Question:
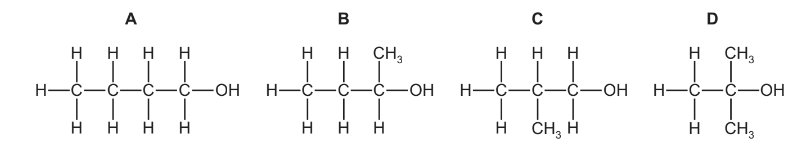
How many tertiary alcohols have the molecular formula \(C_{6}H_{14}O\)
A 1 B 2 C 3 D 4
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:C
Question:
Part of the structure of strobilurin is shown. R and R’ are inert groups.
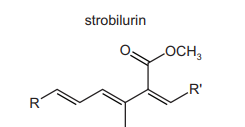
Strobilurin is warmed with aqueous sulfuric acid producing compound X. Compound X is then treated with hydrogen in the presence of a nickel catalyst producing compound Y. What could be the structure of compound Y?
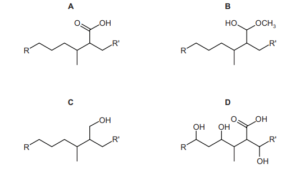
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:A
Question:
Which compound produces a ketone when refluxed with an acidified solution of potassium dichromate(VI)?
A pentan-1-ol
B 2-methylbutan-1-ol
C 2-methylbutan-2-ol
D 3-methylbutan-2-ol
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:D
Question:
The diagram shows the formation of compound Y from compound X in a chemical reaction. \(R_{1}~and~R_{2}\) are alkyl groups.
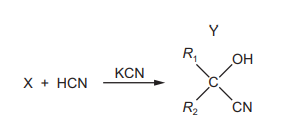
Which row about this reaction is correct?
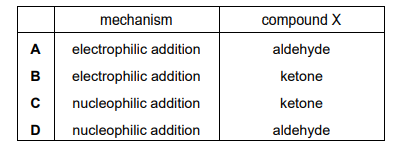
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:C
Question
Methanol, $\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{OH}$, can be produced industrially by reacting $\mathrm{CO}$ with $\mathrm{H}_2$.
$
\mathrm{CO}(\mathrm{g})+2 \mathrm{H}_2(\mathrm{~g}) \rightleftharpoons \mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{OH}(\mathrm{g}) \quad \Delta \mathrm{H}=-91 \mathrm{kJmol}^{-1}
$
The process can be carried out at $4 \times 10^3 \mathrm{kPa}$ and $1150 \mathrm{~K}$.
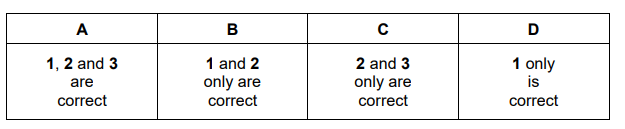
Which statements about this reaction are correct?
1 Increasing the temperature will increase the rate of reaction because more effective collisions will occur.
2 Lowering the temperature will reduce the rate of reaction because the forward reaction is exothermic.
3 Increasing the pressure will reduce the rate of reaction because there are a larger number of moles on the left-hand side of the equation.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:D
Question
Three reactions of primary alcohols are listed.
Which reactions give water as one of the products?
1 reaction with ethanoic acid
2 reaction with concentrated $\mathrm{HBr}$
3 passing the alcohol vapour over heated $\mathrm{Al}_2 \mathrm{O}_3$

▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:A
Question
An alcohol with the molecular formula $\mathrm{C}_5 \mathrm{H}_{12} \mathrm{O}$ decolourises warm acidified potassium manganate(VII). The alcohol also gives a yellow precipitate with alkaline aqueous iodine.
What could be the identity of the alcohol?
A 2-methylbutan-2-ol
B 3-methylbutan-2-ol
C pentan-1-ol
D pentan-3-ol
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:B
Question
Which statement is correct?
A 2,2-dimethylpropanoic acid is an isomer of propyl methanoate.
B 2-methylbutan-2-ol is an isomer of hexan-3-ol.
C 3-methylbutan-2-one is an isomer of pentanal.
D 3,3-dimethylbutan-2-one is an isomer of pentan-3-one.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:C
Question
But-1-ene and but-2-ene are treated separately with cold, dilute acidified manganate(VII) ions.
Four students, W, X, Y and Z, make statements about these alkenes and the diols formed from
them.
W One diol contains two primary alcohol groups.
X One diol contains a primary and a secondary alcohol group.
Y One diol contains two secondary alcohol groups.
Z Both alkenes exhibit cis-trans isomerism
Which two students are correct?
