Question:
Two carbonyl compounds have the molecular formula $\mathrm{C}_3 \mathrm{H}_6 \mathrm{O}$.
Which reagents give different observations with these two compounds?
1 acidified aqueous potassium manganate(VII)
2 Fehling’s reagent
3 alkaline aqueous iodine
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:A
Question:
An organic compound, $\mathrm{T}$, does not fizz when aqueous sodium carbonate is added to it.
Compound $\mathrm{T}$ contains $27.6 \%$ by mass of oxygen.
What could be the identity of T?
1. propanal
2. ethyl butanoate
3. 3-methylpentanoic acid

▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:B
Question:
In this question you can assume that \(^{1}H~and~^{3}H\) have the same chemical properties. A sample of ethanal contains only one isotope of hydrogen, \(^{1}H\). It is reduced to compound Z, \(C_{2}H_{6}O_{3}\), in a nucleophilic addition reaction using \(NaBH_{4}\). All the
hydrogen atoms in the \(NaBH_{4}\) are the ^{3}H isotope.
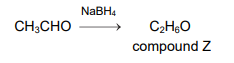
Compound Z is then oxidised back to ethanal and water.
\(C_{2}H_{6}O~+~[O]\rightarrow CH_{3}CHO~+~H_{2}O\). Which statement about the final mixture of products is correct?
A Both ethanal and water contain \(^{3}H\) atoms.
B Ethanal is the only product containing (^{3}H\) atoms.
C Neither ethanal nor water contain (^{3}H\) atoms.
D Water is the only product containing (^{3}H\) atoms
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:A
Question
Which pair of test results would prove that a substance, X, is a ketone?
A $X$ has no reaction with Tollens’ reagent. $X$ reacts with alkaline aqueous iodine.
B $\mathrm{X}$ is reduced by lithium aluminium hydride. $\mathrm{X}$ is oxidised by acidified dichromate(VI).
C $X$ reacts with 2,4-DNPH reagent. $X$ has no reaction with Fehling’s reagent.
D $\mathrm{X}$ reacts with hydrogen cyanide. $\mathrm{X}$ is reduced by lithium aluminium hydride.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:C
Question
Carvone is found in spearmint oil.
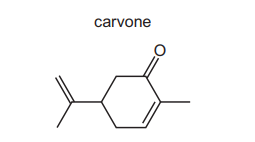
Which product is formed when carvone is reacted with $\mathrm{NaBH}_4$ ?
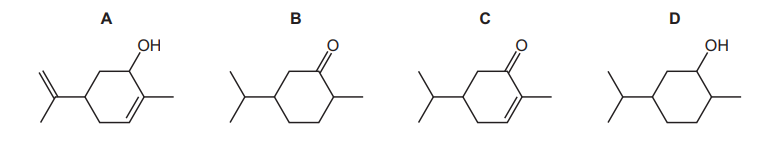
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:A
Question
In which of the reactions is the organic compound oxidised by the given reagent?
1 \(CH_{3}CHO~+~HCN~regeant\)
2 \(CH_{3}CH_{2}CH_{2}CHO~+~Tollen’s~regeant\)
3 \(CH_{3}CH_{2}CH_{2}CHO~+~Fehling’s~regeant\)
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:C
Question
The skeletal formula of compound X is shown.
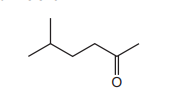
Which row is correct?
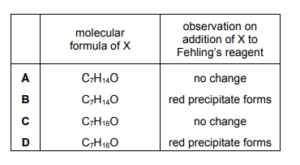
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:A
Question
Which statement is correct?
A 2,2-dimethylpropanoic acid is an isomer of propyl methanoate.
B 2-methylbutan-2-ol is an isomer of hexan-3-ol.
C 3-methylbutan-2-one is an isomer of pentanal.
D 3,3-dimethylbutan-2-one is an isomer of pentan-3-one.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:C
Question
Ethanal and hydrogen cyanide react together. The reaction mechanism involves cyanide ions
![]()
Which statements about this mechanism are correct?
1 CN– acts as a catalyst.
2 CN– is a nucleophile.
3 It is an addition reaction

▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:A
Question
Which compounds react with alkaline aqueous iodine to give a pale yellow precipitate of tri-iodomethane?
