Question
A white powder is a mixture of sodium chloride and sodium iodide. It is dissolved in water in a test-tube. An excess of aqueous silver nitrate is added to the test-tube. A precipitate, X, is observed.
An excess of concentrated ammonia is then added to the test-tube containing X. After the test-tube has been shaken, a precipitate, Y, is observed.
Which statement about X or Y is correct?
A X is a pure white colour.
B X is pure silver iodide.
C Y is pure silver chloride.
D Y is yellow
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:D
Question
In a series of nine experiments, to test the reactivity of the halogens, an aqueous solution of each halogen is added to an equal volume of an aqueous solution containing halide ions, as shown in the table.
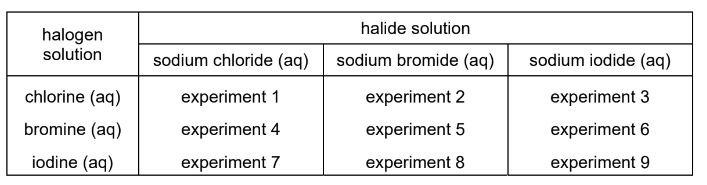
The nine resulting mixtures are then shaken separately with an equal volume of hexane. The nine tubes are left to stand so that the aqueous and organic solvents separate into layers.
How many test-tubes contain a purple upper hexane layer?
A 1 B 2 C 3 D 5
Answer/Explanation
Answer D
Question
The reaction of bromine with warm NaOH(aq) produces products with the same oxidation numbers, in the same ratios, as the reaction of chlorine with hot NaOH(aq). In one reaction between bromine and warm NaOH(aq), 30.2 g of a product containing sodium, bromine and oxygen is produced.
Which mass of NaOH has reacted?
A 8.00 g B 10.2 g C 20.3 g D 48.0 g
Answer/Explanation
Answer D
Question
Concentrated sulfuric acid is added to separate solid samples of sodium chloride, sodium bromide and sodium iodide. With which samples does sulfuric acid act as an oxidising agent?
A sodium chloride only
B sodium chloride and sodium bromide
C sodium bromide and sodium iodide
D sodium iodide only
Answer/Explanation
Answer C
Question
Bromine is extracted from sea-water. In the final stages of the process two redox reactions take place.
Br2(aq) + SO2(g) + 2H2O(l) → 2HBr(aq) + H2SO4(aq)
2HBr(aq) + Cl2(g) → Br2(g) + 2HCl(aq)
Which row is correct?
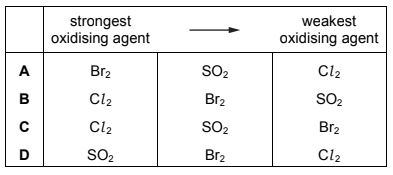
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
B
Question
A reaction pathway diagram is shown.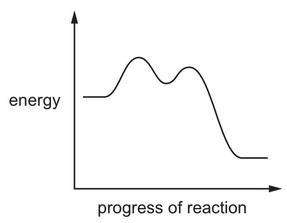
Which reactions would have this reaction pathway diagram?
1 \((CH_3)_3CBr + NaOH → (CH_3)_3COH + NaBr\)
2 \(CH_3CH_2CH_2Br + NaOH → CH_3CH_2CH_2OH + NaBr\)
3 \((CH_3)_3CCH_2CH_2Cl + 2NH_3 → (CH_3)_3CCH_2CH_2NH_2 + NH_4Cl\)
The responses A to D should be selected on the basis of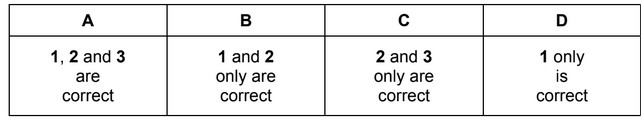
Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Question
When concentrated sulfuric acid reacts with sodium iodide the products include sulfur, iodine, hydrogen sulfide and sulfur dioxide.
Which statement is correct?
A Hydrogen sulfide is the product of a reduction reaction.
B Iodide ions are stronger oxidising agents than sulfate ions.
C Sulfur atoms from the sulfuric acid are both oxidised and reduced.
D Sulfur atoms from the sulfuric acid are oxidised to make sulfur dioxide.
Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Question
The presence of a halogen in an organic compound may be detected by warming the organic compound with aqueous silver nitrate.
Which compound would be the quickest to produce a precipitate?
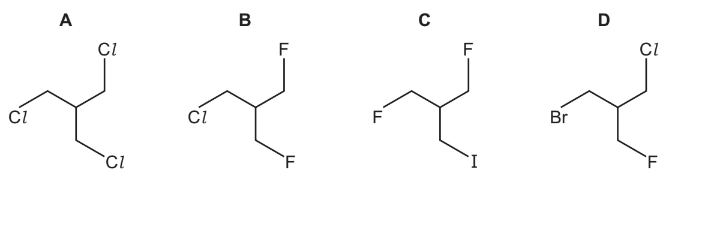
Answer/Explanation
Ans:C
Question
A reaction pathway diagram is shown.
