solid residue is obtained. There is no reaction when the solid residue is shaken with HCl(aq). Shaking the filtrate with H2SO4(aq) produces a white precipitate.
What could be Q?
A BaO + BaSO4
B BaO + MgSO4
C MgO + BaSO4
D MgO + MgSO4
Answer/Explanation
Answer: A
Question
Which substance will not be a product of the thermal decomposition of hydrated magnesium nitrate?
A dinitrogen monoxide
B magnesium oxide
C oxygen
D steam
Answer/Explanation
Answer: A
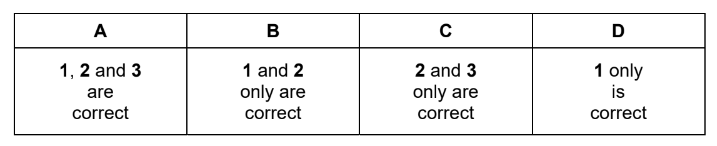
Question
Which statements are correct?
1 Magnesium carbonate decomposes at a lower temperature than calcium carbonate.
2 Calcium hydroxide is more soluble in water than magnesium hydroxide.
3 Calcium is a stronger reducing agent than magnesium.
Answer/Explanation
Answer: A
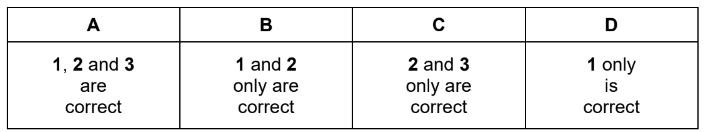
Question
Which statements about calcium oxide are correct?
1 It can be reduced by heating with magnesium.
2 It is produced when calcium nitrate is heated.
3 It reacts with cold water.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Answer C
Question
In which list are all three compounds soluble in water?
A barium chloride, calcium carbonate, magnesium hydroxide
B barium hydroxide, calcium hydroxide, strontium carbonate
C barium chloride, barium hydroxide, magnesium sulfate
D barium sulfate, calcium sulfate, magnesium hydroxide
Answer/Explanation
Answer C
Question
Metal T reacts with water to produce a colourless solution. A white precipitate is produced when this colourless solution is mixed with aqueous sulfuric acid.
What is metal T?
A barium
B magnesium
C potassium
D sodium
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
A
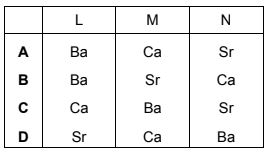
Question
L, M and N are Group 2 metals. L reacts more vigorously with dilute hydrochloric acid than N does. M(OH)2 is more soluble than N(OH)2.
What could be the identities of L, M and N?
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
B
Question
Solutions P and Q each contain a different Group 2 ion at the same concentration. One contains Mg2+, the other contains Ba2+. Tests are carried out on separate 5 cm3 samples of P and Q.
test 1: add 1cm3 of 0.1 mol dm–3 Na2SO4(aq)
test 2: add 1cm3 of 0.1 mol dm–3 NaOH(aq)
What are the results of these tests?
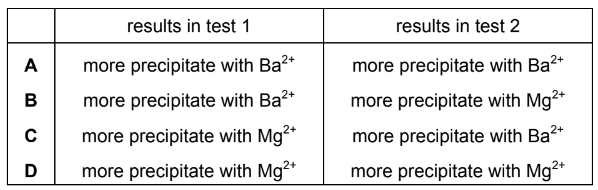
▶️Answer/Explanation
Answer B
Question
A 5.00 g sample of an anhydrous Group 2 metal nitrate loses 3.29 g in mass when heated strongly.
Which metal is present?
A magnesium
B calcium
C strontium
D barium
Answer/Explanation
Answer B
Question
A mixture of magnesium carbonate and magnesium nitrate is heated strongly in a hard-glass test-tube.
Which gases are formed?
1 carbon dioxide
2 nitrogen dioxide
3 oxygen
Answer/Explanation
Answer A
Question
Solutions of 0.1 mol dm–3 Mg(NO3)2 and 0.1 mol dm–3 Ba(NO3)2 separately undergo a series of reactions using pure reagents.