A W and Y B W and Z C X and Y D X and Z
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:C
Question
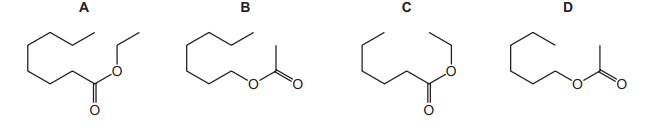
When compound X is heated under reflux with aqueous sodium hydroxide solution two products
are formed: sodium ethanoate and hexan-1-ol.
What is compound X?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:D
Question:
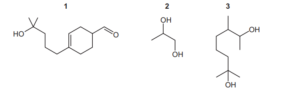
Which compounds will produce a yellow precipitate with alkaline aqueous iodine?

▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:C
Question:
An excess of dry HBr is warmed with compound Y.
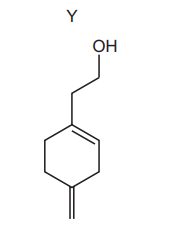
What is the major product of the reaction?
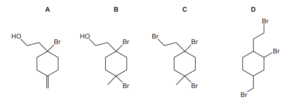
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:C
Question
Ethane-1,2-diol has the following structure.
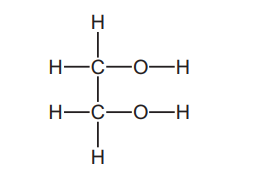
Without breaking the C–C bond, there are five possible oxidation products.
What is the total number of aldehyde groups and carboxylic acid groups in these five products?
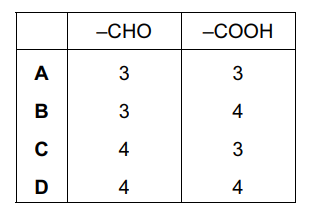
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:D
Question
Propan-2-ol undergoes many reactions.
Which row is correct?
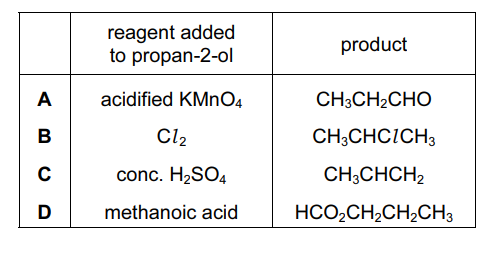
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:C
Question
Diols in which both hydroxy groups are bonded to the same carbon can spontaneously eliminate a molecule of water to produce a carbonyl compound.
Which compound, after complete hydrolysis, gives a positive reaction with Tollens’ reagent?
A 1,1-dibromobutane
B 1,2-dibromobutane
C 1,3-dibromobutane
D 2,2-dibromobutane
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:A
Question
Which row correctly shows a primary, a secondary and a tertiary alcohol?
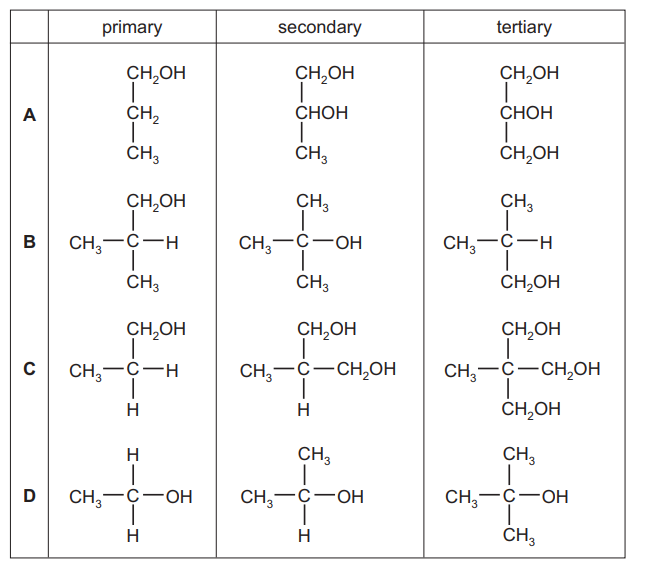
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:D
Question
But-2-ene-1,4-diol is converted in two steps through an intermediate $\mathbf{X}$ into oxobutanedioic acid.
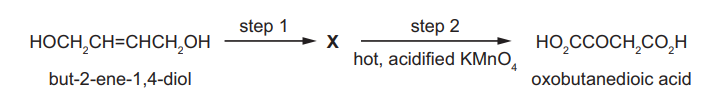
What could be the reagent for step 1 and what is the intermediate X?
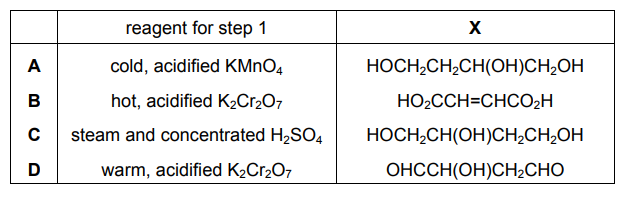
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:C
Question
A sample of 2.30 g of ethanol is mixed with an excess of aqueous acidified potassium dichromate(VI). The reaction mixture is boiled under reflux for one hour. The required organic product is then collected by distillation. The yield of product is 60.0%.