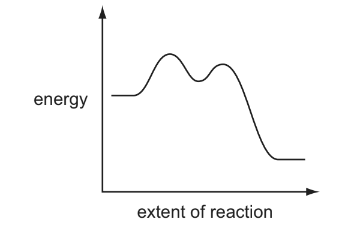
Which reactions would have this profile?
1 \( (CH_{3})_{3}CBr + NaOH → (CH_{3})_{3]COH + NaBr\)
2 \(CH_{3}CH_{2}Br + NaOH → CH_{3}CH_{2}OH + NaBr\)
3 \((CH_{3})_{3}CCH_{2}CH_{2}Cl + 2NH_{3} → (CH_{3})_{3}CCH_{2}CH_{2}NH_{2} + NH_{4}Cl\)
The responses A to D should be selected on the basis of
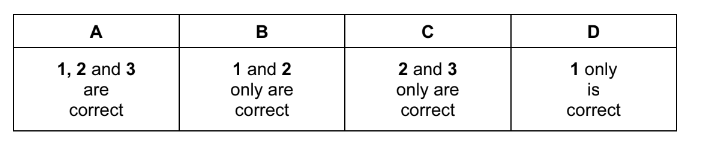
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:D
Question
A test-tube of HI gas and a test-tube of HBr gas are placed together in an environment at temperature, T. Which combinations of observations are possible depending on the temperature, T?
1 A brown vapour appears in one of the test-tubes. No change is apparent in the other test-tube.
2 A brown vapour appears in one of the test-tubes. A purple vapour appears in the other test-tube.
3 No change is apparent in either test-tube.
The responses A to D should be selected on the basis of

Answer/Explanation
Ans:C
Question
Y is a salt of one of the halogens chlorine, bromine, iodine, or astatine (element 85).
The reaction scheme shows a series of reactions using a solution of Y as the starting reagent.
What could Y be?
A sodium chloride
B sodium bromide
C potassium iodide
D potassium astatide
Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Question
What happens when iodine solution is added to a solution of sodium bromide?
A A reaction occurs without changes in oxidation state.
B Bromide ions are oxidised, iodine atoms are reduced.
C Bromide ions are reduced, iodine atoms are oxidised.
D No reaction occurs.
Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Question
\ Strontium metal can be obtained by the electrolysis of molten strontium bromide, \(SrBr_2\), using the apparatus shown in the diagram.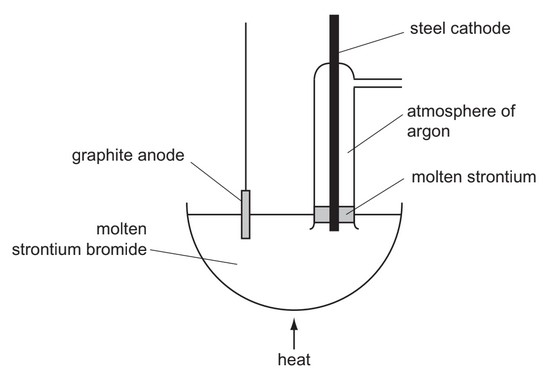
Why is an atmosphere of argon used around the cathode?
A A thin film of a compound of strontium and argon forms on the surface protecting the freshly formed metal.
B The argon keeps the strontium molten.
C The argon stops the molten strontium rising too high in the tube.
D Without the argon, strontium oxide would form in the air.
Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Question
Which statements are correct for all three halogens, chlorine, bromine and iodine?
- They all form hydrides that are strong acids in aqueous solution.
- They all react with aqueous sodium hydroxide to form oxo-anions.
- They all require one more electron to fill the p orbitals of their outer shells.
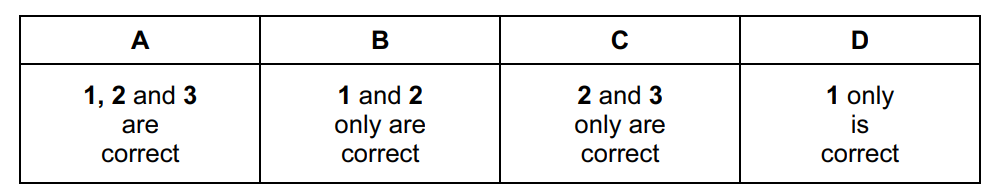
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
A
Question
The presence of halogen in an organic compound may be detected by warming the organic compound with aqueous silver nitrate.
Which compound would produce a precipitate quickest?
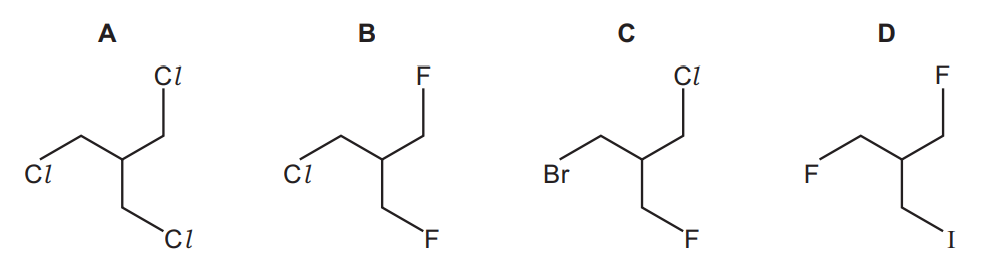
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
D