\(Mg(NO_{3})_{2}(aq)\xrightarrow[]{sodium\: carbonate\: solution}M\xrightarrow[]{excess\: HCl(aq)\: then\: boil}N\xrightarrow[]{excess\: NaOH(aq)}P\)
\(Ba(NO_{3})_{2}(aq)\xrightarrow[]{sodium\: carbonate\: solution}Q\xrightarrow[]{excess\: HCl(aq)\: then\: boil}R\xrightarrow[]{excess\: NaOH(aq)}S\)
M, N and P are magnesium compounds.
Q, R and S are barium compounds.
How many of M, N, P, Q, R and S are white precipitates?
A 2 B 3 C 4 D 5
Answer/Explanation
Answer B
Question
Substance X reacts with water. A gas is given off and the pH of the solution increases. The solution is then reacted with sulfuric acid and a white precipitate forms.
What could be substance X?
A barium
B barium oxide
C magnesium
D magnesium oxide
Answer/Explanation
Answer A
Question
1.15 g of a metallic element needs 300 cm3 of oxygen for complete reaction, under room conditions, to form an oxide which contains O2– ions.
What could be the identity of this metallic element?
A calcium
B magnesium
C potassium
D sodium
Answer/Explanation
Answer D
Question
Which reaction routes can be used to make a pure sample of barium sulfate?
1 \(Ba\: metal \xrightarrow[in\: O_{2}]{heat} product \xrightarrow[HCl]{dilute} product\: 2\xrightarrow[H_{2}SO_{4}]{dilute}product 3\xrightarrow[and\: dry]{filter,wash}\)
2 \(Ba(NO_{3})_{2} \xrightarrow[heat\: in\: air]{strong} solid\: product \xrightarrow[of\: water]{an\: excess} product 2 \xrightarrow[H_{2}SO_{4}]{dilute}product 3\xrightarrow[and\: dry]{filter,wash}\)
3 \(Ba(OH)_{2} \xrightarrow[HNO_{3}]{dilute} product \xrightarrow[H_{2}SO_{4}]{dilute} product 2\xrightarrow[and\: dry]{filter,wash}\)
Answer/Explanation
Answer A
Question
3 solubility of the hydroxides, M(OH)2, in water

Answer/Explanation
Answer A
Question
A sample of anhydrous calcium nitrate is placed in a test-tube and heated in a roaring Bunsen flame until it decomposes. The description of the gas in the test-tube is then noted. A glowing splint is then put into the test-tube and any changes are noted.
Which observations are correct?

Answer/Explanation
Answer B
Question
A transition metal ion, M2+, reacts with acidified dichromate(VI) ions to form M4+ ions, Cr3+ ions, and H2O.
Which equation correctly represents this reaction?
A \(Cr_{2}O_{7}^{2-} + 14H^{+} + M^{2+} \rightarrow 2Cr^{3+} + 7H_{2}O + M^{4+}\)
B \(Cr_{2}O_{7}^{2-} + 14H^{+} + 2M^{2+} \rightarrow 2Cr^{3+} + 7H_{2}O + 2M^{4+}\)
C \(Cr_{2}O_{7}^{2-} + 14H^{+} + 3M^{2+} \rightarrow 2Cr^{3+} + 7H_{2}O + 3M^{4+}\)
D \(Cr_{2}O_{7}^{2-} + 14H^{+} + 6M^{2+} \rightarrow 2Cr^{3+} + 7H_{2}O + 6M^{4+}\)
Answer/Explanation
Answer C
Question
Which row correctly describes one property of barium and one property of barium oxide?

Answer/Explanation
Answer D
Question
When 3.00g of an anhydrous nitrate of a Group 2 metal is decomposed, 1.53g of gas is produced.
What is the nitrate compound?
A beryllium nitrate
B calcium nitrate
C magnesium nitrate
D strontium nitrate
Answer/Explanation
Answer D
Question
Which element has the second smallest atomic radius in its group and the third lowest first ionisation energy in its period?
A boron
B calcium
C magnesium
D sodium
Answer/Explanation
Answer C
Question
A solution contains both Mg2+(aq) and Sr2+(aq) at the same concentration.
The solution is divided into two equal portions. Aqueous sodium hydroxide is added dropwise to one portion. Dilute sulfuric acid is added dropwise to the other portion.
Which row is correct?

Answer/Explanation
Answer:
B
Question
Which oxide is insoluble in aqueous sodium hydroxide?
A MgO B Al2O3 C P4O10 D SO2
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
A
Question
Which statements about the elements barium and calcium and their compounds are correct?