1 butanone
2 ethanal
3 propan-2-ol
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:A
Question
Which compounds can be obtained from but-2-ene in a single reaction?
$1 \mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{CH}(\mathrm{OH}) \mathrm{CH}(\mathrm{OH}) \mathrm{CH}_3$
$2 \mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{CH}(\mathrm{OH}) \mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{CH}_3$
$3 \mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{CO}_2 \mathrm{H}$
The responses A to D should be selected on the basis of
No other combination of statements is used as a correct response.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:A
Question
Compound $\mathrm{X}, \mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{CH}(\mathrm{OH}) \mathrm{CH}(\mathrm{CHO}) \mathrm{CH}_3$, is heated under reflux with an excess of acidified $\mathrm{K}_2 \mathrm{Cr}_2 \mathrm{O}_7$ to form compound $\mathrm{Y}$.
Both $X$ and $Y$ are separately warmed with Fehling’s solution and the observations noted.
What are the observations?
A Both $\mathrm{X}$ and $\mathrm{Y}$ give a red precipitate.
B Only $X$ gives a red precipitate.
C Only $Y$ gives a red precipitate.
D Neither $X$ nor $\mathrm{Y}$ gives a red precipitate.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:B
Question
Which compound gives both:
● an orange precipitate with 2,4-DNPH reagent
● and a yellow precipitate with alkaline I_$2$(aq)?
A ethanol
B methanal
C propanal
D propanone
Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Question
A carbonyl compound, X, reacts with HCN in the presence of NaCN to make a compound with
Mr 85. Compound X does not react with Fehling’s reagent.
What is compound X?
A butanal
B butanone
C propanal
D propanone
Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Question
When an organic compound is oxidised, any oxygen atom gained by the organic molecule is considered to be from a water molecule also producing 2H++ 2e–. Any hydrogen atom lost may be considered to be lost as H++ e–.
These changes can be represented by the following two equations.
\(H_{2}O \rightarrow 2H^{+} + 2e^{-}\)
\([H] \rightarrow H^{+} + e^{-}\)
Compound X is oxidised by heating under reflux with hot, acidified potassium dichromate(VI) for one hour. The half-equation for the reduction reaction is shown.
\(Cr_{2}O_{7}^{2-} + 14H^{+} + 6e^{-} \rightarrow 2Cr^{3+} + 7H_{2}O\)
Under these conditions, one mole of potassium dichromate(VI) oxidises three moles of X.
What could X be?
A propanal
B propan-1-ol
C propan-1,2-diol
D propan-1,3-diol
Answer/Explanation
Answer: A
Question
Which statement is correct for the reaction of carbonyl compounds with HCN?
A The reaction is catalysed by concentrated H2SO4.
B Pentan-2-one and HCN react to give a chiral product.
C The reaction is a condensation reaction.
D The reaction is nucleophilic substitution.
Answer/Explanation
Answer: B
Question
Which pairs of compounds may be distinguished by testing with alkaline aqueous iodine?
1 butanal and butanone
2 pentan-2-one and pentan-3-ol
3 propanone and propan-2-ol
Answer/Explanation
Answer: B
Question
Reduction of compound R with LiAlH4 gives the compound 4-methylpentane-2,3-diol. What could be the identity of compound R?
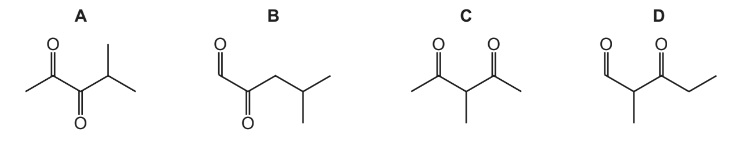
▶️Answer/Explanation
Answer A
Question
CH3CH2COCH2CH3 reacts with hydrogen cyanide to form an organic product called a cyanohydrin.
Which statement is correct?
A The cyanohydrin product has one chiral centre.
B The cyanohydrin product is formed by electrophilic addition.
C The cyanohydrin product is formed via an intermediate which contains a C–OH group.
D The formation of the cyanohydrin product requires the use of cyanide ions as a catalyst.
Answer/Explanation
Answer D
Question
When compound X is heated with Cr2O72– /H+ , a colour change from orange to green is observed.
Two tests are carried out on the organic product of this reaction.
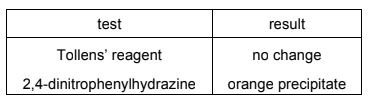
What could be compound X?