Which mass of product is collected?
A 1.32 g B 1.38 g C 1.80 g D 3.00 g
Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Question
Which compound will decolourise Br$_2$(aq)?
A \(CH_3CH_2CH_2CH_2CH_2CO_2H\)
B \(CH_3CH_2CH_2CH_2CH_2CHO\)
C \(CH_3CHCHCH_2CH_2CH_2OH\)
D \(CH_3CH_2CH_2CO_2CH_2CH_3\)
Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Question
Two 1 g samples of Y are reacted separately and completely with sodium and with
sodium carbonate. The volumes of the gases produced are collected and measured.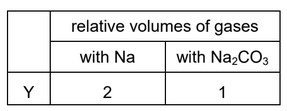
What could Y be?
A \(CH_3CH(OH)CH_2OH\)
B \(CH_3CH(OH)CO_2H\)
C \(CH_3COCH_2OH\)
D \(CH_3COCO_2H\)
Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question
Which compound produces butan-2-ol and ethanoic acid on hydrolysis?
A \(CH_3CO_2CH(CH_3)_2\)
B \(CH_3CO_2CH(CH_3)CH_2CH_3\)
C \(CH_3CH(CH_3)CO_2CH_2CH_3\)
D \(CH_3CH_2CO_2CH(CH_3)CH_2CH_3\)
Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question
The skeletal formulae of two organic compounds are shown.
Which reagents can be used to distinguish these two compounds?
1 alkaline \(I_2(aq)\)
2 acidified \(K_2Cr_2O7\)
3 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine (2,4-DNPH reagent)
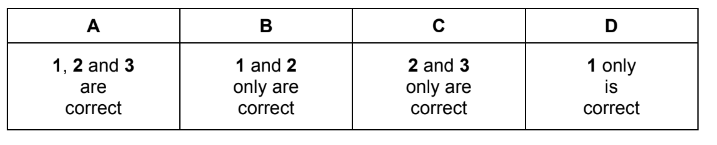
A 1, 2 and 3 B 1 and 3 only C 2 and 3 only D 2 only
Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question
Crotyl alcohol, \(CH_3CH=CHCH_2OH\), is a colourless liquid which is used as a solvent.
Crotyl alcohol will react separately with \(Br_2,K_2Cr_2O_7 /H^+\), conc. \(KMnO_4 /H^+\) and \(PCl_5\) under suitable conditions.
Which row is correct?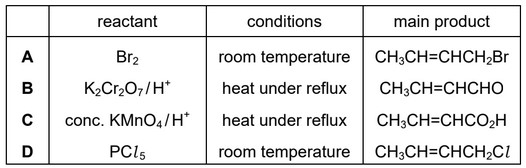
Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Question
Ethanol combines with ethanoic acid to form ethyl ethanoate according to the following reaction.
\(C_{2}H_{5}OH(l) + CH_{3}CO_{2}H(l) \rightleftharpoons CH_{3}CO_{2}C_{2}H_{5}(l) + H_{2}O(l)\) ∆Ho = –6 kJmol–1
9.2 g ethanol, 12 g ethanoic acid and 8.8 g ethyl ethanoate are mixed and allowed to stand at 298K, until equilibrium is reached.
(Mr: C 2H5OH, 46; CH3CO2H, 60; CH3CO2C 2H5, 88)
The resulting equilibrium mixture is found to contain 4.8 g ethanoic acid. The experiment is repeated at 323K.
Which statements are correct?
1 There are 0.22 moles of ethyl ethanoate in the mixture at equilibrium at 298K.
2 The equilibrium mixture at 323K will contain more than 4.8 g of ethanoic acid.
3 If a small amount of water is added at the start of either experiment the value of KC would not
be affected.
Answer/Explanation
Answer: A
Question
Which reactions have a coloured organic product?
1 ethanal + 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine reagent
2 ethanol + acidified potassium dichromate(VI)
3 ethene + cold dilute acidified potassium manganate(VII)
Answer/Explanation
Answer: D
Question
Which reactions of propan-1-ol have water as one of the products?
1 passing propan-1-ol vapour over hot Al2O3
2 mixing propan-1-ol with warm ethanoic acid and a few drops of concentrated sulfuric acid
3 warming propan-1-ol with HBr
Answer/Explanation
Answer A
Question
Ethylene glycol, HOCH2CH2OH, is used as a de-icer. It allows ice to melt at temperatures below 0 °C.
Which statements are correct?
1 Ethylene glycol disrupts the extensive network of hydrogen bonds in ice.
2 Ethylene glycol molecules form hydrogen bonds with other ethylene glycol molecules.
3 Ethylene glycol molecules will dissolve in the water formed from the ice.
Answer/Explanation
Answer A
Question
Alcohol Y gives a yellow precipitate with alkaline aqueous iodine. It can be oxidised to give a mixture of products including substance Z. Substance Z gives a red-brown precipitate with Fehling’s solution.
