Question
Structural and stereoisomerism should be considered when answering this question. Compounds X, Y and Z are shown.
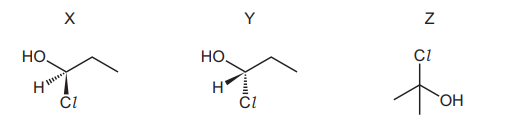
How many other isomers of $\mathrm{C}_3 \mathrm{H}_7 \mathrm{ClO}$ are there that are alcohols?
A 2
B 3
C 4
D 5
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:D
Question
An alcohol has the molecular formula \(C_{5}H_{12}O\). It has several isomers.
Which isomer forms a yellow precipitate with alkaline aqueous iodine?
A 2,2-dimethylpropan-1-ol
B 2-methylbutan-2-ol
C 3-methylbutan-2-ol
D pentan-3-o
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:C
Question
The structure of compound Q is shown.
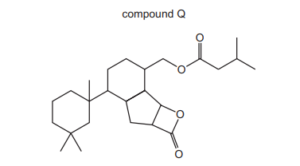
How many chiral centres are present in a molecule of Q?
A 4 B 5 C 6 D 7
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:D
Question:
Structural isomerism and stereoisomerism should be considered when answering this question.
How many non-cyclic isomers have the molecular formula \(C_{5}H_{10}\)
A 3 B 4 C 5 D 6
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:D
Question
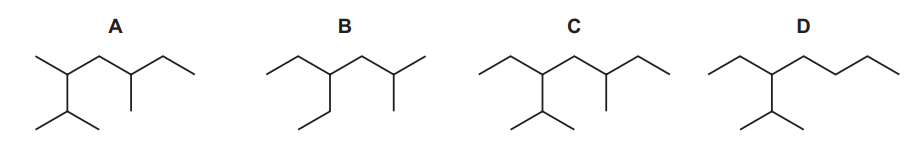
Kerosene is used as an aircraft fuel. Q is one of the molecules in kerosene and has the skeletal formula shown.
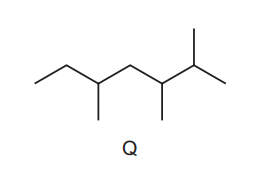
Other structural isomers of this molecule are also found in kerosene.
Which structure is a structural isomer of Q?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:D
Question
Compound $\mathbf{X}$ has the molecular formula $\mathrm{C}_3 \mathrm{H}_6 \mathrm{O}_3$.
Heating $\mathbf{X}$ under reflux with acidified $\mathrm{K}_2 \mathrm{Cr}_2 \mathrm{O}_7$ forms $\mathrm{HO}_2 \mathrm{CCOCO}_2 \mathrm{H}$.
Reacting $\mathbf{X}$ with $\mathrm{NaBH}_4$ forms $\mathrm{HOCH}_2 \mathrm{CH}(\mathrm{OH}) \mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{OH}$.
What is a possible structural formula for $\mathbf{X}$ ?
$1 \mathrm{HOCH}_2 \mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{CO}_2 \mathrm{H}$
$2 \mathrm{HOCH}_2 \mathrm{CH}(\mathrm{OH}) \mathrm{CHO}$
$3 \mathrm{HOCH}_2 \mathrm{COCH}_2 \mathrm{OH}$
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:C
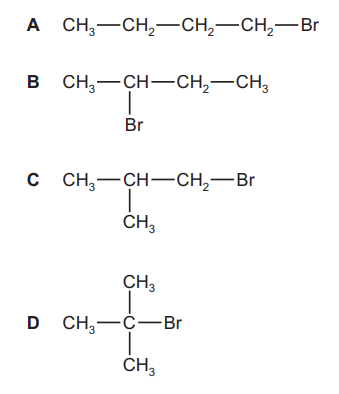
Question
Structural isomerism and stereoisomerism should be considered in answering this question.
Compound $\mathrm{J}$ is reacted with $\mathrm{KOH}$ dissolved in ethanol. Three isomeric alkenes with molecular formula $\mathrm{C}_4 \mathrm{H}_8$ are formed.
What is $\mathrm{J}$ ?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:B
Question
Geraniol and nerol are compounds found in some flower fragrances. They are isomers of each other.
