Question
Two students each make a statement about 2-methylbut-1-ene.
Student 1 states that 2-methylbut-1-ene has geometrical isomers.
Student 2 states that 2-methylbut-1-ene reacts with $\mathrm{HBr}$ in an addition reaction to give 1-bromo-2-methylbutane as the main product.
Which students are correct?
A both 1 and 2
B 1 only
C 2 only
D neither 1 nor 2
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:D
Question
Poly(propene) is an addition polymer.
What are the C–C–C bond angles along its polymer chain?
A They are all 109°.
B Half of them are 109° and half are 120°.
C Half of them are 90° and half are 180°.
D They are all 120°.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:A
Question
What is the major product Z of the following reaction?
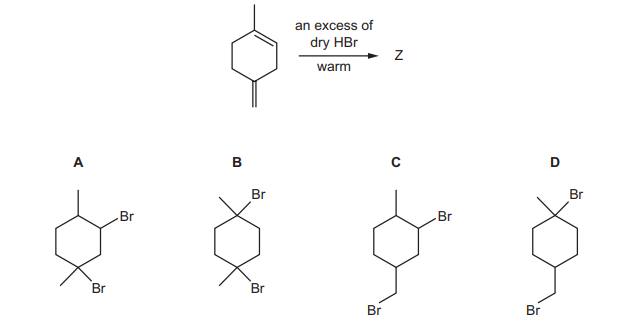
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:B
Question:
Which statements comparing ethene and ethane are correct?
1 The bond angles in ethene are larger than the bond angles in ethane.
2 Ethene reacts much more quickly with bromine in the dark than ethane does.
3 Complete combustion of 0.01 mol of ethene or ethane produces the same volume of gas measured at room temperature and pressure

▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:A
Question
Polymerisation of ethene gives poly(ethene).
How does the bonding between carbon atoms in poly(ethene) compare with that in ethene?
A longer and stronger in poly(ethene)
B longer and weaker in poly(ethene)
C shorter and stronger in poly(ethene)
D shorter and weaker in poly(ethene)
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:B
Question
Alkenes react with aqueous hydrogen bromide. The reaction proceeds via an intermediate carbocation. The more stable the intermediate, the faster the reaction.
Which sequence correctly shows an increase in the speed of reaction of the alkenes with hydrogen bromide?
A ethene, propene, 2-methylpropene
B 2-methylpropene, ethene, propene
C propene, ethene, 2-methylpropene
D propene, 2-methylpropene, ethene
Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Question
Oct-1-ene, \(CH_3(CH_2)_5CH=CH_2\), can be thermally cracked.
Which of the compounds W, X, Y and Z can be obtained by thermally cracking oct-1-ene?
A W, X, Y and Z
B W, X and Y only
C W, X and Z only
D W and X only
Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Question
Which compound would produce two different carboxylic acids when treated with hot, concentrated, acidified manganate(VII) ions?
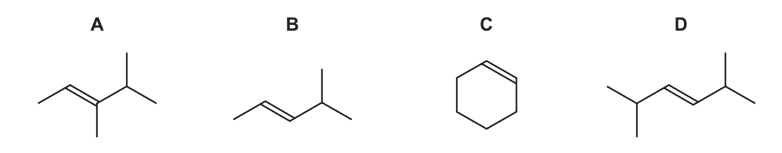
Answer/Explanation
Answer: B
Question
Limonene is a hydrocarbon found in the rind of citrus fruits.
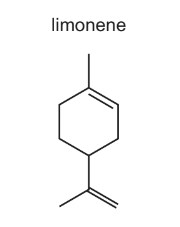
What is the molecular formula of limonene?
A C10H12 B C10H14 C C10H16 D C10H18
Answer/Explanation
Answer: C
Question
An alkene reacts with hot, concentrated, acidified potassium manganate(VII) to produce a single
organic product as shown.
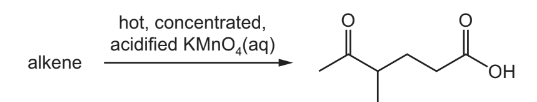
What is the structure of the alkene?
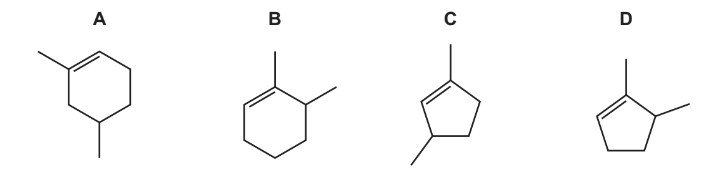
Answer/Explanation
Answer D
Question
Which statements about poly(alkene)s are correct?