Which alcohol could be Y?
A CH3CH(OH)CH(CH3)CH2OH
B CH3C(OH)(CH3)CH2CH2OH
C CH3CH(OH)CH2CH(OH)CH3
D CH2(OH)CH2CH(OH)CH2CH3
Answer/Explanation
Answer A
Question
When 2-bromo-2-methylpropane reacts with aqueous sodium hydroxide, an alcohol is formed.
Which diagram describes the first step in the reaction mechanism?
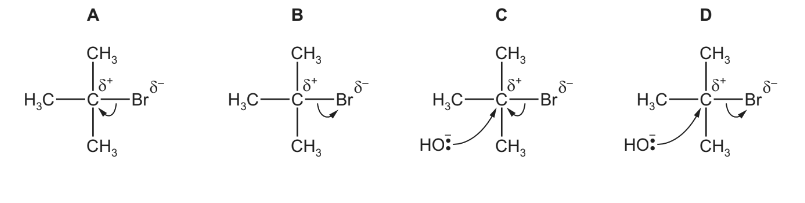
▶️Answer/Explanation
Answer B
Question
Which product is formed when 3-methylpentane-1,3,4-triol is heated under reflux with an excess of acidified potassium dichromate(VI)?
A HO2CCH2C(CH3)(OH)COCH3
B HO2CCH2COC(OH)(CH3)2
C OHCCH2C(CH3)(OH)COCH3
D HO2CCH2CO(CH3)COCH3
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
A
Question
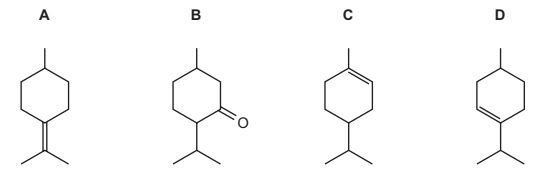
Menthol is a naturally occurring alcohol.
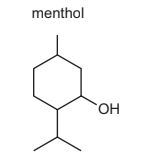
When menthol is heated with concentrated sulfuric acid it reacts. The products formed include compound T.
What could be the structure of compound T?
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
D
Question
1 mole of each of the following four compounds is reacted separately with:
● an excess of sodium
● an excess of sodium carbonate.
Which compound produces the same volume of gas with each of the two reagents?
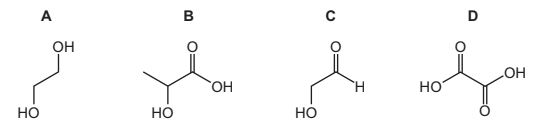
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
D
Question
The diagram shows the structure of cholesterol.
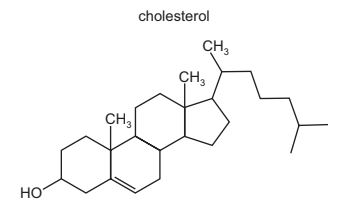
Which statements about cholesterol are correct?
1 The molecule contains a secondary alcohol group.
2 The molecule contains two π bonds.
3 All carbon atoms in the four rings lie in the same plane.
The responses A to D should be selected on the basis of
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
D
Question
Which compounds, on heating with an excess of concentrated sulfuric acid, produce only one
product with molecular formula C7H10?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Answer B
Question
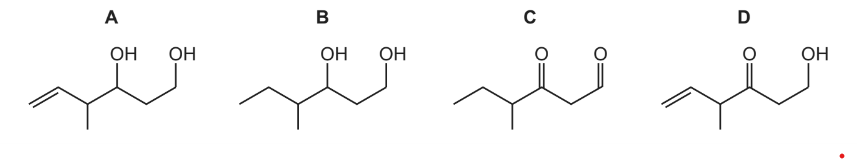
The diagram shows the structure of compound Z.
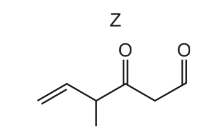
What is the product of the reaction between compound Z and an excess of NaBH4?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Answer A
Question
Alcohol X is oxidised to form compound Y.
The composition of Y is 54.54% carbon, 36.36% oxygen and 9.10% hydrogen. The Mr of Y is 88.0.
What could be the structure of alcohol X?
A CH3CH2CH(OH)CH3
B CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2OH
C CH3CH2CH2CH2OH
D CH3CH2CH(OH)CH2CH3
Answer/Explanation
Answer C
Question
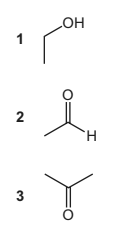
Compound Y
● reacts with alkaline aqueous iodine to form a yellow precipitate
● changes the colour of warm, acidified potassium dichromate(VI) solution.
What could be compound Y?