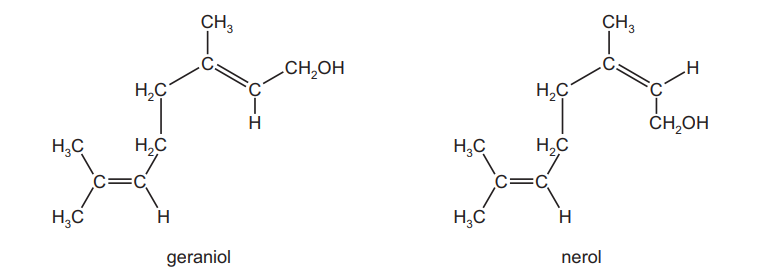
Which type of isomerism is shown here?
A chain
B geometrical (cis-trans)
C optical
D positional
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:B
Question
In this question, alkenes and cyclic alkanes should be considered.
How many structural isomers of \(C_4H_8\) are there?
A 3 B 4 C 5 D 6
Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Question
Structural isomerism and stereoisomerism should be taken into account when answering this question.
How many isomeric alkenes with formula \(C_5H_8\) are present in the mixture produced when
1,4-dibromopentane is reacted with NaOH in ethanol?
A 1 B 2 C 3 D 4
Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
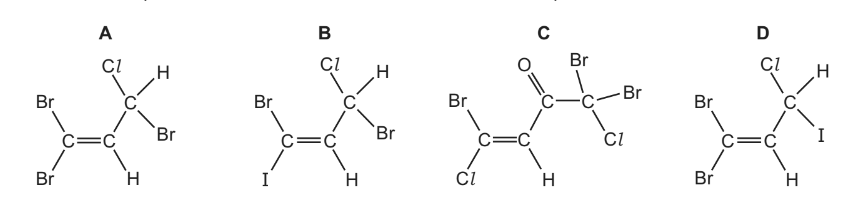
Question
Which compound could show both cis-trans isomerism and optical isomerism?
Answer/Explanation
Answer: B
Question
Structural isomerism and stereoisomerism should be considered when answering this question.
A colourless liquid, C5H11Cl , exists as a mixture of two optical isomers.
When heated with sodium hydroxide in ethanol, a mixture of only two alkenes is formed.
What could the colourless liquid be?
A (CH3CH2)2CHCl
B CH3CH2CH2CHClCH3
C CH3CH2CCl(CH3)2
D (CH3)2CHCHClCH3
Answer/Explanation
Answer D
Question
Structural isomerism only should be considered when answering this question.
Molecule X contains three C=C double bonds. One mole of X is reacted with three moles of HBr.
The carbon skeleton is unchanged.
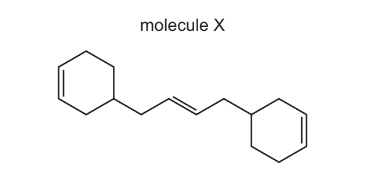
How many different products are formed?
A 3 B 4 C 6 D 8
Answer/Explanation
Answer B
Question
Structural isomerism only should be considered when answering this question.
Molecule X contains three C=C double bonds. One mole of X is reacted with three moles of HBr.
The carbon skeleton is unchanged.

How many different products are formed?
A 3 B 4 C 6 D 8
Answer/Explanation
Answer B
Question
How many structural isomers are there of trichloropropane, C3H5Cl3?
A 3 B 4 C 5 D 6
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
C
Question
Structural isomerism and stereoisomerism should be considered when answering this question. 2-bromopentane is heated with an excess of ethanolic sodium hydroxide.
How many different hydrocarbons are produced?
A 1 B 2 C 3 D 4
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
C
Question
Structural isomerism only should be considered when answering this question.
All the isomeric alcohols with the molecular formula C5H12O are added separately to warm alkaline aqueous iodine.
How many of the isomers give a yellow precipitate?
A 0 B 1 C 2 D 3
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
C
Question
Which compound is chiral?
A 1-chloro-3-methylbutane
B 2-chloro-2-methylbutane
C 2-chloro-3-methylbutane
D 3-chloropentane
Answer/Explanation
Answer C
Question
Structural isomerism and stereoisomerism should be considered when answering this question.
3-methylhexan-3-ol reacts with hot, concentrated sulfuric acid to form several isomeric compounds with the molecular formula C7H14.
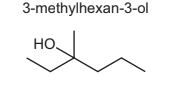
How many isomeric compounds could be formed in this reaction?
A 3 B 4 C 5 D 6
Answer/Explanation
Answer C
Question
The diagrams show two different compounds.
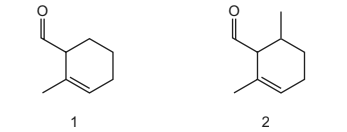
What is
● the total number of structural isomers, including compound 2, that could be formed
by adding a second methyl group to the ring of compound 1,
● the number of π electrons in each compound?
