Question:
In which reactions is the major product formed by a nucleophilic substitution reaction?
1 bromoethane + potassium cyanide in ethanol
2 bromoethane + ammonia in ethanol under pressure
3 bromoethane + hot concentrated sodium hydroxide in ethano
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:B
Question:
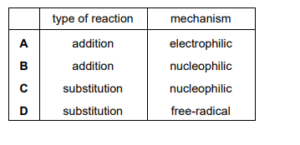
The diagram shows the structure of a bromo compound that may be formed by the reaction of bromine with a hydrocarbon.
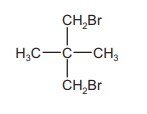
Which row is correct?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:D
Question
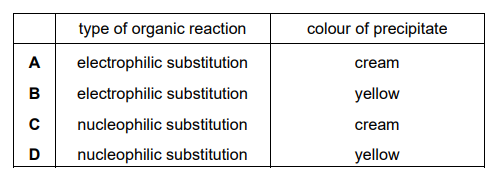
lodoethane, $\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{I}$, reacts with aqueous silver nitrate at $50^{\circ} \mathrm{C}$. A precipitate forms during this reaction.
Which row of the table is correct about this reaction?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:D
Question
A student converts 1-iodopropane, $\mathrm{C}_3 \mathrm{H}_7 \mathrm{I}$, into butanoic acid, $\mathrm{C}_3 \mathrm{H}_7 \mathrm{CO}_2 \mathrm{H}$, by a two-stage chemical synthesis.
In the first of the two stages, which reagent is reacted with 1-iodopropane?
A aqueous sodium hydroxide
B ethanolic ammonia
C ethanolic potassium cyanide
D ethanolic sodium hydroxide
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:C
Question
1-chloro-1-methylcyclohexane is hydrolysed by heating with $\mathrm{NaOH}(\mathrm{aq})$.
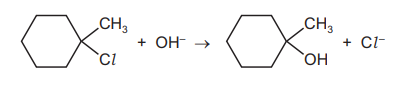
The reaction pathway is shown.
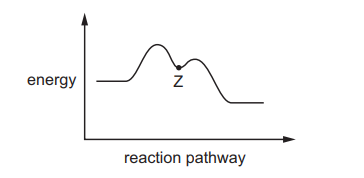
One carbon atom in 1-chloro-1-methylcyclohexane is bonded to three other carbon atoms.
What is the charge on this carbon atom at point $Z$ ?
A $1-$
B $\delta-$
C $\delta^{+}$
D $1+$
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:D
Question
2-bromo-2-methylpentane is a tertiary halogenoalkane.
Which organic products are formed when 2-bromo-2-methylpentane reacts with a hot
concentrated ethanolic solution of sodium hydroxide?
A 2-methylpent-1-ene only
B 2-methylpent-1-ene and 2-methylpent-2-ene
C 2-methylpent-2-ene only
D 2-methylpent-2-ene and 4-methylpent-2-ene
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:B
Question
Chlorofluoroalkanes that diffuse into the stratosphere are broken down by ultraviolet radiation.
Radicals are generated that cause depletion of ozone.
What are these radicals?
1 chlorine radicals
2 fluorine radicals
3 alkyl radicals
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:D
Question:
Which statements apply to tetrafluoromethane?
1 It is rapidly decomposed by ultraviolet radiation.
2 It is less harmful to the ozone layer than dichlorodifluoromethane.
3 It is a non-polar molecule.

▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:C
Question
Which statements help to explain the mechanism of the reaction between 1-chloropropane and ammonia?
1 1-chloropropane has a $\delta$ – chlorine atom that forms hydrogen bonds with a $\delta+$ hydrogen atom in ammonia.
2 1-chloropropane is a polar compound with a $\delta+$ carbon atom.
3 There is a lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom in ammonia.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:C
Question
Propene undergoes a variety of reactions.
Which row is correct?
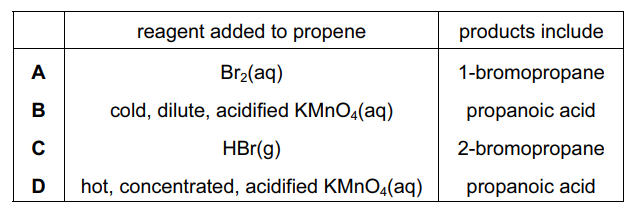
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:C
Question
Which radical is most likely to form by the homolytic fission of one covalent bond in bromochloromethane, $\mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{BrCl}$ ?
A $\cdot \mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{Cl}$
B $\cdot \mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{Br}$
C $\cdot \mathrm{CHBrCl}$
D $\cdot \mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{BrCl}$
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:A
Question
The diagram shows the structures of three halogenoalkanes.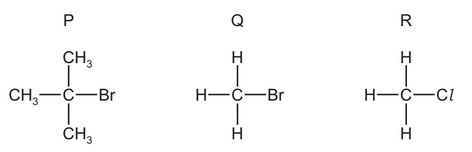
P, Q and R can all be hydrolysed.