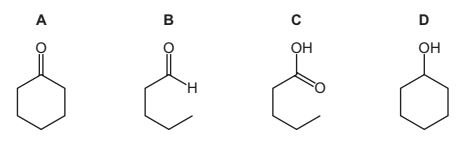
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
D
Question
1 mole of each of the following four compounds is reacted separately with:
● an excess of sodium
● an excess of sodium carbonate.
Which compound produces the same volume of gas with each of the two reagents?
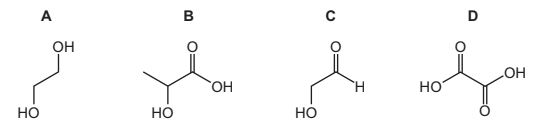
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
D
Question
The compounds listed are reacted with hydrogen cyanide.
Which compounds produce a molecule containing a chiral centre?
1 butanal
2 butanone
3 pentan-2-one
The responses A to D should be selected on the basis of
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
A
Question
Hydrogen cyanide reacts with propanone in the presence of potassium cyanide.
Which statements about this reaction are correct?
1 The cyanide ion is a catalyst for the reaction.
2 This is an addition reaction.
3 The intermediate behaves as a base.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Answer A
Question
Compound Q shows the following reactions.
● It gives an orange precipitate with 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine.
● It gives a red-brown precipitate with Fehling’s reagent.
● It gives a pale yellow precipitate with alkaline aqueous iodine.
What could be the identity of Q?
A ethanal
B propan-2-ol
C propanal
D propanone
Answer/Explanation
Answer A
Question
Compound Y
● reacts with alkaline aqueous iodine to form a yellow precipitate
● changes the colour of warm, acidified potassium dichromate(VI) solution.
What could be compound Y?
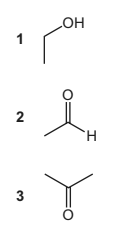
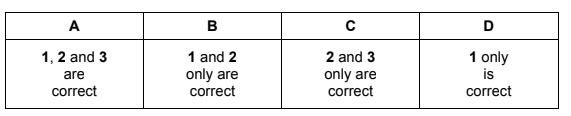
Answer/Explanation
Answer B
Question
Compound X is treated with two reagents successively, forming compound Z.
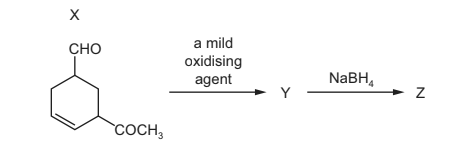
What could be Z?
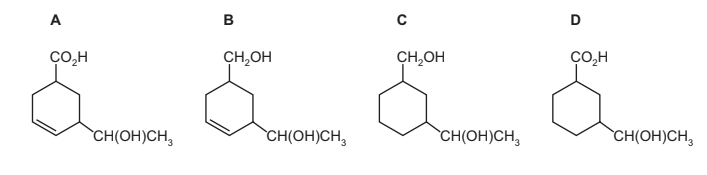
Answer/Explanation
Answer A
Question
Ethanal reacts with HCN in the presence of KCN.
Which changes in bonding occur during this reaction?
1 A carbon-carbon bond is formed.
2 A carbon-hydrogen bond is broken.
3 A carbon-nitrogen bond is broken.
Answer/Explanation
Answer B
Question
The Mr of compound X is 72. The composition by mass of X is 66.7% carbon, 11.1% hydrogen and 22.2% oxygen. X gives an orange precipitate with 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine reagent. X does not react with Fehling’s reagent.
What can be deduced from this information?
1 X is a carbonyl compound.
2 X is a ketone.
3 X is butanone.

Answer/Explanation
Answer A
Question
What is the mechanism for the reaction of ethanal, CH$_3$CHO, with hydrogen cyanide, HCN, in the presence of NaCN?
