Question
Ibuprofen and paracetamol are pain-relief drugs.
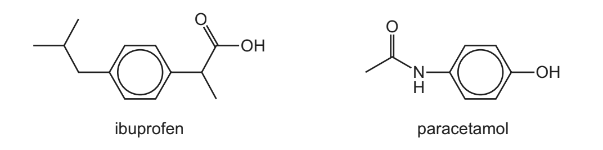
(a) Ibuprofen and paracetamol both contain the aryl (benzene) functional group.
Name the other functional groups present in each molecule.
(b) Ibuprofen contains a chiral centre and shows stereoisomerism.
(i) State what is meant by the term chiral centre.
(ii) Draw the two stereoisomers of ibuprofen.

(c) Draw the structures of the organic products when ibuprofen and paracetamol react separately
with LiAlH4.
(d) A student carried out some reactions with solutions of ibuprofen and paracetamol using
reagents D and E and the following results were obtained.
(✓ means a reaction took place.)
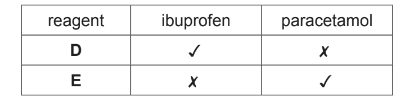
(i) Suggest a possible identity for each reagent D and E.
(ii) Give the structure of the organic product formed when reagent D reacted with ibuprofen.
(iii) Give the structure of the organic product formed when reagent E reacted with paracetamol.
(e) One of the steps in the manufacture of ibuprofen is shown.
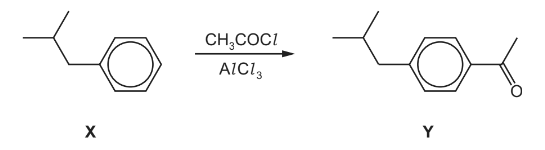
(i) Write an equation for the reaction between CH3COCl and AlCl3.
(ii) Complete the mechanism for the conversion of X into Y. Include all necessary curly arrows,
any relevant dipoles and charges.
(iii) Name the mechanism in (ii).
Answer/Explanation
Answer: (a) ibuprofen: carboxylic acid / carboxyl
paracetamol: phenol and amide
any two = 1 mark
all three = 2 marks
(b)(i) (chiral centre is a) carbon OR atom that has four different groups /atoms / species attached to it
(b)(ii) 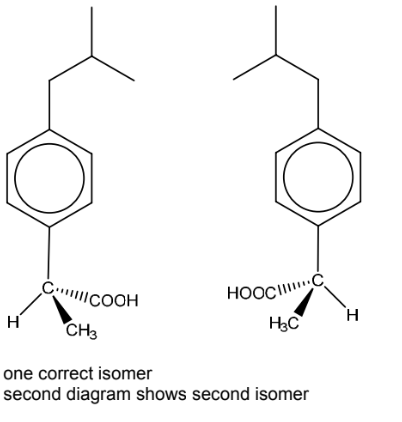
(c) 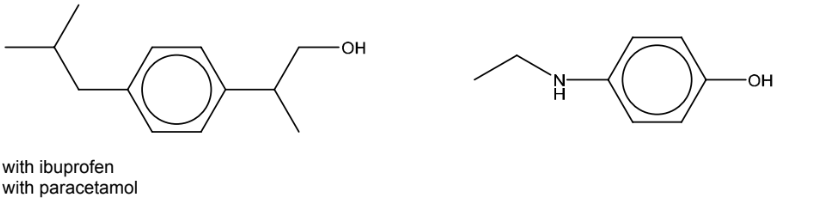
(d)(i) (reagent D) Na2CO3 / any carbonate
(reagentE) Cl2 /Br2
(d)(ii) 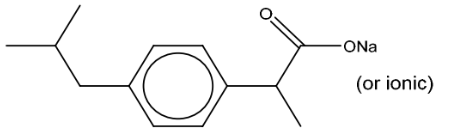
(d)(iii) 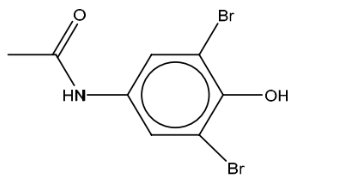
(e)(i) CH3COCl + AlCl3→CH3CO+ + AlCl4–
(e)(ii) 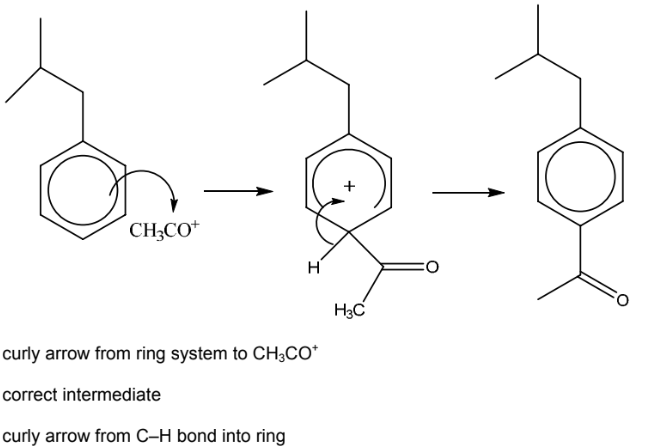
6(e)(iii) electrophilic substitution
Question
(a) Below is a list of species which can react with organic compounds.
$
