Question
(a) (i) Using the symbol HZ to represent a Brønsted-Lowry acid, write equations which show the following substances acting as Brønsted-Lowry bases.
\(NH_3\) + →
\(CH_3OH\) + →
(ii) Using the symbol B– to represent a Brønsted-Lowry base, write equations which show the following substances acting as Brønsted-Lowry acids.
\(NH_3\) + →
\(CH_3OH\) + →
(b) State briefly what is meant by the following terms.
(i) reversible reaction
(ii) dynamic equilibrium
(c) (i) Explain what is meant by a buffer solution.
(ii) Explain how the working of a buffer solution relies on a reversible reaction involving a Brønsted-Lowry acid such as HZ and a Brønsted-Lowry base such as Z–.
(d) Propanoic acid, \(CH_3CH_2CO_2H\), is a weak acid with \(K_a = 1.34 × 10^{–5}\) mol \(dm^{–3}\).
(i) Calculate the pH of a 0.500 mol \(dm^{–3}\) solution of propanoic acid.
Buffer solution F was prepared by adding 0.0300 mol of sodium hydroxide to 100 \(cm^3\) of a 0.500 mol \(dm^{–3}\) solution of propanoic acid.
(ii) Write an equation for the reaction between sodium hydroxide and propanoic acid.
(iii) Calculate the concentrations of propanoic acid and sodium propanoate in buffer solution F.
[propanoic acid] = …………………………..mol \(dm^{–3}\)
[sodium propanoate] = …………………………..mol \(dm^{–3}\)
(iv) Calculate the pH of buffer solution F.
pH = …………………………..
(e) Phenyl propanoate cannot be made directly from propanoic acid and phenol.
Suggest the identities of the intermediate G, the reagent H and the by-product J in the following reaction scheme.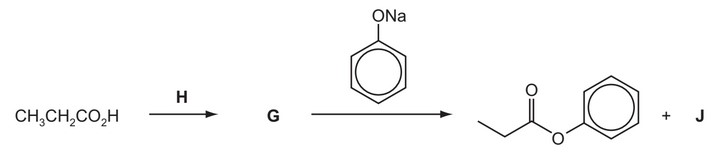
G is ………………………………………………….
H is ………………………………………………….
J is ………………………………………………….
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
(a) (i) \(NH_3 + HZ → NH_4^+ + Z^-\)
\(CH_3OH + HZ → CH_3OH_2^+ + Z^-\)
(ii) \(NH_3 + B^- → NH_2^- + BH\)
\(CH_3OH + B^- → CH_3O^- + BH\)
(b) (i) a reaction that can go in either direction
(ii) rate of forward = rate of backward reaction
or forward/back reactions occurring but concentrations of all species do not change
(c) (i) a solution that resists changes in pH
when small quantities of acid or base/alkali are added
(ii) in the equilibrium system \(HZ + H_2O \leftrightarrow Z^- + H_3O^+\)
addition of acid: reaction moves to the left
or \(H^+\) combines with \(Z^-\) and forms HZ
addition of base: the reaction moves to the right
or \(H^+\) combines with \(OH^-\) and more \(Z^-\) formed
(d)
(i) \([H^+] = √(0.5 × 1.34 × 10^{-5}) = 2.59 × 10^{-3}\) (mol \(dm^{-3}\))
pH = 2.59/2.6 (min 1 d.p)
(ii) \(CH_3CH_2CO_2H + NaOH → CH_3CH_2CO_2Na + H_2O\)
(iii) n(acid) in 100 \(cm^3\) = 0.5 × 100/1000 = 0.05 mol
n(acid) remaining = 0.05 – 0.03 = 0.02 mol
[acid remaining] = 0.2 (mol \(dm^-3\))
likewise, n(salt) = 0.03 mol
[salt] + 0.3 (mol \(dm^{-3}\))
(iv) pH = 4.87 + log(0.3/0.2) = 5.04–5.05
(e) G is \(CH_3CH_2COCl\)
H is \(SOCl_2\) or \(PCl_5\)
J is NaCl
(or corresponding Br compounds for G, H and J; \(CH_3CH_2COBr, SOBr_2, NaBr)\)
Question
Compound B is a liquid with a fruity smell.
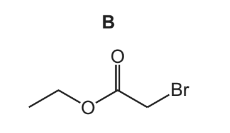
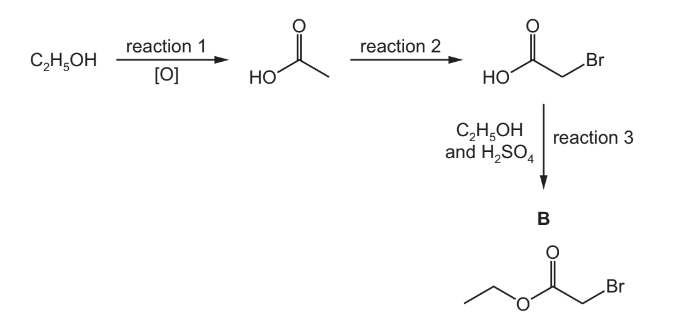
The reaction scheme shows how B can be made from ethanol, C2H5OH.
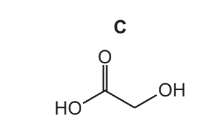
If C is present in the reaction mixture of reaction 3, a different compound, compound D, will
also form. Compound D has two identical functional groups.
The infrared spectrum of D shows strong absorptions at 1100cm-1 and 1720cm-1, but no
absorption due to O–H bonds.
Use the Data Booklet to identify the functional group present in D.
Explain your answer as fully as you can.
(c) Some other reactions of C are shown.
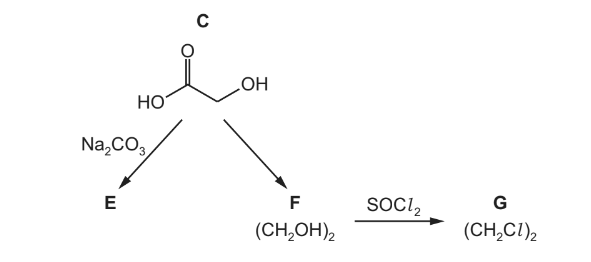
(i) Draw the structure of E.
Explain your answer.
(iii) Construct an equation for the reaction of (CH2OH)2 with SOCl2 to form G, (CH2Cl)2.
(d) Explain why C is very soluble in water.
Answer/Explanation
Answer: (a)(i) potassium/sodium dichromate [(VI)] / K 2Cr2O7 / Na2Cr2O7
acidified AND (heat) under reflux
(a)(ii) C2H5OH + 2[O] → CH3CO2H + H2O
(a)(iii) substitution
(a)(iv) in the same phase / in same state
(b) M1 ester
M2 1100 cm-1 linked to C—O AND 1720 cm-1 linked to C=O
M3 No COOH / carboxylic acid and No OH / alcohol in D (but present in C)
OR
COOH / carboxylic acid and OH / alcohol reacted /lost (in C to form D)
(c)(i) 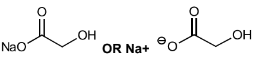
(c)(ii) Not a strong (enough) reducing agent
(c)(iii) Construct an equation
(CH2OH)2 + SOCl2 → (CH2Cl)2+ SO2 + H2O
(d) Forms hydrogen bonds with water