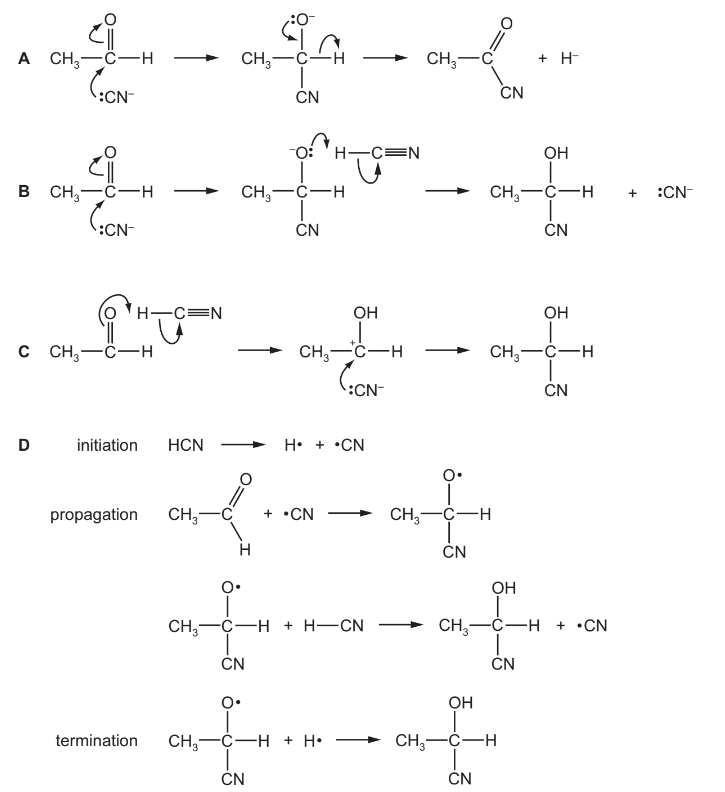
▶️Answer/Explanation
Answer B
Question
Compound Q
● contains a chiral centre,
● gives a positive result with Fehling’s reagent,
● gives a positive result with alkaline aqueous iodine.
What could compound Q be?
A 1-hydroxybutanone
B 2-hydroxybutanal
C 3-hydroxybutanal
D 3-hydroxybutanone
Answer/Explanation
Answer C
Question
Propanal reacts with hydrogen cyanide to form 2-hydroxybutanenitrile. A suitable catalyst for this reaction is sodium cyanide.
$\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{CHO}+\mathrm{HCN} \stackrel{\mathrm{NaCN}}{\longrightarrow} \mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{CH}(\mathrm{OH}) \mathrm{CN}$
Which statements about the reaction of propanal with hydrogen cyanide are correct?
1 HCN is a weaker nucleophile than the nucleophile provided by NaCN.
2 The reaction mechanism involves two steps.
3 The product of the reaction has a chiral carbon atom.
The responses A to D should be selected on the basis of
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
A
Question
Compound X produces a carboxylic acid when heated under reflux with acidified potassium dichromate(VI). Compound X does not react with sodium metal.
What could be the identity of compound X?
A propanal
B propanone
C propan-1-ol
D propan-2-ol
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
A
Question
The reaction of ethanal, \(CH_3CHO\), with HCN to form 2-hydroxypropanenitrile is catalysed by NaCN.
What are features of the intermediate of this reaction?
1 It is chiral.
2 It has a single negative charge on one of its atoms.
3 It is a nucleophile.The responses A to D should be selected on the basis of
Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Question
3-methylbutanone is treated with alkaline aqueous iodine. The mixture of products is then acidified.
Which compound is present in the final mixture of products?
A 3-methylbutanoic acid
B butanoic acid
C methylpropanoic acid
D propanoic acid
Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Question
For which reactions are the colour changes described correctly?
The responses A to D should be selected on the basis of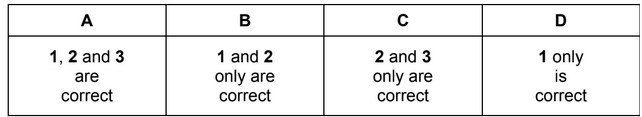
Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question
Propanone reacts with an aqueous mixture of HCN and NaCN by a nucleophilic addition mechanism.
The first stage of the mechanism involves attack by cyanide ions.
Which diagram correctly represents this?
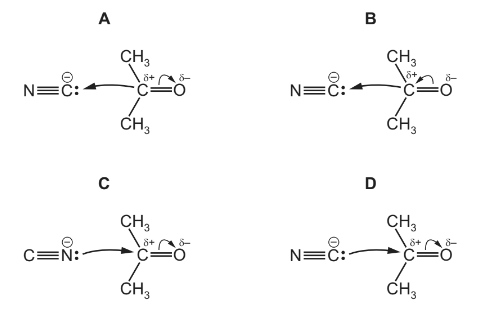
Answer/Explanation
Answer: D
Question
P, Q and R are carbonyl compounds.