1 Barium nitrate decomposes at a higher temperature than calcium nitrate.
2 Barium hydroxide is more soluble in water than is calcium hydroxide.
3 Calcium is more reactive with water than is barium.
The responses A to D should be selected on the basis of
Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question
Compound Q is a white crystalline solid which dissolves easily in water. When concentrated sulfuric acid is added to a dry sample of Q steamy white fumes are formed which, when passed through aqueous silver nitrate solution, form a white precipitate. This precipitate is soluble in dilute ammonia solution.
What could be the identity of compound Q?
A AgCl B NaBr C NaCl D \(PbBr_2\)
Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Question
The mineral dolomite is a mixture of magnesium carbonate and calcium carbonate.
An aqueous reagent, X, was added to a small sample of dolomite. Effervescence was seen and a white solid, Y, was formed.
What could be the correct identity of reagent X and solid Y?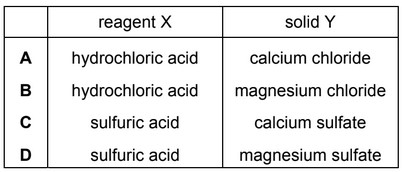
Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Question
Which compound would most usually be added to soil to reduce its acidity?
A aluminium hydroxide
B calcium hydroxide
C magnesium hydroxide
D sodium hydroxide
Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question
Samples of magnesium carbonate, \(MgCO_3\), are placed in crucibles R and S. The sample in crucible R is heated until there is no further loss in mass, and then allowed to cool. The sample in crucible S is left unheated. Dilute hydrochloric acid is then added to both crucibles.
On adding the dilute hydrochloric acid, which observations are correct?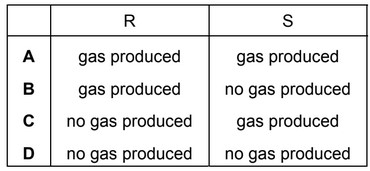
Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Question
An excess of MgO is shaken with water. The resulting mixture is filtered into test-tube X.
An excess of BaO is shaken with water. The resulting mixture is filtered into test-tube Y.
Which oxide reacts more readily with water and which filtrate has the lower pH?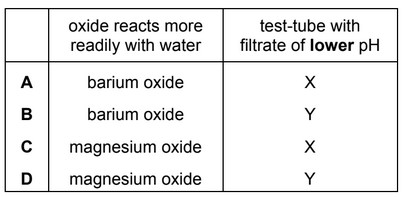
Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Question
Which row of the table gives correct comparisons between the solubilities of calcium and barium hydroxide and the thermal stabilities of calcium and barium carbonate?
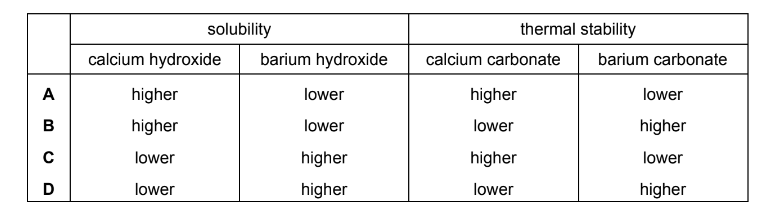
Answer/Explanation
Answer: D
Question
Sodium azide, NaN3 is an explosive used to inflate airbags in cars when they crash. It consists of positive sodium ions and negative azide ions.
What are the numbers of electrons in the sodium ion and the azide ion?
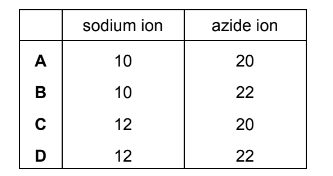
Answer/Explanation
Answer: B
Question
In some areas lime, Ca(OH)2, is added to soil to improve crop growth.
Which statement correctly describes a reason why lime improves crop growth?
A Lime acts as a catalyst which speeds up the release of nitrates into the soil.
B Lime is an effective pesticide and protects the plants from damage.
C Lime is used to reduce the acidity of the soil.
D Lime lowers the pH of the soil.
Answer/Explanation
Answer: C
Question
The solids sodium chloride and sodium iodide both react with concentrated sulfuric acid at room temperature.
With NaCl , the products are NaHSO4 and HCl.
With NaI, the products are NaHSO4, HI, I2, SO2, H2O, S and H2S.
What is the best explanation for this difference in products?
A Chloride ions will displace iodine from solution.
B Hydrogen chloride is more volatile than hydrogen iodide.
C Iodide ions are better reducing agents than chloride ions.