1 Poly(alkene)s do not react with Br2(aq) in the dark.
2 Disposal of poly(alkene)s by combustion can produce harmful products.
3 Poly(alkene)s do not readily biodegrade.
Answer/Explanation
Answer A
Question
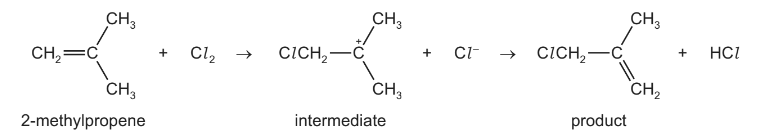
Which statements about this mechanism are correct?
1 The intermediate has all carbon atoms in the same plane.
2 There is an electrophilic attack on the double bond.
3 It is a free radical mechanism.
Answer/Explanation
Answer B
Question
Limonene is found in lemons.
Limonene is heated with concentrated acidified potassium manganate(VII).
Which compounds are produced?
1 CH3COCH2CH2CH(CH2CO2H)2
2 CO2
3 CH3COCH2CH2CH(COCH3)CH2CO2H

Answer/Explanation
Answer C
Question
Which reagent could detect the presence of alcohol in a mixture consisting mainly of alkanes and alkenes?
A Na
B Br2 (in CCl4)
C KMnO4(aq)
D 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine
Answer/Explanation
Answer A
Question
A reaction occurs when a sample of 1-chloropropane is heated under reflux with sodium hydroxide dissolved in ethanol.
Which row is correct?
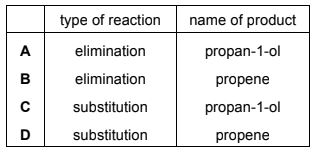
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
B
Question
The compounds below are used to make perfumes.
Which compounds will produce a yellow precipitate with alkaline aqueous iodine?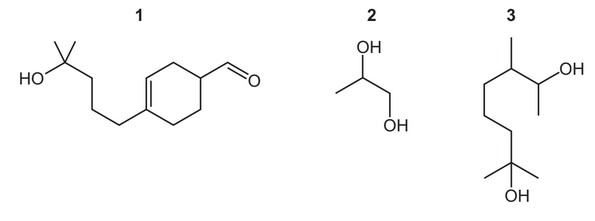
The responses A to D should be selected on the basis of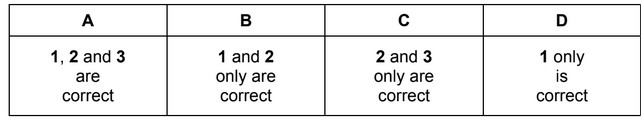
Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Question
Ethene is reacted with steam in the presence of concentrated \(H_3PO_4\). The product of this reaction is added to acidified potassium dichromate(VI) and heated under reflux for one hour. The final organic product is collected and labelled X.
But-2-ene is treated with hot, concentrated, acidified potassium manganate(VII). The final organic product is collected and labelled Y.
Which statement is correct?
A One molecule of X has more carbon atoms than one molecule of Y.
B One molecule of Y has more carbon atoms than one molecule of X.
C X and Y have different functional groups.
D X is the same compound as Y.
Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Question
An alkene is reacted with acidified manganate(VII) ions, \(MnO_4^–\). The desired organic product has a relative molecular mass greater than that of the alkene by 34.
What conditions should be used?
A cold, concentrated \(MnO_4^–\)
B cold, dilute \(MnO_4^–\)
C hot, concentrated \(MnO_4^–\)
D hot, dilute \(MnO_4^–\)
Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question
The diagram shows the structure of cyclohexene.
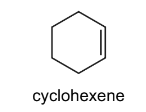
Which structures could be formed by addition reactions with cyclohexene as the only reactant?
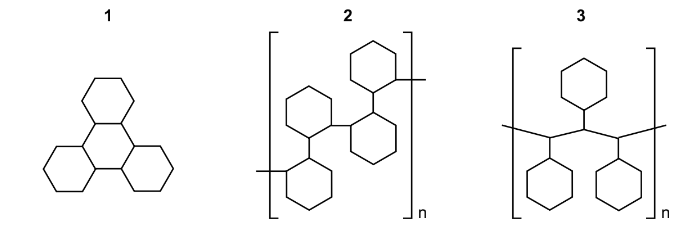
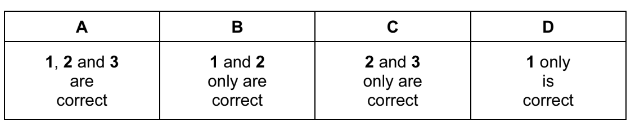
Answer/Explanation
Answer: B
Question
The diagram shows the structure of an alkene molecule.