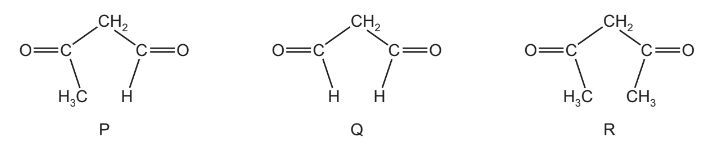
Fehling’s solution can be used to help identify these compounds.
Which compounds form a red-brown precipitate on warming with Fehling’s solution?
A P, Q and R B P and Q only C P only D Q only
Answer/Explanation
Answer: B
Question
Which reagent cannot be used to distinguish between ethanal and propanone?
A acidified sodium dichromate(VI) solution
B alkaline aqueous iodine
C cold acidified potassium manganate(VII) solution
D Fehling’s reagent
Answer/Explanation
Answer: B
Question
Which compounds will react with HBr to give the compound R?
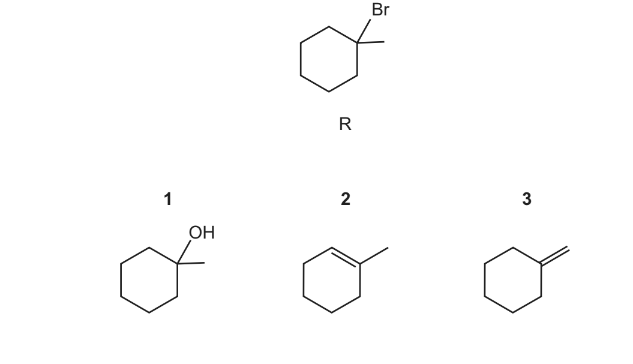
The responses A to D should be selected on the basis of
Answer/Explanation
Ans:A
Question
An oxidising agent that can oxidise ethanal to ethanoic acid, or to ethanoate ions, will also oxidise methanoic acid, \(HCO_{2}\)H, to carbon dioxide and water.
Which reagents, on heating, will react differently with \(HCO_{2}\)H and \(CH_{3}CO_{2}\)H?
1 \(Na_{2}CO_{3}\)(aq)
2 Fehling’s reagent
3 dilute acidified \(KMnO_{4}\)
The responses A to D should be selected on the basis of
Answer/Explanation
Ans:C
Question
Each of the compounds below is treated separately with excess \(NaBH_{4}\). The product of each reaction is then heated with excess concentrated \(H_{2}SO_{4}\).
In each case, one or more products are formed with molecular formula \(C_{7}H_{10}\).
Which compounds give only one final product with the molecular formula \(C_{7}H_{10}\)?
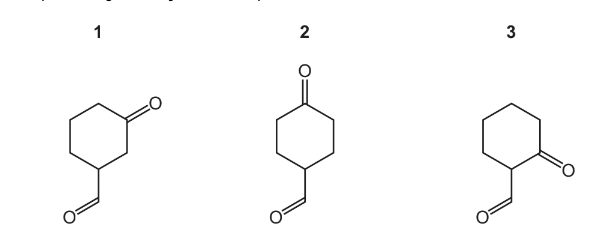
The responses A to D should be selected on the basis of

Answer/Explanation
Ans:C
Question
Tollens’ reagent can be used to help identify compounds P, Q and R.
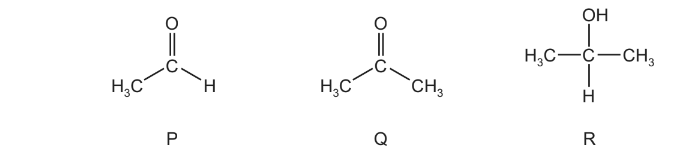
Which compound(s) form a silver precipitate on warming with Tollens’ reagent?
A P and Q B P only C Q only D R only
Answer/Explanation
Ans:B
Question
Butan-2-ol can be made by reducing X with \( H_{2}\) /Ni. Butan-2-ol can be dehydrated to form Y and Z which are structural isomers of each other.
Which row is correct?
