Question
Hydrogen bromide can be added to T to give compound U. Compound U can be hydrolysed to compound V.
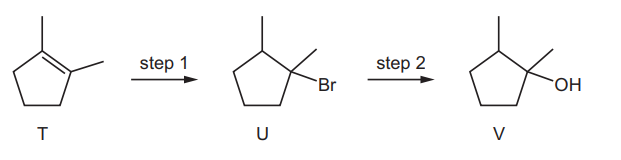
Four students, W, $X, Y$ and $Z$, made the following statements.
W All the atoms in a molecule of compound T lie in the same plane.
$X$ Compound V contains only one chiral centre.
$Y$ Step 1 is an electrophilic addition reaction.
Z Step 2 is a nucleophilic substitution reaction.
Which two students are correct?
A W and $Y$ B W and Z C $X$ and $Y$ D $\mathrm{Y}$ and $\mathrm{Z}$
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:D
Question
What is true of every nucleophile?
A It attacks a double bond.
B It donates a lone pair of electrons.
C It is a single atom.
D It is negatively charged.
Answer/Explanation
Answer B
Question
Sodium methoxide, Na+CH3O–, reacts with 2-chloro-2-methylpropane in a nucleophilic substitution reaction. The nucleophile is the CH3O– ion.
Which row is correct?
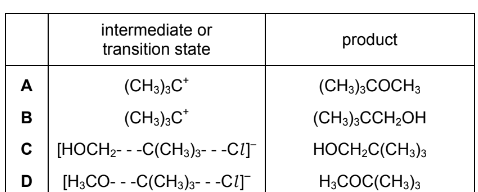
Answer/Explanation
Answer A
Question
An organic ion containing a carbon atom with a negative charge is called a carbanion.
An organic ion containing a carbon atom with a positive charge is called a carbonation.
The reaction between aqueous sodium hydroxide and 1-bromobutane proceeds by an SN2 mechanism.
What is the first step in the mechanism?
A attack by a nucleophile on a carbon atom with a partial positive charge
B heterolytic bond fission followed by attack by an electrophile on a carbanion
C heterolytic bond fission followed by attack by a nucleophile on a carbocation
D homolytic bond fission followed by attack by a nucleophile on a carbocation
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
A
Question
Many, but not all, organic reactions need to be heated before a reaction occurs.
Which reaction occurs quickly at room temperature, 20 °C?
A \(C_2H_4 + Br_2 → C_2H_4Br_2\)
B \(C_2H_4 + H_2O → CH_3CH_2OH\)
C \(CH_3CH_2OH → C_2H_4 + H_2O\)
D \(CH_3CH_2OH + HBr → CH_3CH_2Br + H_2O\)
Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Question
Which organic reaction is an example of nucleophilic substitution?
A \(CH_3CH_2Br + NaOH → CH_2CH_2 + H_2O + NaBr\)
B \(CH_3CH_2Br + NaOH → CH_3CH_2OH + NaBr\)
C \(CH_2CH_2 + HCl → C_2H_5Cl\)
D \(C_2H_6 + Cl_2 → C_2H_5Cl + HCl\)
Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question
Many, but not all, organic reactions need to be heated before a reaction occurs.
Which reaction occurs quickly at room temperature, 20 °C?
A \(C_2H_4 + Br_2 → C_2H_4Br_2\)
B \(C_2H_4 + H_2O → CH_3CH_2OH\)
C \(CH_3CH_2OH → C_2H_4 + H_2O\)
D \(CH_3CH_2OH + HBr → CH_3CH_2Br + H_2O\)
Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Question
When onions are peeled in air, the reaction shown is thought to occur.
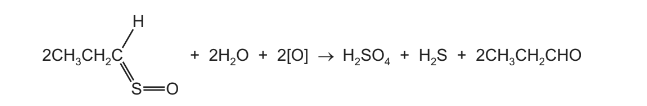
Which tests would give a positive reaction with the organic product?
1 warming with Tollens’ reagent
2 warming with acidified potassium manganate(VII)
3 warming with alkaline aqueous iodine
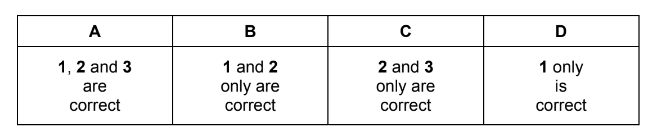
Answer/Explanation
Answer: B
Question
What is the organic product when ethanamide, \(CH_{3}CONH_{2}\), is boiled with excess aqueous sodium hydroxide?
A CH_{3}CN
B \(CH_{3}CO_{2}^{–}
NH4^{+}\)
C \(CH_{3}CONH^{–}Na^{+}\)
D \(CH_{3}CO_{2}^{–} Na^{+}\)
Answer/Explanation
Ans:D
Question
The cyclic compound M is heated with dilute hydrochloric acid.
What are the products of the reaction?
A \(HOCH_{2}CO_{2}H\) and \(H_{2}NCH_{2}CO_{2}H\)
B\( HO_{2}CCH_{2}OH\) and \(HO_{2}CCH_{2}NH_{3}^{+}\)
C \(H_{2}NCOCH_{2}OH\) and\( HOCH_{2}CHO\)
D \(HOCH_{2}CONH_{3}^{+}\) and \(HOCH_{2}CHO\)
Answer/Explanation
Ans:B
Question
Which reagent will give a different observation with compounds P and Q?