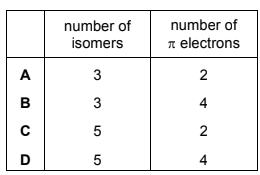
Answer/Explanation
Answer D
Question
Which compound shows optical isomerism and gives a positive test with alkaline aqueous iodine?
A CH3COCH(OH)CH3
B CH3COCH2CH2OH
C HOCH2CH(CH3)CHO
D (CH3)2C(OH)CHO
Answer/Explanation
Answer A
Question
A new jet fuel has been produced that is a mixture of different structural isomers of compound Q.
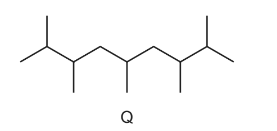
Which skeletal formula represents a structural isomer of Q?
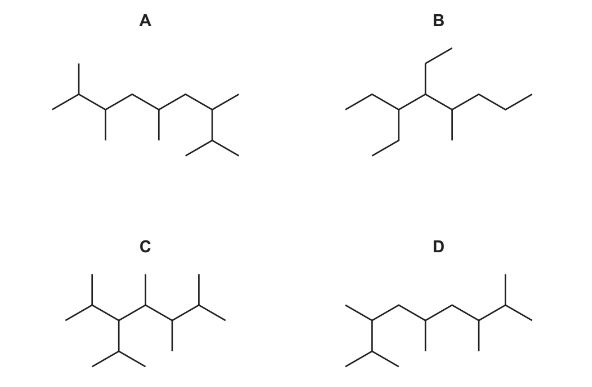
Answer/Explanation
Answer C
Question
X has the molecular formula C5H12O. X has a branched carbon skeleton and a secondary alcohol functional group.
How many structural isomers fit this description of X?
A 1 B 2 C 3 D 4
Answer/Explanation
Answer A
Question
Which types of stereoisomerism are shown by 2,4-dimethylhex-2-ene?
A both cis-trans isomerism and optical isomerism
B cis-trans isomerism only
C neither cis-trans isomerism nor optical isomerism
D optical isomerism only
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
D
Question
In which molecules do all the carbon atoms lie in the same plane?
1 2,3-dimethylbut-2-ene
2 propane
3 cyclohexane
The responses A to D should be selected on the basis of
No other combination of statements is used as a correct response.
Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question
The structural formula of compound Q is shown.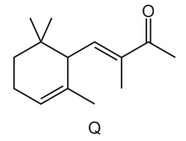
How many stereoisomers exist with this structural formula?
A 1 B 2 C 4 D 8
Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Question
P and Q are a pair of cis-trans isomers.
What must be the same for P and Q?
1 their empirical formula
2 their functional groups
3 their skeletal formula
The responses A to D should be selected on the basis of
Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question
Which compound gives a positive test with alkaline aqueous iodine and does not show optical isomerism?
A \(CH_3COCH_2CH_2OH\)
B \(CH_3CH_2CH(OH)CHO\)
C \(CH_3COCH(OH)CH_3\)
D \((CH_3)_2C(OH)CHO\)
Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Question
The drug cortisone has the formula shown.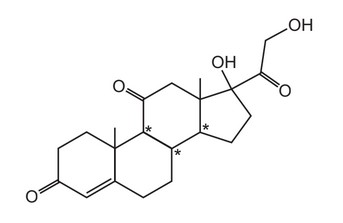
In addition to those chiral centres marked by an asterisk (*), how many other chiral centres are present in the cortisone molecule?
A 0 B 1 C 2 D 3
Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Question
Structural isomerism and stereoisomerism should be considered when answering this question.
Each of the following carbonyl compounds is reacted with \(NaBH_4\). The product of each reaction is
heated with \(Al_2O_3\) at 600 °C, generating one product or a mixture of isomers.
Which carbonyl compound will produce the most isomers?
A butanal
B butanone
C pentan-3-one
D propanone
Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question
Several structural isomers of C3H6O3 are listed below.
HOCH2COCH2OH
HOCH2CH(OH)CHO
HOCH2CH2CO2H
CH3CH(OH)CO2H
Which statements about these structural isomers are correct?
1 One mole of each reacts with two moles of sodium.
2 Only one of the isomers contains a tertiary alcohol group.
3 They all contain a primary alcohol group.
Answer/Explanation
Answer: D
Question
The diagram shows the structure of vitamin A.