Answer/Explanation
Answer B
Question
Which reagent may be used to distinguish between propanone and ethanol?
A 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine
B bromine water
C Fehling’s reagent
D Tollens’ reagent
Answer/Explanation
Answer A
Question
An organic compound T undergoes the following reactions.
● T is oxidised by hot, acidified potassium manganate(VII).
● T reacts with sodium to give hydrogen.
What could be compound T?
A CH3CH2CH(OH)CH3
B CH3CH2CH2CHO
C (CH3)3COH
D CH3CH2COCH3
Answer/Explanation
Answer A
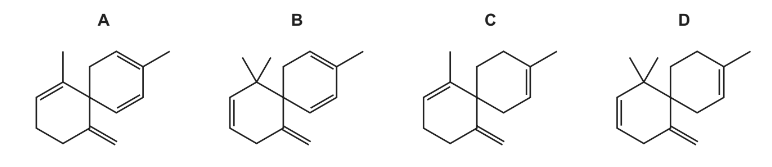
Question
Compound J, C15H23Br2Cl, is reacted with an excess of a hot concentrated solution of
sodium hydroxide in ethanol. One of the products is X.
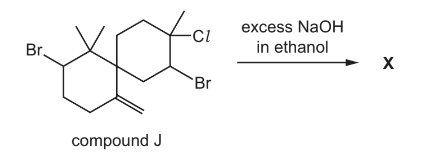
What could be the skeletal formula of X?
Answer/Explanation
Answer B
Question
Which reagent could detect the presence of alcohol in a mixture consisting mainly of alkanes and alkenes?
A Na
B Br2 (in CCl4)
C KMnO4(aq)
D 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine
Answer/Explanation
Answer A
Question
Which alcohol can be dehydrated to give two products which are structural isomers of each other?
Answer/Explanation
Answer B
Question
Fructose is a sugar with more than one chiral centre. The fructose molecule is shown with X, Y and Z indicating three carbon atoms.
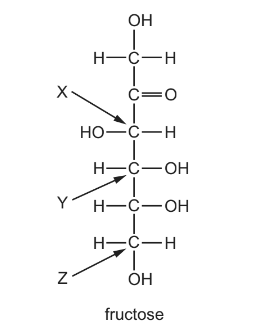
Which carbon atoms are chiral centres?
A X, Y and Z B X and Y only C X only D Y only
Answer/Explanation
Answer B
Question
Which pair of alcohols are isomers of each other?
A butan-1-ol and 2,2-dimethylpropan-1-ol
B butan-2-ol and 2-methylpropan-2-ol
C pentan-1-ol and 2-methylpropan-2-ol
D propan-2-ol and 2-methylpropan-2-ol
Answer/Explanation
Answer B
Question
The compounds below are used to make perfumes.
Which compounds will produce a yellow precipitate with alkaline aqueous iodine?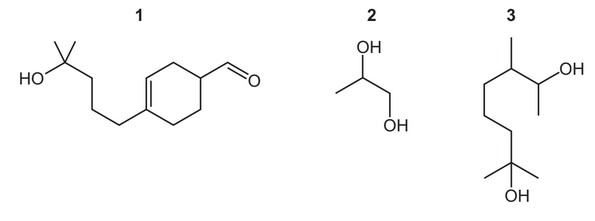
The responses A to D should be selected on the basis of
Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Question
Glucose can be used to prepare sorbitol, a compound used as a sugar substitute.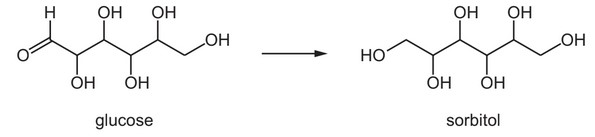
Which reagent may be used for this conversion?
A acidified potassium dichromate(VI)
B sodium borohydride
C sodium hydroxide
D Tollens’ reagent
Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question
Which statements about ethanol and ethanoic acid are correct?
1 Both react with a suitable reagent to form an ester.
2 Both react with sodium.
3 Both are soluble in water.
The responses A to D should be selected on the basis of
Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Question
Q is a compound with the molecular formula \(C_4H_{10}O\). Q can be oxidised with acidified potassium dichromate(VI). Q cannot be made by reducing a carboxylic acid with \(LiAlH_4\).
What is the structure of Q?
A \(CH_3CH(OH)CH_2CH_3\)
B \(CH_3CH_2CH_2CH_2OH\)
C \((CH_3)_3COH\)
D \((CH_3)_2CHCH_2OH\)
Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Question
Diols in which both hydroxy groups are bonded to the same carbon atom spontaneously eliminate
a molecule of water to produce a carbonyl compound.
Which compound is hydrolysed to form a product that gives a positive reaction with
2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine but not with Fehling’s reagent?