\mathrm{CN}^{-} \mathrm{HCl} \quad \mathrm{Cl} \quad \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O} \quad \mathrm{CO}_3^{2-}
$
(i) From the list, identify a species which can react with ethane.
(ii) From the list, identify two species which can attack the $\pi$ bond in ethene.[1]
(iii) From the list, identify a species which can be used to distinguish between solutions of propanoic acid and propan-1-ol. Describe any relevant observations.[2]
(b) $\mathrm{Cl}(\mathrm{g})$ can be made from $\mathrm{Cl}_2(\mathrm{~g})$.
(i) Describe the conditions required for this process.[1]
(ii) Name this process.[1]
(c) (i) Name an organic functional group which reacts with a nucleophile in an addition reaction.
(ii) Name an organic functional group which tends to react with a nucleophile in an $\mathrm{S}_{\mathrm{N}} 1$ substitution mechanism.[1]
(d) But-1-ene reacts with steam in the presence of concentrated phosphoric acid to form two isomers of molecular formula $\mathrm{C}_4 \mathrm{H}_{10} \mathrm{O}$.
Each reaction occurs via a different intermediate ion.
(i) Draw the structure of both intermediate ions.[2]
(ii) Circle the more stable intermediate ion drawn in (d)(i). Explain your answer.[2][Total: 12]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a)(i) Cl
(a)(ii) $\mathrm{HC} l$ AND $\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}$
(a)(iii) $\begin{aligned} & \text { M1 } \mathrm{CO}_3{ }^{2-} \\ & \text { M2 propanoic acid-effervesce. (Propan-1-ol-no reaction) }\end{aligned}$
(b)(i) ultraviolet light / uv
(b)(ii) homolytic fission (of chlorine (gas) $/ \mathrm{Cl}_2$ )
(c)(i) carbonyl / aldehyde / ketone
(c)(ii) tertiary halogenoalkane
(d)(i) Two structures representing the intermediate
$
\begin{aligned}
& \text { M1 } \mathrm{C}_2 \mathrm{H}_5 \mathrm{C}^{+} \mathrm{HCH}_3 \\
& \text { M2 } \mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{C}^{+} \mathrm{H}_2
\end{aligned}
$
(d)(ii)
Identify the most stable intermediate
M1 $\mathrm{C}_2 \mathrm{H}_5 \mathrm{C}^{+} \mathrm{HCH}_3$
explanation
M2 (more / 2 alkyl groups attached so) it has the greater inductive / electron donating effect