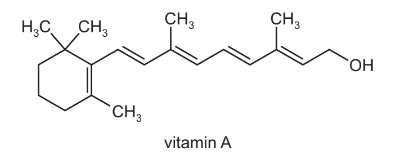
How many chiral centres are present in one vitamin A molecule?
A 0 B 1 C 2 D 3
Answer/Explanation
Answer: A
Question
In 1865 Kekulé suggested a ring structure for benzene, C6H6, in which a hydrogen atom is attached to each carbon atom.
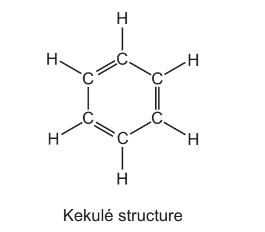
In this structure all of the bonds remain in the places shown. Assuming this is the structure of benzene, how many isomers of dichlorobenzene, C6H4Cl2, would exist?
A 3 B 4 C 5 D 6
Answer/Explanation
Answer: B
Question
Geranyl ethanoate is present in ginger and cocoa, and is used in shampoos and soaps as a
perfume. It reacts with an excess of bromine in an organic solvent to give X, a bromo-derivative.
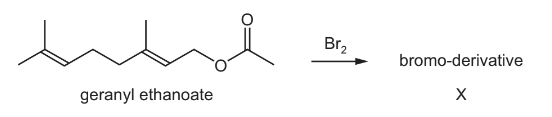
Including geranyl ethanoate, how many cis-trans isomers are there of geranyl ethanoate, and
how many chiral centres are there in X?
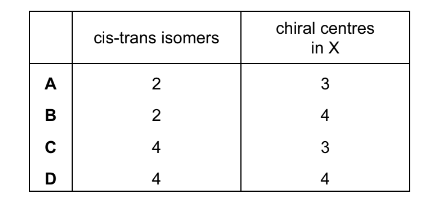
Answer/Explanation
Answer: A
Question
The diagrams show two different compounds.
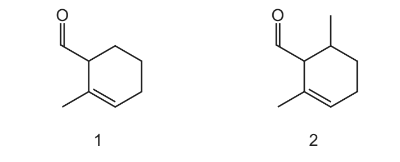
What is
-
-
- the total number of structural isomers, including compound 2, that could be formed by adding a second methyl group to the ring of compound 1,
- the number of π electrons in each compound?
-
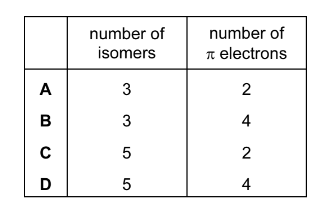
Answer/Explanation
Answer: D
Question
In 1869 Ladenburg suggested a structure for benzene, \(C_{6}H_{6}\), in which one hydrogen atom is attached to each carbon atom.
A compound \(C_{6}H_{4}Cl _{2}\) could be formed with the same carbon skeleton as the Ladenburg structure.
How many structural isomers would this compound have?
A 3 B 4 C 5 D 6
Answer/Explanation
Ans:D
Question
Sorbitol is a naturally-occurring compound with a sweet taste. It is often used as a substitute for
sucrose by the food industry.
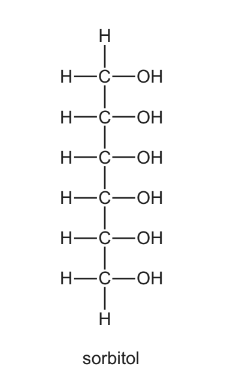
How many chiral centres are present in sorbitol?
A 3 B 4 C 5 D 6
Answer/Explanation
Ans:B
Question
A new jet fuel has been produced that is a mixture of different structural isomers of compound Q.
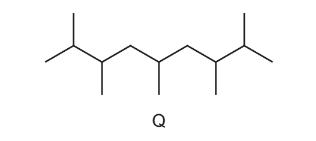
Which skeletal formula represents a structural isomer of Q?
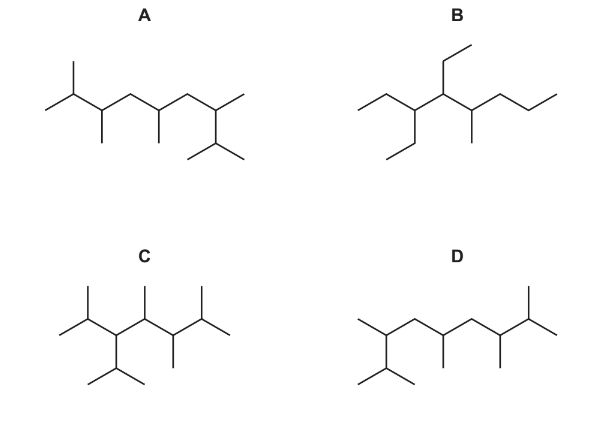
Answer/Explanation
Ans:C
Question
How many isomeric esters have the molecular formula \(C_{4}H_{8}O_{2} \)?
