Question
Alkanes and alkenes both react with bromine.
(a) Explain how and why bromine can be used to distinguish between an alkene and an alkane.
(b) The reaction of ethane with bromine forms a mixture of products.
(i) State the essential conditions for this reaction to occur.
(ii) Give the full name of the mechanism of this reaction.
(iii) Give the equation for a termination step that could occur, producing a hydrocarbon.
(iv) Give the equation for one propagation step involved in the formation of dibromoethane
from bromoethane during this reaction.
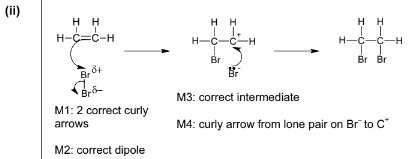
(c) The reaction of ethene with bromine forms a single product.
(i) Give the full name of the mechanism of this reaction.
(ii) Complete the diagram below to illustrate this mechanism. Include all relevant charges, partial charges, curly arrows and lone pairs.
![]()
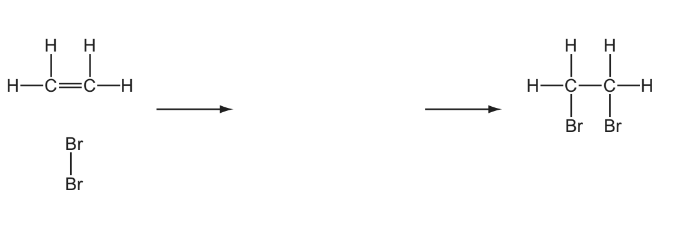
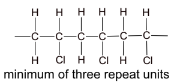
(d) Chloroethene can be polymerised to form a polymer commonly known as PVC. Draw a diagram of the structure of PVC including three repeat units.
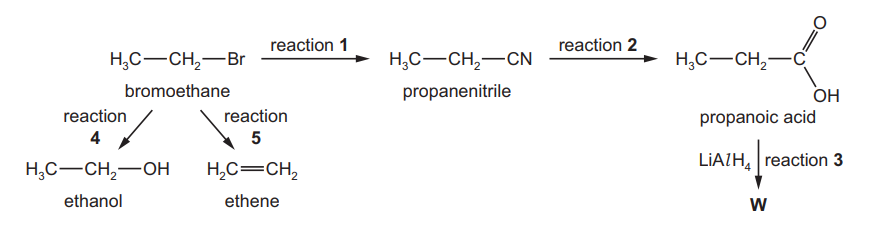
(e) Chloroethane undergoes a series of reactions as shown in the diagram below.
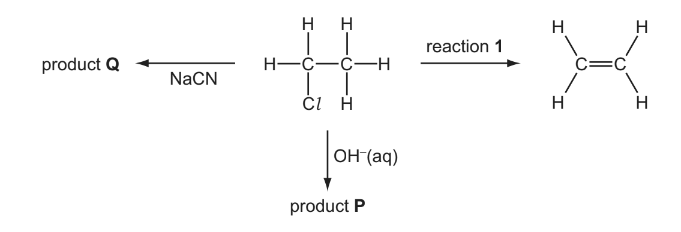
(i) Give the reagent and conditions necessary for reaction 1.
(ii) Give the skeletal formula of product P.
(iii) Give the displayed formula and the name of product Q.
Answer/Explanation
(a) decolourisation with an alkene at room conditions / quickly / easily /
OR alkane needs higher temp/UV/ is slow at room conditions double/ π /pi bond/C =C present in alkenes
(b) (i) UV light/ sunlight/ high temperature
(ii) (Free) radical
Substitution
(iii) \(•C_{2}H_{5} + •C_{2}H_{5} \rightarrow C_{4}H_{10}\)
(iv) \(C_{2}H_{5}Br + Br^{•}\rightarrow •C_{2}H_{4}Br + HBr\) OR
\(•C2H4Br + Br_{2} \rightarrow C_{2}H_{4}Br_{2} + Br^{•}\)
(c) (i) Electrophilic
Addition
(d)
(e) (i) NaOH/KOH
ethanolic / alcoholic AND heat/reflux
(ii)![]()
(iii) 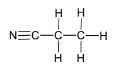
Propanenitrile/propanonitrile/ propionitrile/ ethyl cyanide/ cyanoethane
Question
A reaction sequence is shown.
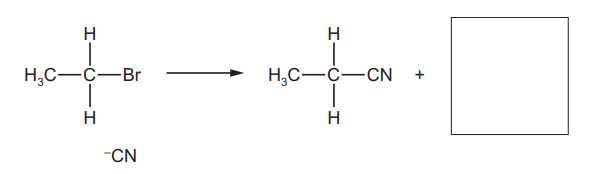
(a) Complete the diagram to show the mechanism of reaction 1. Include all necessary charges, partial charges, lone pairs and curly arrows.
