Question
(a) Explain what is meant by the term ionisation energy.
(b) The first seven ionisation energies of an element, A, in \( kJmol^{–1},\) are
1012 1903 2912 4957 6274 21269 25 398.
(i) State the group of the Periodic Table to which A is most likely to belong. Explain your answer.
(ii) Complete the electronic configuration of the element in Period 2 that is in the same group as A.\( 1s^{2}\)
(c) Another element, Z, in the same period of the Periodic Table as A, reacts with chlorine to form a compound with empirical formula \(ZCl _{2}\). The percentage composition by mass of \(ZCl_{ 2}\) is Z, 31.13; Cl, 68.87.
(i) Define the term relative atomic mass.
(ii) Calculate the relative atomic mass,\( A_{r} \), of Z.
Give your answer to three significant figures.
(d) The chlorides of elements in Period 3 of the Periodic Table show different behaviours on addition to water, depending on their structure and bonding.
(i) Write equations to show the behaviour of sodium chloride, NaCl, and silicon chloride,
\(SiCl_{ 4}\) , when separately added to an excess of water.NaCl
\(SiCl_{4 }\)
(ii) State and explain the differences in behaviour of these two chlorides when added to water, in terms of their structure and the bonding found in the compounds.
(e) Sulfur reacts with fl uorine to form\( SF_{6}\). State the shape and bond angle of \(SF_{6}.\)
shape of\( SF_{6}\)
bond angle of\( SF_{6}\)
▶️Answer/Explanation
(a) The amount of energy required/ energy change/ enthalpy change when one electron is
removed
from each atom/(cat)ion in one mol
of gaseous atoms /(cat)ions
OR energy change when 1 mole of electrons is removed from one mole of gaseous
atoms / ions
\(X(g) → X+(g)^{ +} e^{–}\) gains 2 marks
(b) (i) Group V/ 5/ 15
Big difference between fifth and sixth ionisation energies
(ii)\( 1s^{2} 2s^{2} 2p^{3}\)
ecf from (b)(i) if period 2
(c) (i) (Weighted) mean/ average mass of an atom(s) (of an element)
Relative to\( 1 / 12^{th}\) of (the mass of an atom of) carbon-12 OR
relative to carbon-12 which is (exactly) 12 (units)
allow as an expression
(ii) Z Cl
\(\frac{31.13}{A_{r}} \frac{68.87}{35.5}\)=1:2
so \(\frac{6887/35.5}{31.13/A}\)=2
$A_{r}=\frac{2\times 31.13\times 35.5}{68.87}=32.023=32.1$ to 3sf.
Question
Gallium is a metal in Group 13 of the Periodic Table.
(a) There are two stable isotopes of gallium, \(^{69}Ga~and~^{71}Ga\)
(i) State, with reference to subatomic particles, how the isotopes \(^{69}Ga~and~^{71}Ga\) differ from each other.
(ii) State what further information is needed to calculate the relative atomic mass of gallium. [1]
(b) Gallium and its compounds show similar properties to aluminium and its compounds. Gallium reacts with excess chlorine to form gallium trichloride.
(i) At $500^{\circ} \mathrm{C}$, gallium trichloride is a gas.
Suggest the type of attraction that exists at $500^{\circ} \mathrm{C}$
- between atoms within a gallium trichloride molecule
- between gallium trichloride molecules. [5]
(ii) When gallium trichloride is cooled a solid, $\mathrm{Ga}_2 \mathrm{Cl}_6$, forms.
Suggest the name of the attraction formed between two gallium trichloride molecules to form $\mathrm{Ga}_2 \mathrm{Cl}_6$. [1]
(c) Gallium metal reacts rapidly when exposed to air. A white solid layer is formed on its surface.
(i) Suggest an equation to describe the reaction occurring when gallium metal is exposed to air. [2]
(ii) The table gives the formula of each gallium-containing product formed when gallium oxide reacts separately with hot aqueous hydrochloric acid and hot aqueous sodium hydroxide.
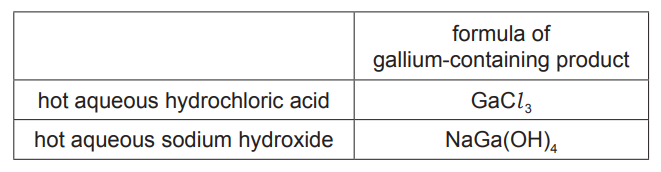
Give the name of the type of behaviour shown by gallium oxide in these reactions [1] [Total: 8]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a)(i) (different) number of neutrons. 1
(a)(ii) the relative abundance / % abundance of (each) the isotopes. 1
(b)(i) M1 attractions between atoms within a gallium trichloride molecule
covalent (bonds)
M2 attractions between gallium trichloride molecules
temporary induced dipoles
(b)(ii) coordinate / dative (covalent)
(c)(i)
$
4 \mathrm{Ga}+3 \mathrm{O}_2 \rightarrow 2 \mathrm{Ga}_2 \mathrm{O}_3
$
M1 correct formula of $\mathrm{Ga}_2 \mathrm{O}_3$
M2 correctly balanced equation based on $\mathrm{Ga}+\mathrm{O}_2$ and formula of gallium oxide in $\mathrm{M} 1$
(c)(ii) amphoteric