Question
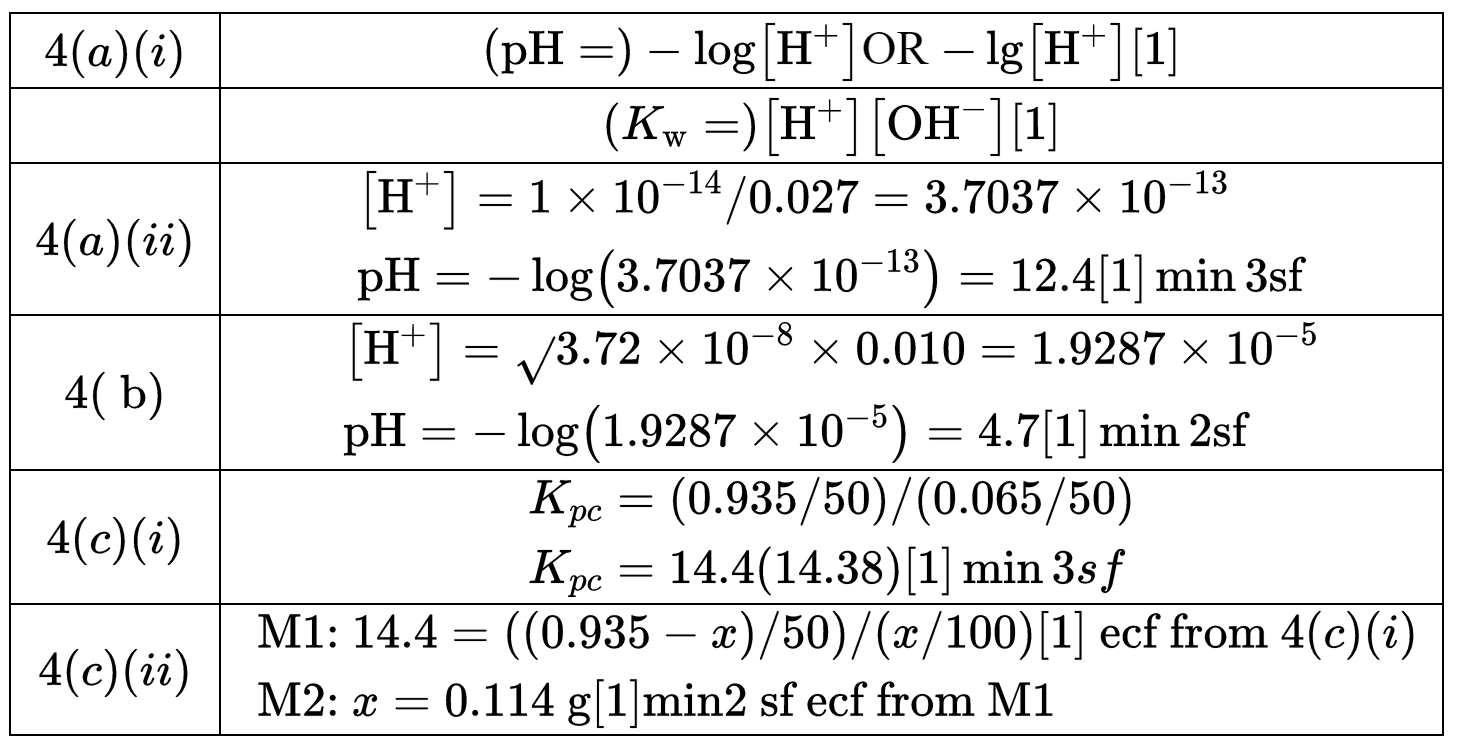
(a) (i) Give the mathematical expression for each of the terms $\mathrm{pH}$ and $K_{\mathrm{w}}$.
$\begin{aligned} & \mathrm{pH}= \\ & K_{\mathrm{w}}=\end{aligned}$
(ii) Calculate the $\mathrm{pH}$ of $0.027 \mathrm{~mol} \mathrm{dm}^{-3} \mathrm{NaOH}(\mathrm{aq})$.
pH = ………………………… [1]
(b) The $K_{\mathrm{a}}$ value of chloric(I) acid, $\mathrm{HClO}$, is $3.72 \times 10^{-8} \mathrm{moldm}^{-3}$. Calculate the $\mathrm{pH}$ of $0.010 \mathrm{moldm}^{-3} \mathrm{HClO}(\mathrm{aq})$.
pH = ………………………… [1]
(c) Water and octan-1-ol form two layers when mixed.