(b) (i) Give the name of the type of reaction involved in reaction 3.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… [1]
The infra-red spectrum of the propanoic acid produced by reaction 2 is shown.
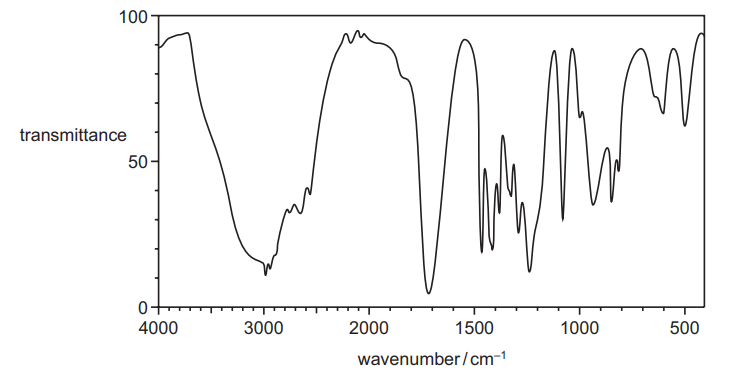
(ii) Describe and explain the main difference between the infra-red spectrum of W and that of propanoic acid………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. [2]
(c) (i) Reactions 4 and 5 use the same reagent.
Give the reagent and conditions needed for reaction 4.
reagent
conditions[2]
(ii) Give the conditions needed for reaction 5.[1]
(d) Under appropriate conditions, ethanol and propanoic acid undergo a condensation reaction.
(i) State the condition necessary for the reaction.[1]
(ii) Draw the skeletal formula of the organic product of this reaction.[1]
(iii) Name the organic product of this reaction.[1]
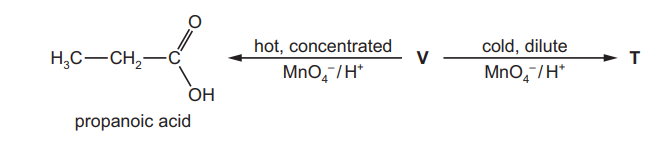
(e) V reacts with acidified manganate(VII) ions in two different ways depending on the conditions, as shown in the reaction sequence below
 \
\
$\mathbf{V}$ decolourises bromine water.
When the acidified manganate(VII) is hot and concentrated, propanoic acid is the only organic product.
When the acidified manganate(VII) is cold and dilute, the organic product is $\mathbf{T}$ which has two chiral centres.
(i) Give the structural formulae of $\mathbf{V}$ and $\mathbf{T}$.
V…………………………………………….. T………………………………….[2]
(ii) Identify the types of stereoisomerism shown by $\mathbf{V}$ and $\mathbf{T}$.
V …………………………………………….T…………………………………………..[2][Total: 15]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
5 (a) 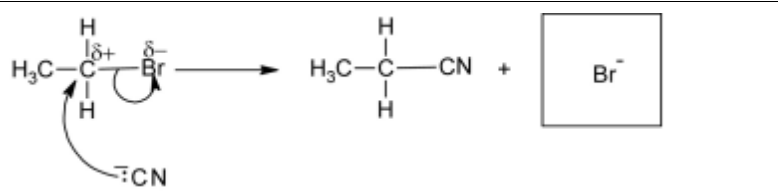
(b) (i) reduction
(ii) disappearance of peak / dip/ trough/ absorption at 1680–1730
due to (loss of) C=O
OR
peak at 3200–3650
due to (alcohol) O—H (formation)
(c) (i) sodium/potassium hydroxide
aqueous
(ii) ethanol
(d) (i) (conc) $\mathrm{H}^{+} /$(conc) acid $/$(conc) $\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{SO}_4 /$ (conc) $\mathrm{H}_3 \mathrm{PO}_4$
(ii)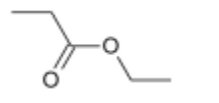
(e) (i) $\quad \begin{aligned} & \mathbf{v}=\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{CHCHCH} \mathrm{CH}_3 / \mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{CH}=\mathrm{CHCH}_2 \mathrm{CH}_3 \\ & \mathbf{T}=\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{CH}(\mathrm{OH}) \mathrm{CH}(\mathrm{OH}) \mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{CH}_3\end{aligned}$
(ii) V = geometric(al)/ cis-trans /E–Z
T = optical