A 1,1-dibromopropane
B 1,2-dibromopropane
C 1,3-dibromopropane
D 2,2-dibromopropane
Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Question
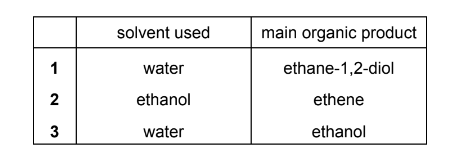
Answer/Explanation
Answer: C
Question
X, Y and Z are three isomeric alcohols.
X CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2OH
Y CH3CH2CH(OH)CH2CH3
Z (CH3)2C(OH)CH2CH3
Two or more of these alcohols react with mild oxidising agents.
One of these alcohols, when dehydrated, will give a pair of cis-trans isomers with molecular formula C5H10.
Which row is correct?
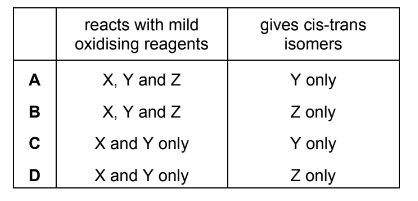
Answer/Explanation
Answer: C
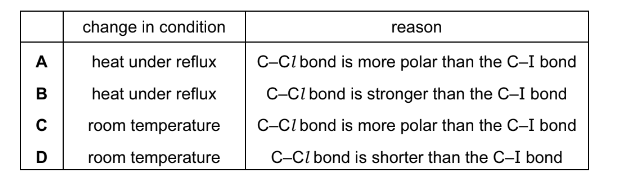
Question
A student prepares pentan-1-ol by the alkaline hydrolysis of 1-iodopentane. She gently warms the reaction mixture for 20 minutes.
\(CH_{3}CH_{2}CH_{2}CH_{2}CH_{2}I + OH^{-} \rightarrow CH_{3}CH_{2}CH_{2}CH_{2}CH_{2}OH + I^{-}\)
When the student uses 1-chloropentane to prepare the same alcohol she has to change the condition of the reaction.
Which change in condition should she use and what is the correct reason for its use?
Answer/Explanation
Answer: B
Question
Alcohol Y gives product Z after mild oxidation. Z gives a positive result with Tollens’ reagent and with 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine reagent.
What could be the identity of alcohol Y?
A butan-1-ol
B butan-2-ol
C butan-2,3-diol
D 2-methylbutan-2-ol
Answer/Explanation
Answer: A
Question
Which compounds will react with HBr to give the compound R?
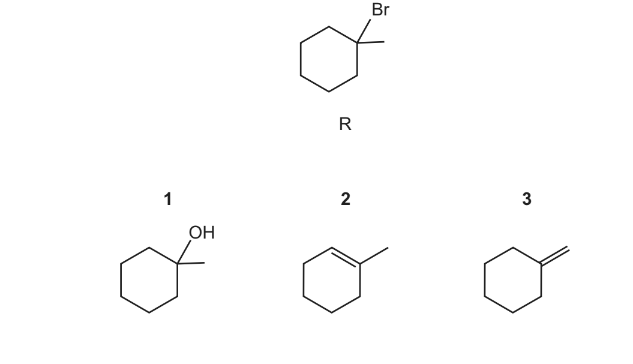
The responses A to D should be selected on the basis of
Answer/Explanation
Ans:A
Question
Which reagent will give a different observation with compounds W and X?
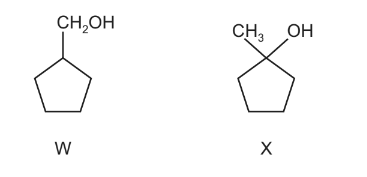
A \( hot SOCl _{2}\)
B hot acidified \(K_{2}Cr_{2}O_{7}\)
C NaOH(aq)
D warm Fehling’s reagent
Answer/Explanation
Ans:B
Question
2-bromopropane reacts with a hot concentrated solution of sodium hydroxide in ethanol.
Which substance is the major product of this reaction?
A propan-1-ol
B propan-2-ol
C 2-hydroxypropene
D propene
Answer/Explanation
Ans:D
Question
Which compound produces butan-2-ol and ethanoic acid on hydrolysis?
A \(CH_{3}CO_{2}CH(CH_{3})_{2}\)
B \( CH_{3}CO_{2}CH(CH_{3})CH_{2}CH_{3}\)
C\( CH_{3}CH(CH_{3})CO_{2}CH_{2}CH_{3}\)
D\( CH_{3}CH_{2}CO_{2}CH(CH_{3})CH_{2}CH_{3}\)
Answer/Explanation
Ans:B
Question
Tollens’ reagent can be used to help identify compounds P, Q and R.
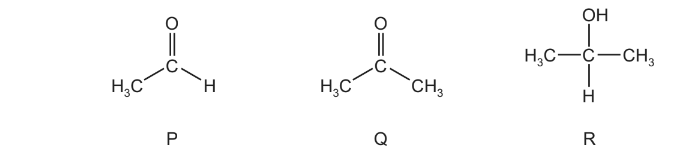
Which compound(s) form a silver precipitate on warming with Tollens’ reagent?