Ethanamide is more soluble in water than it is in octan-1-ol. When $1.00 \mathrm{~g}$ of ethanamide is added to $50.0 \mathrm{~cm}^3$ of water and this is then shaken with $50.0 \mathrm{~cm}^3$ of octan-1-ol, it is found that the water layer contains $0.935 \mathrm{~g}$ of ethanamide at equilibrium.
(i) Calculate the partition coefficient, $K_{\mathrm{pc}}$, for ethanamide in water and octan-1-ol.
$K_{\mathrm{pc}}=$
(ii) The $50.0 \mathrm{~cm}^3$ of water containing $0.935 \mathrm{~g}$ of ethanamide is then shaken with $100.0 \mathrm{~cm}^3$ of pure octan-1-ol under the same conditions.
Calculate the mass of ethanamide that is dissolved in the $100.0 \mathrm{~cm}^3$ of octan-1-ol at equilibrium.
mass of ethanamide = ………………………… g [2] [Total: 7]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
Question
(a) The molecular formulae of three nitrogen-containing compounds are given.
S $\mathrm{C}_6 \mathrm{H}_5 \mathrm{CONH}_2$
T $\mathrm{C}_6 \mathrm{H}_5 \mathrm{NH}_2$
U $\mathrm{C}_6 \mathrm{H}_5 \mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{NH}_2$
Describe and explain the relative basicities of $\mathbf{S}, \mathbf{T}$ and $\mathbf{U}$.
……………………………… > ……………………………… > ………………………………
most basic least basic [3]
(b) Compound $\mathbf{U}$ can be prepared by two different methods as shown.
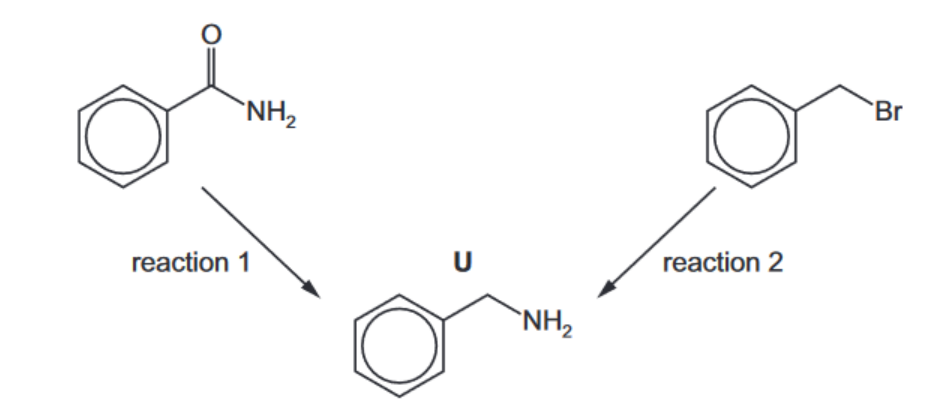
(i) Suggest reagents and conditions for reaction 1 and for reaction 2 .
reaction 1………………………………………..
reaction 2……………………………………………….[2]
(ii) State the type of reaction in reaction 1 and name the mechanism in reaction 2. type of reaction in reaction 1 mechanism of reaction 2 [2] [Total: 7]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
M1 phenylmethanamine / U > phenylamine / T > benzamide / S [1]
any two from:
• alkyl group is electron donating so lone pair more able to accept a proton
• lone pair on N overlaps with delocalised system so less able to accept a proton
• presence of electron-withdrawing oxygen / carbonyl group means lone pair is not available to accept a proton OR
amides are neutral
4(b)(i) reaction $1 \quad \mathrm{LiAlH}_4$
reaction 2 heat $\mathrm{NH}_3$ under pressure/ heat $\mathrm{NH}_3$ in a sealed tube
(b)(ii) reaction 1 reduction
reaction 2 nucleophilic substitution