D Sulfuric acid is able to act as a dehydrating agent with NaI.
Answer/Explanation
Answer: C
Question
X and Y are both Group 2 metals.
X and Y both form hydroxide compounds, but X(OH)2 is more soluble in water than Y(OH)2.
If a piece of metal Y is put into cold water a very slow reaction occurs, and only a very few, small hydrogen bubbles can be seen.
What could be the identities of X and Y?
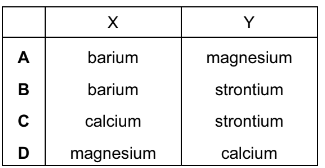
Answer/Explanation
Answer: A
Question
X is a Group II metal. It forms a sulfate which is more soluble than barium sulfate. It forms a hydroxide which is more soluble than calcium hydroxide. What could be the identity of X?
1 strontium
2 magnesium
3 beryllium
The responses A to D should be selected on the basis of
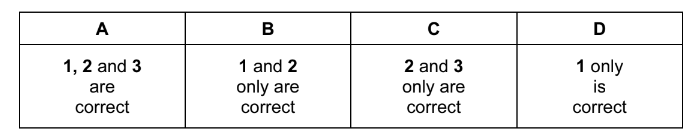
Answer/Explanation
Ans:D
Question
Mohr’s salt is a pale green crystalline solid which is soluble in water. It contains two cations, one of which is\( Fe2^{+}0\), and one anion which is \(SO_{4}^{2–}\).
The identity of the second cation was determined by heating Mohr’s salt with aqueous sodium hydroxide. A colourless gas was evolved which readily dissolved in water giving an alkaline solution. A green precipitate was also formed.
What are the identities of the gas and the precipitate?
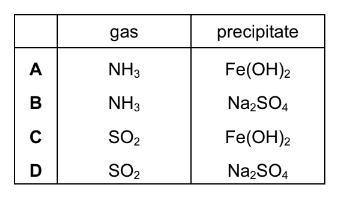
Answer/Explanation
Ans:A
Question
Which statements concerning the Group II elements magnesium, calcium and barium are correct?
1 Their reactivity increases with increasing relative atomic mass.
2 The oxidation number exhibited in their stable compounds is +2.
3 On strong heating, their nitrates give off oxygen only.
The responses A to D should be selected on the basis of
Answer/Explanation
Ans:B
Question
Rat poison needs to be insoluble in rain water but soluble at the low pH of stomach contents. What is a suitable barium compound to use for rat poison?
A barium carbonate
B barium chloride
C barium hydroxide
D barium sulfate
Answer/Explanation
Ans:A
Question
X is a Group II metal. The carbonate of X decomposes when heated in a Bunsen flame to give carbon dioxide and a white solid residue as the only products. This white solid residue is sparingly soluble in water. Even when large amounts of the solid residue are added to water the pH of the saturated solution is less than that of limewater. What could be the identity of X?
A magnesium
B calcium
C strontium
D barium
Answer/Explanation
Ans:A
Question
Which property is not associated with the element sodium?
A It can react with cold water to form hydrogen.
B It forms a basic oxide.
C It forms a neutral chloride.
D It is an oxidising agent.
Answer/Explanation
Ans:D
Question
Group II nitrates undergo thermal decomposition according to the following equation.
\(X(NO_{3})_{2}\rightarrow XO+2NO_{2}+\frac{1}{2}O_{2}\)
Which Group II nitrate requires the highest temperature to bring about its thermal decomposition?
A barium nitrate
B calcium nitrate
C magnesium nitrate
D strontium nitrate
Answer/Explanation
Ans:A
Question
The Group II metals have higher melting points than the Group I metals.
Which factors could contribute towards the higher melting points?
1 There are smaller interatomic distances in the metallic lattices of the Group II metals.
2 More electrons are available from each Group II metal atom for bonding the atom into the
metallic lattice.
3 Group II metals have a higher first ionisation energy than the corresponding Group I metal.
Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question
Solids W, X, Y and Z are compounds of two different Group II metals. Some of their applications are described below.
Compound W is used as a refractory lining material in kilns.
Compound X is used as a building material. It can also be heated in a kiln to form compound Y.
When Y is hydrated, it forms compound Z which is used agriculturally to treat soils.
Which statements about these compounds are correct?