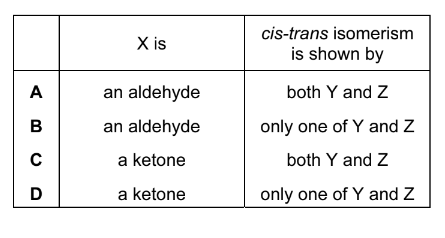
Answer/Explanation
Ans:D
Question
For which mixtures of reagents are the colour changes described correctly?

The responses A to D should be selected on the basis of
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:B
Question
Propanal will react with hydrogen cyanide to form 2-hydroxybutanenitrile. A suitable catalyst for
this reaction is sodium cyanide.
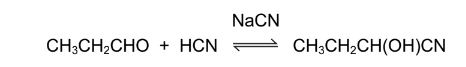
Which statements about the reaction of propanal with hydrogen cyanide are correct?
1 The \(CN^{–}\) ion attacks the propanal molecule to form an intermediate ion.
2 The product of the reaction has a chiral carbon atom.
3 The\( CN^{–}\0ion is a stronger electrophile than the HCN molecule.
The responses A to D should be selected on the basis of

▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:B
Question
β-carotene is responsible for the orange colour of carrots.
β-carotene is oxidised by hot, concentrated, acidified \(KMnO_{4}\). When an individual molecule of β-carotene is oxidised in this way, many product molecules are formed.
How many of these product molecules contain a ketone functional group?
A 4 B 6 C 9 D 11
Answer/Explanation
Ans:B
Question
Corticosterone is a hormone involved in the metabolism of carbohydrates and proteins.
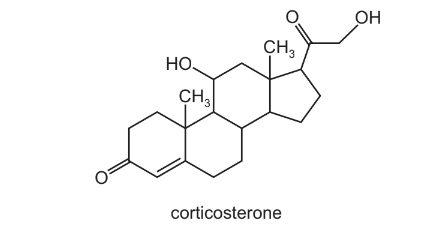
How many chiral centres are there in one molecule of corticosterone?
A 5 B 6 C 7 D 8
Answer/Explanation
Ans:C
Question
1,1-dichloropropane reacts with aqueous sodium hydroxide in a series of steps to give propanal.
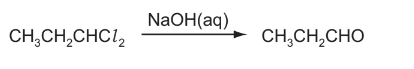
Which term describes the first step of this reaction?
A addition
B elimination
C oxidation
D substitution
Answer/Explanation
Ans:D
Question
Which pairs of reagents will take part in a redox reaction?
1 \( CH_{3}COCH_{3} +\) Tollens’ reagent
2 \( CH_{3}CH_{2}CHO +\) Fehling’s reagent
3 \(CH_{3}CH=CH_{2} + Br_{2}\)
The responses A to D should be selected on the basis of
Answer/Explanation
Ans:C
Question
Hydroxyethanal, \(HOCH_{2}CHO \), is heated under reflux with an excess of acidified potassium dichromate(VI) until no further oxidation takes place.
What is the skeletal formula of the organic product?
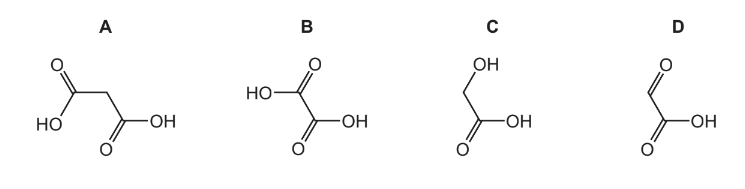
Answer/Explanation
Ans:B
Question
In which reactions is the organic compound oxidised by the given reagent?
1 \(CH_3CH_2CHO\) + Fehling’s reagent
2 \(CH_3CH_2CH_2CHO\) + Tollens’ reagent
3 \(CH_3CHO\) + 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine reagent
The responses A to D should be selected on the basis of
No other combination of statements is used as a correct response.
Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question
The structural formula of a compound X is shown below.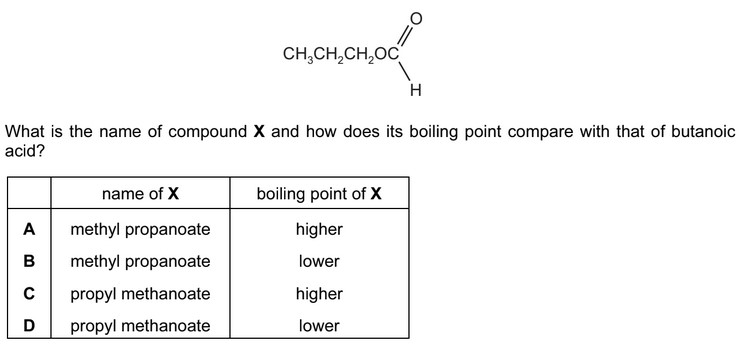
Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Question
Burnt sugar has a characteristic smell caused partly by the following compound.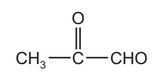
This compound contains two functional groups.