\(HOCH_{2}CH(OH)CHO \) : P
\( HOCH_{2}COCH_{2}OH\) : Q
A \( Br_{2}(aq)\)
B hot acidified \(KMnO_{4}\)
C silver nitrate in ammonia solution
D warm acidified K-\({2}Cr_{2}O_{7}\)
Answer/Explanation
Ans:C
Question
Which compound undergoes an SN1 substitution reaction with NaOH(aq)?
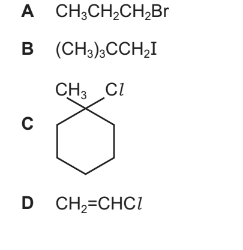
Answer/Explanation
Ans:C
Question
Compound Q contains three double bonds per molecule.
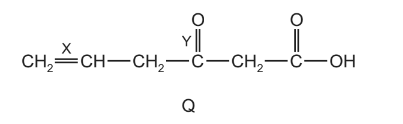
Which bond, X or Y, will be ruptured by hot, concentrated acidified \(KMnO_{4}\) and how many lone pairs of electrons are present in one molecule of Q?
Answer/Explanation
Ans:B
Question
\(CH_{3}CH_{2}COCH_{2}CH_{3}\) reacts with hydrogen cyanide to form an organic product called a cyanohydrin. Which feature applies to the cyanohydrin product?
A It has one chiral centre.
B It is formed by electrophilic addition.
C It is formed via an intermediate which contains the C–OH group.
D Its formation requires the use of cyanide ions as a catalyst.
Answer/Explanation
Ans:D
Question
Many organic reactions need to be heated before reaction occurs, but some do not require heating. Which reaction occurs quickly at room temperature?
A\( C_{2}H_{4} + Br2 → C_{2}H_{4}Br_{2}\)
B \( C_{2}H_{4} + H_{2}O → CH_{3}CH_{2}OH\)
C \( CH_{3}CH_{2}OH → C_{2}H_{4} + H_{2}O\)
D \( CH_{3}CH_{2}OH + HB_{r} → CH_{3}CH_{2}Br + H_{2}O\)
Answer/Explanation
Ans:A
Question
A sun protection cream contains the following ester as its active ingredient.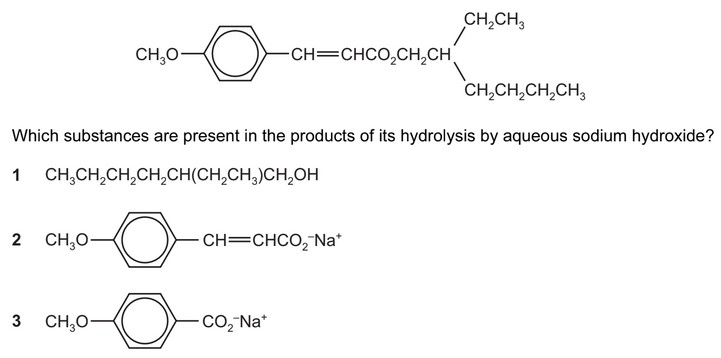
The responses A to D should be selected on the basis of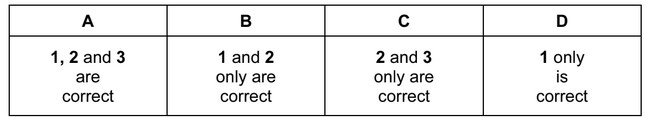
Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question
Bromine reacts with ethene to form 1,2-dibromoethane.
What is the correct description of the organic intermediate in this reaction?
A It has a negative charge.
B It is a free radical.
C It is a nucleophile.
D It is an electrophile.
Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Question
In which reaction is the organic compound oxidised?
A \(CH_3CH_2OH\) + concentrated \(H_3PO_4\)
B \(CH_3CH_2CH_2CHO\) + Tollens’ reagent
C \(CH_3COCH_3\) + 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine reagent
D \(CH_3CN\) + dilute \(H_2SO_4\)
Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question
A carbanion is an organic ion in which a carbon atom has a negative charge. A carbocation is an
organic ion in which a carbon atom has a positive charge.
The reaction between aqueous sodium hydroxide and 1-bromobutane proceeds by an SN2
mechanism.
How should the first step in the mechanism be described?
A attack by a nucleophile on a carbon atom with a partial positive charge
B heterolytic bond fission followed by an attack by an electrophile on a carbanion
C heterolytic bond fission followed by an attack by a nucleophile on a carbocation
D homolytic bond fission followed by an attack by a nucleophile on a carbocation
Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Question
Many, but not all, organic reactions need to be heated before reaction occurs.
Which reaction occurs at a good rate at room temperature (20°C)?
- \(CH_{3}OH+PCl_{5}\rightarrow CH_{3}Cl+POCl_{3}+HCl\)
- \(CH_{3}CH_{2}Br+KCN\rightarrow CH_{3}CH_{2}CN+KBr\)
- \(CH_{3}CH_{2}OH\rightarrow C_{2}H_{4}+H_{2}O\)
- \(CH_{3}CH_{2}CN + 2H_{2}O → CH_{3}CH_{2}CO_{2}H + NH_{3}\)
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
A