1 More acid is neutralised by 1g of W than by 1g of X.
2 The metallic element in W reacts with water more quickly than the metallic element in Y.
3 Adding Z to a soil decreases the pH of the soil.
The responses A to D should be selected on the basis of
No other combination of statements is used as a correct response.
Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Question
Which reagents, when used in an excess, can be used to make sodium lactate,
\(CH_3CH(OH)CO_2Na\), from lactic acid, \(CH_3CH(OH)CO_2H\)?
1 Na
2 \(NaHCO_3\)
3 NaOH
The responses A to D should be selected on the basis of
Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Question
Use of the Data Booklet is relevant to this question.
Magnesium nitrate, Mg(NO3)2, will decompose when heated to give a white solid and a mixture of gases. One of the gases released is an oxide of nitrogen, X. 7.4g of anhydrous magnesium nitrate is heated until no further reaction takes place.
What mass of X is produced?
A 1.5g B 2.3g C 3.0g D 4.6g
Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Question
In which row of the table are all statements comparing the compounds of magnesium and barium correct?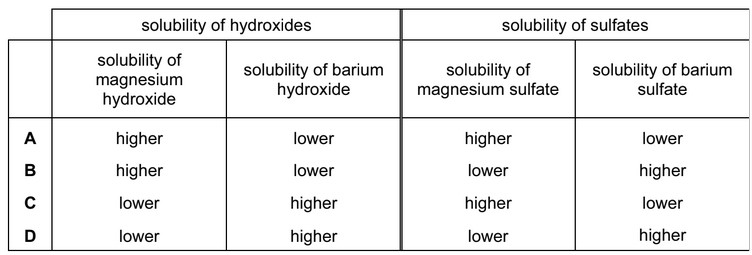
Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Question
Which statement explains the observation that magnesium hydroxide dissolves in aqueous
ammonium chloride, but not in aqueous sodium chloride?
A The ionic radius of the \(NH_4^+\) ion is similar to that of \(Mg^{2+}\) but not that of \(Na^+\).
B \(NH_4Cl\) dissociates less fully than NaCl.
C The \(Na^+\) and \(Mg^{2+}\) ions have the same number of electrons.
D The \(NH_4^+\) ion can donate a proton.
Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Question
Which row correctly identifies the uses of some of the compounds of Group II metals?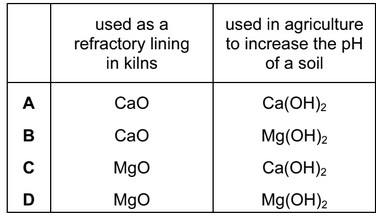
Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Question
Which property increases in value going down Group II?
A electronegativity
B ionic radius
C maximum oxidation number
D second ionisation energy
Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question .
When added to water, which oxides will not cause a change in pH?
- Al2O3
- SiO2
- P4O10
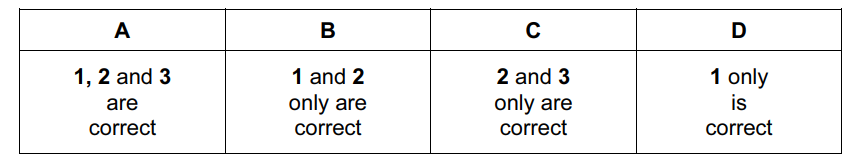
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
B
Question
Aluminium is extracted by the electrolysis of a molten mixture containing aluminium oxide. By a similar method, magnesium is extracted by the electrolysis of a molten mixture containing magnesium chloride.
Which statement about the extraction of magnesium is correct?
- Magnesium ions travel to the anode and are oxidised to magnesium metal.
- Magnesium ions travel to the anode and are reduced to magnesium metal.
- Magnesium ions travel to the cathode and are oxidised to magnesium metal.
- Magnesium ions travel to the cathode and are reduced to magnesium metal.
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
D
Question
The oxides BaO, CaO, MgO and SrO all produce alkaline solutions when added to water.
Which oxide produces the saturated solution with the highest pH?
A BaO(aq) B CaO(aq) C MgO(aq) D SrO(aq)
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
A
Question
Use of the Data Booklet is relevant to this question.
The reaction between aluminium powder and anhydrous barium nitrate is used as the propellant in some fireworks. The metal oxides and nitrogen are the only products.
Which volume of nitrogen, measured under room conditions, is produced when 0.783 g of anhydrous barium nitrate reacts with an excess of aluminium?
A 46.8 cm3 B 72.0 cm3 C 93.6 cm3 D 144 cm3
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
B