Which reagent will react with only one of the functional groups?
A acidified potassium dichromate(VI)
B 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine
C hydrogen cyanide
D sodium hydroxide
Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Question
Aqueous sodium hydroxide reacts with 1-bromopropane to give propan-1-ol.
How should the first step in the mechanism be described?
A by a curly arrow from a lone pair on the \(OH^–\) ion to the \(C^{δ+}\) atom of 1-bromopropane
B by a curly arrow from the \(C^{δ+}\) atom of 1-bromopropane to the \(OH^–\) ion
C by a curly arrow from the C–Br bond to the C atom
D by the homolytic fission of the C–Br bond
Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Question
The organic compound X gives a precipitate when warmed with aqueous silver nitrate. This precipitate dissolves when concentrated aqueous ammonia is added.
What is a possible identity for X?
1 1-bromopropane
2 2-chlorobutane
3 2-iodo,2-methylpropane
Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question
The compounds below are treated with hydrogen cyanide.
Which compounds react and produce a molecule containing a chiral centre?
1 butanal
2 pentan-3-one
3 2-chlorobutane

Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Question
How many of the compounds shown will react with aqueous sodium hydroxide to form the sodium salt of a carboxylic acid?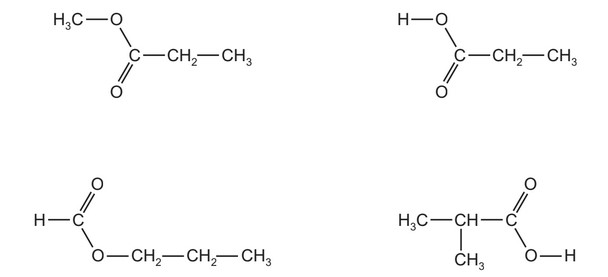
A 1 B 2 C 3 D 4
Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Question
Primary alcohols can be oxidised to aldehydes using either acidified potassium dichromate(VI) or acidified potassium manganate(VII). Both these oxidising agents change colour as they are reduced.
What is the colour of each oxidising agent before and after it has reacted?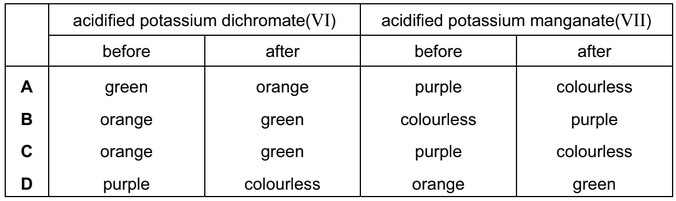
Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Question
In 1903 Arthur Lapworth became the first chemist to investigate a reaction mechanism. The reaction he investigated was that of hydrogen cyanide with propanone.
What do we now call the mechanism of this reaction?
- electrophilic addition
- electrophilic substitution
- nucleophilic addition
- nucleophilic substitution
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
C
Question
Which reagents react with butanone, C2H5COCH3?
- Tollens’ reagent
- sodium borohydride
- 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine reagent
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
C
Question
The compound cis-hex-3-enal is responsible for the characteristic smell of cut grass. The human nose is particularly sensitive to this compound, being able to detect 0.25 parts per billion in air.
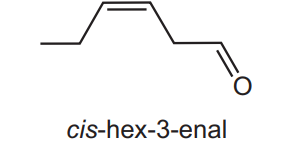
Which reagents will react with cis-hex-3-enal?
- sodium
- sodium borohydride
- Fehling’s reagent
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
C
Question
A number of alcohols with the formula C4H10O are separately oxidised. Using 70 g of the alcohols a 62% yield of organic product is achieved.
What mass of product could be obtained?
- 42.2g of butanone
- 51.6g of butanoic acid
- 51.6g of 2-methyl propanoic acid

Answer/Explanation
Ans:
A