A P and Q B P only C Q only D R only
Answer/Explanation
Ans:B
Question
Butan-2-ol can be made by reducing X with \( H_{2}\) /Ni. Butan-2-ol can be dehydrated to form Y and Z which are structural isomers of each other.
Which row is correct?
Answer/Explanation
Ans:D
Question
Considering only structural isomers, what is the number of alcohols of each type with the formula \(C_{5}H_{12}O\)?
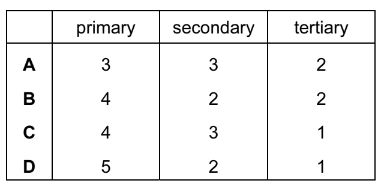
Answer/Explanation
Ans:C
Question
Methylpropan-1-ol and butan-1-ol are structural isomers. Methylpropan-1-ol has a lower boiling point.
Which statement explains why the boiling point of methylpropan-1-ol is lower than that of butan-1-ol?
A Methylpropan-1-ol cannot form hydrogen bonds.
B Methylpropan-1-ol has weaker covalent bonds than butan-1-ol.
C Methylpropan-1-ol has weaker van der Waals’ forces than butan-1-ol.
D Methylpropan-1-ol molecules have more surface area than butan-1-ol molecules.
Answer/Explanation
Answer/Explanation
Ans:C
Question
The compound pentan-1,4-diol has two OH groups per molecule and can be oxidised.
Which statements about pentan-1,4-diol or its oxidation products are correct?
1 When one mole of pentan-1,4-diol reacts with an excess of sodium metal, one mole of hydrogen molecules is produced.
2 At least one of the possible oxidation products of pentan-1,4-diol will react with 2,4 dinitrophenylhydrazine reagent.
3 Dehydration of pentan-1,4-diol could produce a compound with empirical formula\( C_{5}H_{8}\)
The responses A to D should be selected on the basis of

Answer/Explanation
.Ans:A
Question
Use of the Data Booklet is relevant to this question.
In an organic synthesis, a 62% yield of product is achieved. Which conversions are consistent with this information?
1 74.00g of butan-2-ol → 44.64g of butanone
2 74.00g of butan-1-ol → 54.56g of butanoic acid
3 74.00g of 2-methylpropan-1-ol → 54.56g of 2-methylpropanoic acid
The responses A to D should be selected on the basis of

Answer/Explanation
Ans:A
Question
Compound X has the molecular formula \(C_{4}H_{10}O_{2}\). X has an unbranched carbon chain and contains two OH groups. On reaction with an excess of hot, acidified, aqueous manganate(VII) ions, X is converted into a compound of molecular formula\( C_{4}H_{6}O_{4}\).
To which two carbon atoms in the chain of X are the two OH groups attached?
A 1st and 2nd
B 1st and 3rd
C 1st and 4th
D 2nd and 3rd
Answer/Explanation
Ans:C
Question
In which reactions is the organic compound oxidised by the given reagent?
1 \(CH_3CH_2CHO\) + Fehling’s reagent
2 \(CH_3CH_2CH_2CHO\) + Tollens’ reagent
3 \(CH_3CHO\) + 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine reagent
The responses A to D should be selected on the basis of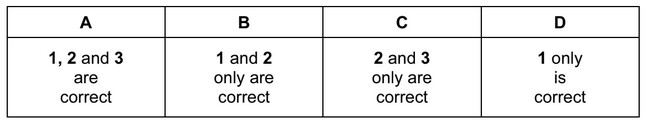
No other combination of statements is used as a correct response.
Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question
Synthetic resins, plasticisers and many other chemicals can be made by polymerisation of a
variety of monomers including prop-2-en-1-ol, \(CH_2=CHCH_2OH\).
Which structure represents the repeat unit in poly(prop-2-en-1-ol)?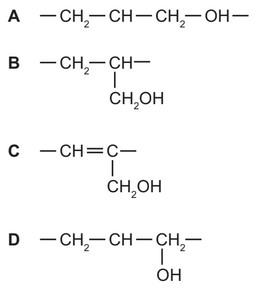
Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question
Aqueous sodium hydroxide reacts with 1-bromopropane to give propan-1-ol.
How should the first step in the mechanism be described?
A by a curly arrow from a lone pair on the \(OH^–\) ion to the \(C^{δ+}\) atom of 1-bromopropane
B by a curly arrow from the \(C^{δ+}\) atom of 1-bromopropane to the \(OH^–\) ion
C by a curly arrow from the C–Br bond to the C atom
D by the homolytic fission of the C–Br bond
Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Question
Which reactions can be used to make an alcohol in the laboratory?