Which row is correct?
Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Question
A reaction occurs when a sample of 1-chloropropane is heated under reflux with sodium hydroxide dissolved in ethanol.
Which row is correct?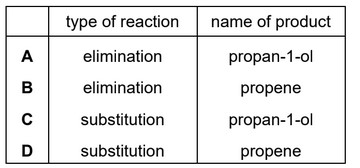
Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question
Bromoethane reacts with cyanide ions, producing propanenitrile.
Which statement about the SN2 mechanism of this reaction is correct?
A The lone pair of electrons on C of CN– attacks the carbon atom of the C–Br bond.
B The lone pair of electrons on C of CN– attacks the carbocation formed when the C–Br bond breaks.
C The lone pair of electrons on N of CN– attacks the carbon atom of the C–Br bond.
D The lone pair of electrons on N of CN– attacks the carbocation formed when the C–Br bond breaks.
Answer/Explanation
Answer: A
Question
The table describes four reactions of propene.
Which row is correct?

Answer/Explanation
Answer: C
Question
Which statements are correct?
1 1,1-difluoroethane is less reactive than 1,1-dichloroethane.
2 1,1-difluoroethane is polar.
3 The C–F bond is stronger than the C–Cl bond.
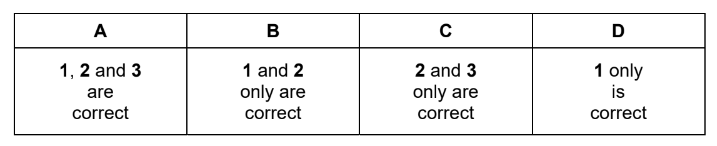
Answer/Explanation
Answer: A
Question
Which statements about chlorofluoroalkanes are correct?
1 Both the C–Cl and C–F bonds are readily dissociated by ultra-violet light.
2 They have caused ozone depletion.
3 They are relatively chemically inert.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Answer C
Question
When an organic compound, Q, is treated with phosphorus pentachloride, fumes of hydrogen chloride are evolved. When Q is warmed with acidified aqueous potassium dichromate(VI), the solution turns green.
What is Q?
A CH 3CH 2CHO
B CH3CH2CO2H
C CH3CH(OH)CH3
D (CH3)3COH
Answer/Explanation
Answer C
Question
Bromopropane reacts with water as shown.
CH3CH2CH2Br + H2O → CH3CH2CH2OH + HBr
Which statement is correct?
A This is an elimination reaction.
B This is a hydrolysis reaction.
C This is a redox reaction.
D This reaction tends to proceed via the SN1 mechanism.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
B
Question
Bromoethane and chloroethane are added separately to water. Hydrolysis reactions occur.
Which compound hydrolyses more rapidly and what is the mechanism?

Answer/Explanation
Answer B
Question
A tertiary bromoalkane, indicated here by ![]() , reacts with aqueous NaOH. The mechanism has the reaction pathway shown.
, reacts with aqueous NaOH. The mechanism has the reaction pathway shown.
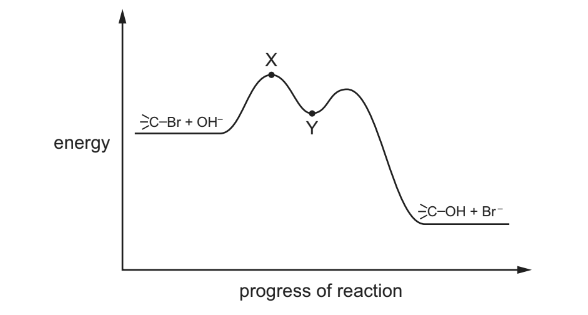
Which point in the diagram is correctly identified?
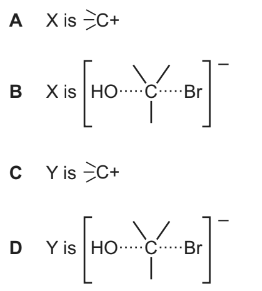
Answer/Explanation
Answer C
Question
The structure of coniine is shown.
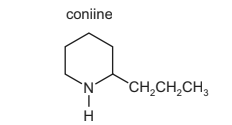
Coniine can be synthesised by reacting ammonia with a dibromo compound, X.
NH3 + C8H16Br2 → coniine + 2HBr
X
What is the name of compound X?
A 1,1-dibromo-2-propylcyclopentane
B 1,2-dibromo-2-propylcyclopentane
C 1,4-dibromooctane
D 1,5-dibromooctane
Answer/Explanation
Answer D
Question
Which reaction is most likely to involve the formation of a positively charged intermediate?