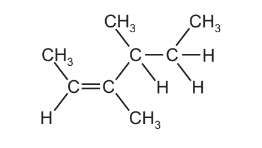
Which statements about this molecule are correct?
1 All the carbon atoms are in the same plane.
2 It has geometrical isomers.
3 It is optically active.
The responses A to D should be selected on the basis of
No other combination of statements is used as a correct response.
Answer/Explanation
Ans:C
Question
Which intermediate ion forms in the greatest amount during the addition of HBr to propene?
A \(CH_{3}CH^{+} CH_{3}\)
B \(CH_{3}CH_{2}CH_{2}^{+}\)
C \( CH_{3}CH^{–} CH_{2}Br\)
D \( CH_{3}CHBrCH_{2}\)
Answer/Explanation
Ans:A
Question
Crude oil is a mixture of many hydrocarbons ranging in size from 1 to 40 carbon atoms per molecule. The alkanes in crude oil can be separated because they have different boiling points.
The table below shows the boiling points of some alkanes.
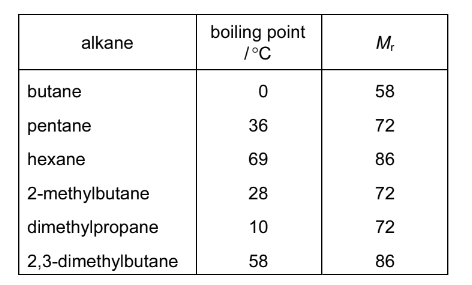
What is the correct explanation for the difference in the boiling points of the three isomers with \(M_{r}\) = 72?
A Boiling point is dependent upon the length of the carbon chain only.
B Increased branching on a carbon chain increases the boiling point.
C Increased branching reduces the strength of the intermolecular hydrogen bonding.
D Increased branching reduces the strength of the intermolecular van der Waals’ forces.
Answer/Explanation
Ans:D
Question
Total removal of the pollutant sulfur dioxide, is difficult. The quantities emitted from furnace chimneys can be lowered by using desulfurisation plants. The gases are reacted with calcium hydroxide to remove the \(SO_{2}\). What is the main product formed initially?
A \(Ca(HSO_{4})_{2} \) B CaS C \(CaSO_{3}\) D CaSO$_4$
Answer/Explanation
Ans:C
Question
Which pairs of reagents will take part in a redox reaction?
1 \( CH_{3}COCH_{3} +\) Tollens’ reagent
2 \( CH_{3}CH_{2}CHO +\) Fehling’s reagent
3 \(CH_{3}CH=CH_{2} + Br_{2}\)
The responses A to D should be selected on the basis of
Answer/Explanation
Ans:C
Question
Oleic acid is found in olive oil. It has the following formula.
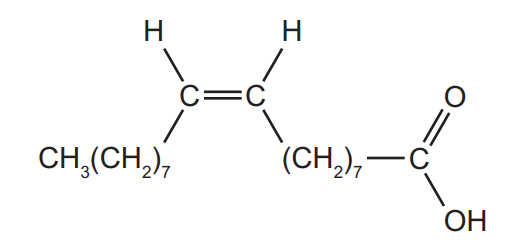
Which reagents will give a positive result with oleic acid?
- aqueous bromine
- acidified potassium dichromate(VI)
- Fehling’s reagent
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
D
Question
A reaction pathway diagram is shown.
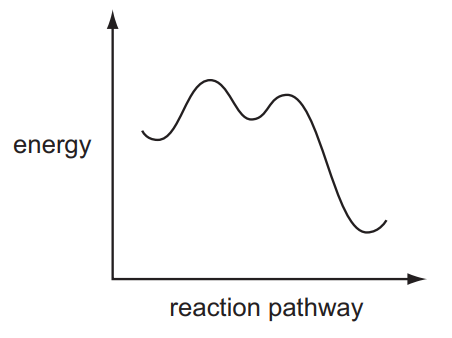
Which reaction does not have such a profile?
- \(CH_{3}CHO+HCN\xrightarrow[]{NaCN}CH_{3}CH\left ( OH \right )CN\)
- \(C_{2}H_{5}Br+NaOH\rightarrow C_{2}H_{5}OH+NaBr\)
- \(\left ( CH_{3} \right )_{3}CBr+NaOH\rightarrow \left ( CH_{3} \right )_{3}COH+NaBr\)
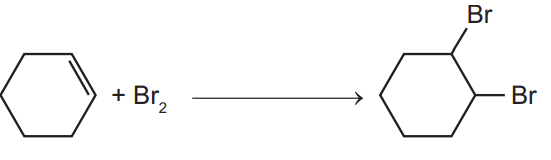
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
B