1 hydrolysis of a bromoalkane with NaOH(aq)
2 reduction of a ketone with \(NaBH_4\)
3 reduction of an aldehyde with \(NaBH_4\)
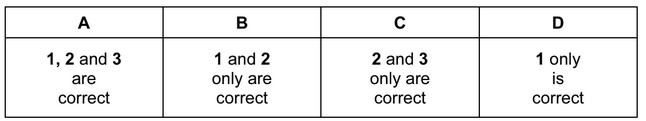
Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Question
What are the only structures formed when butan-2-ol is heated with concentrated \(H_2SO_4\)?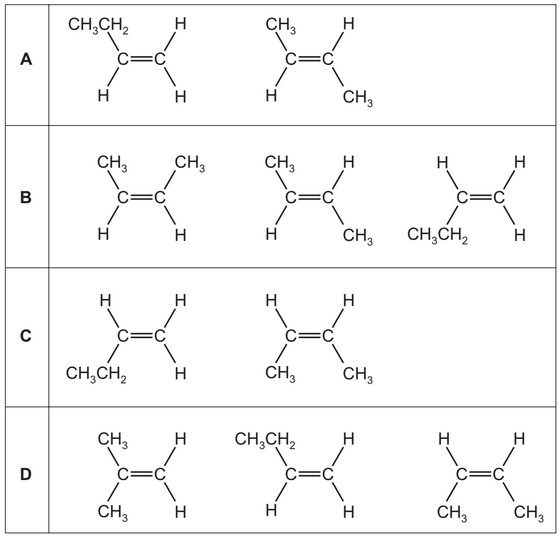
Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question
The compound ‘leaf alcohol’ is partly responsible for the smell of new-mown grass.
\(CH_3CH_2CH=CHCH_2CH_2OH\)
leaf alcohol
What will be formed when ‘leaf alcohol’ is oxidised using an excess of hot, acidified \(K_2Cr_2O_7(aq)\)?
A \(CH_3CH_2CH(OH)CH(OH)CH_2CO_2H\)
B \(CH_3CH_2COCOCH_2CO_2H\)
C \(CH_3CH_2CH=CHCH_2CO_2H\)
D \(CH_3CH_2CO_2H\) and \(HO_2CCH_2CO_2H\)
Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Question
A new industrial preparation of ethyl ethanoate has been developed using cheap sources of ethanol.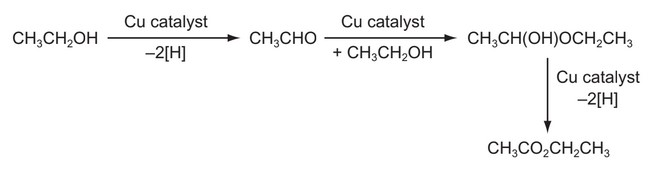
Which process is involved at some stage in this reaction sequence?
A electrophilic addition
B nucleophilic addition
C nucleophilic substitution
D reduction
Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question
Compound X, C6H12O, is oxidised by acidified sodium dichromate(VI) to compound Y.
Compound Y reacts with ethanol in the presence of a little concentrated sulfuric acid to give liquid Z.
What is the formula of Z?
- CH3(CH2)4COCH2CH3
- CH3(CH2)4CO2CH2CH3
- CH3CH2CO2(CH2)4CH3
- CH3CO2(CH2)5CH3
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
B
Question
But-2-ene-1,4-diol is converted in two steps through an intermediate X into ketobutanedioic acid.
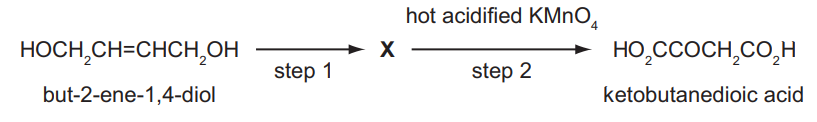
What could be the reagent for step 1 and the intermediate X?
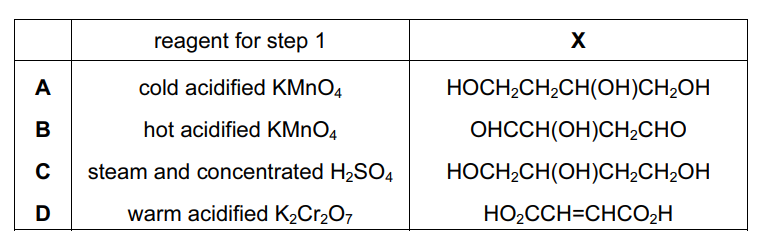
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
C
Question
CH3COCH2CH2OH = W CH3COCH2CHO = X CH3CH(OH)CH2CH3 = Y CH3CH2CH2CHO = Z
Which of these compounds can be oxidised by acidified dichromate(VI) solution and also gives a positive response to Tollens’ reagent?
- W and X only
- W and Y only
- X and Z only
- Y and Z only
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
C