A 2 B 3 C 4 D 5
Answer/Explanation
Ans:C
Question
Considering only structural isomers, what is the number of alcohols of each type with the formula \(C_{5}H_{12}O\)?
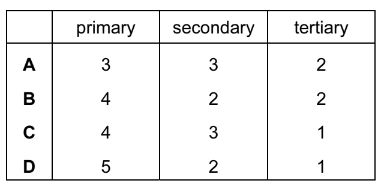
Answer/Explanation
Ans:C
Question
How many geometrical (cis-trans) isomers are there of hex-2,4-diene, CH_{3}CH=CHCH=CHCH ?
A none; hex-2,4-diene does not show geometric isomerism
B 2
C 3
D 4
Answer/Explanation
Ans:C
Question
There are three structural isomers with the formula \(C_{5}H_{12}\). Which formulae correctly represent these three structural isomers?
A \(CH_{3}CH_{2}CH_{2}CH_{2}CH_{3} \) \(CH_{3}CH_{2}CHCH_{3}CH_{3}\) \(CH_{3}CH_{3}CCH_{3}CH_{3}\)
B \(CH_{3}CH_{2}CH_{2}CH_{2}CH_{3}\) \(CH_{3}CH_{2}(CH)CH_{3}CH_{3}\) \(C(CH_{3})_{4}\)
C \(CH_{3}CH_{2}CH_{2}CH_{2}CH_{3}\) \(CH_{3}CH(CH_{3})CH_{3}\) \(CH_{3}C(CH_{3})2CH_{3}\)
D \(CH_{3}CH_{2}CH_{2}CH_{2}CH_{3} \) \(CH_{3}CH(CH_{3})CH_{2}CH_{3}\) \(CH_{3}CH_{2}CH(CH_{3})CH_{3}\)
Answer/Explanation
Ans:C
Question
The following compounds are found in the seaweed Asparagopsis taxiformis.
Which compound could show both cis-trans isomerism and optical isomerism?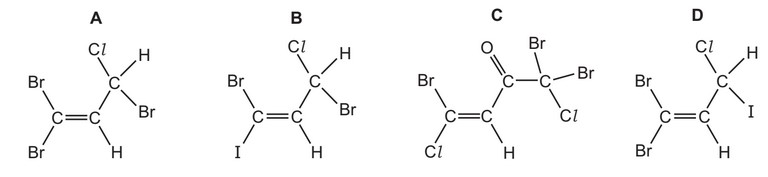
Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question
An organic compound Y, molecular formula \(C_6H_{14}O\), may be oxidised to compound Z, molecular formula \(C_6H_{12}O_2\).
What could be the structural formula of Y?
1 \(CH_3CH_2CH(CH_2OH)CH_2CH_3\)
2 \((CH_3)_3CCH_2CH_2OH\)
3 \(CH_3CH_2CH(CH_3)CH_2CH_2OH\)
Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Question
Which compound exhibits stereoisomerism?
A \(CH_3CHClCH_3\)
B \(CH_3CHClCH_2Cl\)
C \(CH_3CCl_2CH_3\)
D \(CH_2ClCH_2CH_2Cl\)
Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question
Menthol is an important compound extracted from the peppermint plant.
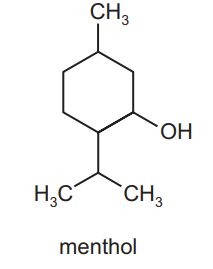
How many chiral centres are there in one molecule of menthol?
A 1 B 2 C 3 D 4
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
C
Question
An alkene has the formula CH3CH=CRCH2CH3 and does not possess cis-trans isomers.
What is R?
A H B Cl C CH3 D C2H5
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
D
Question
Which compound, on reaction with hydrogen cyanide, produces a compound with a chiral centre?
- CH3CHO
- CH3CH2COCH2CH3
- CH3CO2CH3
- HCHO
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
A
Question
How many isomeric esters have the molecular formula C4H8O2?
A 2 B 3 C 4 D 5
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
C