A 1-bromopentane and warm dilute NaOH(aq)
B 1-bromo-2,2-dimethylpropane and warm dilute NaOH(aq)
C 1-bromo-3-methylbutane and warm dilute NaOH(aq)
D 2-bromo-2-methylbutane and warm dilute NaOH(aq)
Answer/Explanation
Answer D
Question
The halogenoalkanes listed below all react with NaOH(aq).
Which reactions proceed mainly by an SN1 mechanism?
1 1-iodopropane
2 2-iodo-2-methylpropane
3 2-bromo-2-methylbutane
Answer/Explanation
Answer C
Question
Chlorofluoroalkanes have been used as the refrigerant in refrigerators but care has to be taken in
disposing of old refrigerators.
Which statements about chlorofluoroalkanes are correct?
1 C–Cl bonds more readily undergo homolytic fission than C–F bonds.
2 Care is taken in the disposal of old refrigerators because of possible ozone depletion.
3 C2H4ClF is more volatile than C2H6.

Answer/Explanation
Answer B
Question
Organic compound X gives a precipitate when warmed with aqueous silver nitrate. This precipitate dissolves when concentrated aqueous ammonia is added.
What could X be?
1 1-bromopropane
2 2-chlorobutane
3 2-iodo-2-methylpropane
The responses A to D should be selected on the basis of
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
B
Question
The following statements are about the reaction of NaOH(aq) with the three chloroalkanes shown.
\(CH_3CH_2CHClCH_3\) \((CH_3)_2CHCH_2Cl\) \((CH_3)_3CCl\)
Which statements are correct?
1 \((CH_3)_2CHCH_2Cl\) reacts with NaOH(aq) by an \(S_N2\) mechanism.
2 The tertiary chloroalkane reacts more quickly than the others because the carbon atom bonded to the Cl atom is more positive in this molecule.
3 The Cl atoms in the three chloroalkanes are attacked by \(OH^–\)
The responses A to D should be selected on the basis of
Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Question
Which types of reaction can occur with 1-bromobutane?
1 elimination
2 hydrolysis
3 free radical substitution
Answer/Explanation
Answer: A
Question
If the starting material is iodoethane, which sequence of reactions will produce propanoic acid as the main final product in good yield?
A add NaOH(aq), isolate the organic product, add acidified \(K_{2}Cr_{2}O_{7}\) and boil under reflux
B add NaOH(aq), isolate the organic product, add \\(H_{2}SO_{4}\)(aq) and boil under reflux
C heat with HCN in ethanol, isolate the organic product, add\( H_{2}SO_{4}\)(aq) and boil under reflux
D heat with KCN in ethanol, isolate the organic product, add \(H_{2}SO_{4}\)(aq) and boil under reflux
Answer/Explanation
Ans:D
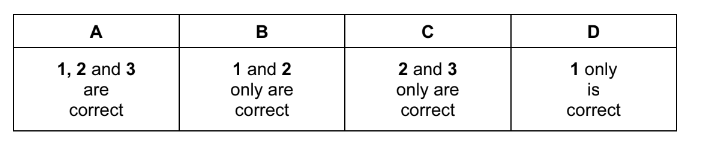
Question
X is an organic compound that gives a precipitate with aqueous silver nitrate. This precipitate remains undissolved when concentrated aqueous ammonia is added.
What is a possible identity for X?
1 iodomethane
2 2-bromobutane
3 2-chlorobutane
The responses A to D should be selected on the basis of
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:D
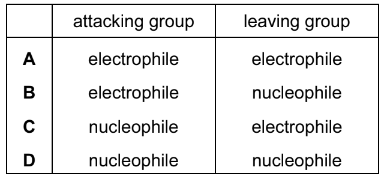
Question
In the hydrolysis of bromoethane by aqueous sodium hydroxide, what is the nature of the attacking group and of the leaving group?
Answer/Explanation
Ans:D
Question
The hydrolysis of 1- chloropropane to produce propan-1-ol is much slower than the corresponding hydrolysis of 1-iodopropane.
Which statement explains this observation?
A Chlorine is more electronegative than iodine.
B The bond strength of the C–I bond is less than that of the C–Cl bond.
C The carbon atom in the C–Cl bond is more δ+ than that in the C–I bond.
D The hydrolysis involves a nucleophilic addition reaction.
Answer/Explanation
Ans:B
Question
Which reaction will give the best yield of 1-chloropropane?
A chlorine gas with propene gas in the dark
B propan-1-ol with dilute NaCl(aq)
C propan-1-ol with \(PCl_5\)
D propene with dilute HCl(aq)
Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Question
Aluminium chloride catalyses certain reactions by forming carbocations with chloroalkanes as shown.
RCl + Al Cl3 → R++ Al Cl 4–
Which property makes this reaction possible?
- AlCl3 exists as the dimer Al 2Cl 6 in the vapour.
- AlCl3 is a covalent molecule.
- The aluminium atom in Al Cl3 has an incomplete octet of electrons.
- The chlorine atom in RCl has a vacant p orbital.
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
C