Question
Compound T is made by a three-stage synthesis.
(a) In stage 1, phenylethanoic acid reacts with a suitable reagent to form compound R.
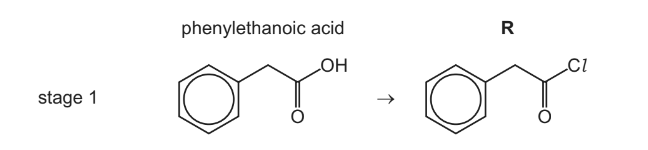
Suggest a suitable reagent for stage 1.
(b) In stage 2, compound R reacts with ethylamine to form compound S.
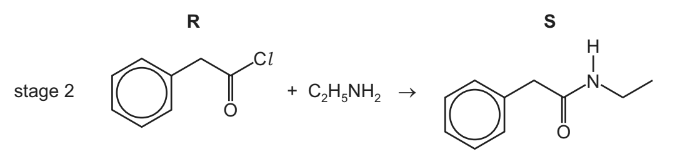
(i) Name the functional group formed in stage 2.
(ii) Identify the other product formed in stage 2.
(c) In stage 3, compound S reacts with a suitable reagent to form compound T.
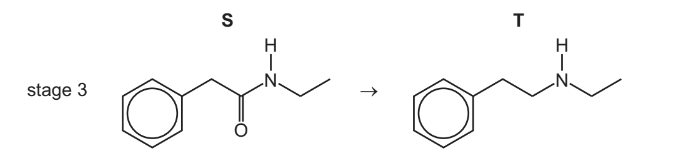
(i) State the formula of a suitable reagent for stage 3.
(ii) Name the type of reaction that occurs in stage 3.
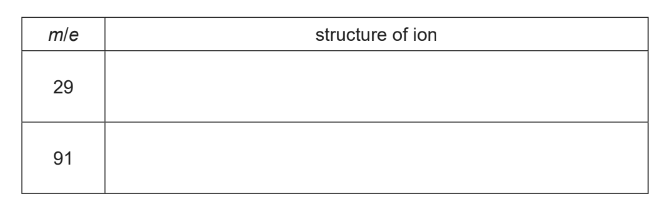
Draw the structures of the ions responsible for these peaks.
(e) The proton (1H) NMR spectrum of compound T shows hydrogen atoms in different environments. Six of these environments are shown on the structure using letters a, b, c, d, e and f.
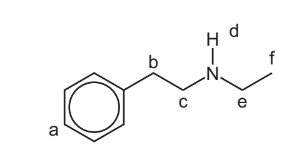
Use the letters a, b, c, d, e and f to answer the questions that follow. The questions relate to the proton (1H) NMR spectrum of T.
Proton d does not cause splitting of the peaks for protons c or e under the conditions used.
Each answer may be one, or more than one, of the letters a, b, c, d, e and f.
(i) Identify the proton or protons with a chemical shift (δ) in the range 6.0 to 9.0.
(ii) Identify the proton or protons whose peak will disappear if D2O is added.
(iii) Identify the proton or protons whose peak is a triplet.
(iv) Identify the proton or protons with the lowest chemical shift (δ).
Answer/Explanation
Answer (a) PCl5 OR PCl3 OR SOCl2 (b)(i) amide (b)(ii) HCl / hydrogen chloride OR C2H5NH3Cl / ethylammonium chloride
(c)(i) LiAl H4
(c)(ii) reduction
(d)(i) relative abundance = 2 carbons × 1.1 × 0.62 = 1.36 / 1.4 min 2sf
(d)(ii) CH3CH2 + / C2H5+ C6H5CH2+ (e)(i) a
(e)(iii) d
(e)(iii) b, c, f
(e)(iv) f
Question
The names of many drugs used in medicine often include parts of the names of the functional groups their molecules contain.
(a) Suggest two functional groups present in a molecule of the drug named chloramphenicol.
(b) The drug named ketamine readily reacts with protons as shown.
\(ketamine + H^{+} \rightarrow [ketamine-H]^{+}\)
(i) State the role of ketamine in this reaction.
Ketamine gives an orange precipitate with 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine (2,4-DNPH).
(ii) Suggest the functional group in the ketamine molecule responsible for this observation.
The mass spectrum of ketamine is determined. Two peaks close to the molecular ion peak, M, are observed with the relative abundances shown in the table.
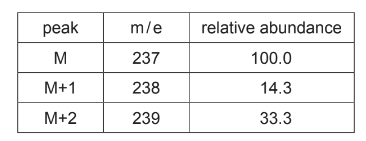
(iii) Use the numbers in the table to show that there are 13 carbon atoms in a ketamine molecule.
In addition to carbon and hydrogen atoms, each molecule of ketamine contains one atom of
each of three different elements. These are called heteroatoms. One of these heteroatoms is
a halogen.
(iv) Use the figures in the table to suggest the identity of this halogen. Explain your answer.
(v) Another peak in the mass spectrum of ketamine has an m/e value of 240.
Predict the relative abundance of this peak.
(vi) Use the information in (b) to complete the molecular formula of ketamine by working
out the identities of the three different heteroatoms and the number of hydrogen atoms present.
\(C_{13}H\)
Answer/Explanation
Answer a) Any two of:
chloro
amine / amino
alcohol / hydroxyl / phenol
benzene / phenyl ring / aryl / arene
(b)(i) ketamine is acting as a base
(b)(ii) carbonyl group
(b)(iii) n = (100 / 1.1) x (14.3 / 100) = 13.0 OR n = (14.3 / 1.1) = 13.0
(b)(iv) the ratio of the (M:M+2) peaks is 3:1 AND halogen is chlorine / Cl
(b)(v) relative abundance = 14.3 / 3 = 4.77 (4.8) OR RA = 14.3 × 33.3 / 100 = 4.76 (4.8)
(b)(vi) C13H16NOCl
(c)(i) six
(c)(ii) M1 peak at δ 0.9 is due to 12 H
M2 peak at 2.2 is due to 2 H
M3/M4 peaks at 1.2, 1.4 and 1.7 are all singlets
(c)(iii) 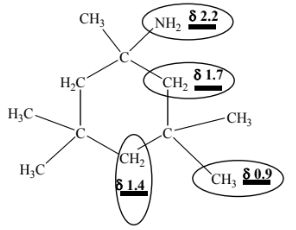
(c)(iv) NH / NH2 protons AND exchange with D2O / D
OR –NH2 + D2O → –ND2 + H2O