Question:
In which substance are the only intermolecular forces temporary dipole-induced dipole attractions?
A hydrogen chloride
B methanol
C octane
D water
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:C
Question
In which of the following, when in liquid form, are there only intermolecular forces based on temporary dipoles between the particles?
A bromine
B ethanol
C hydrogen chloride
D water
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:A
Question
Copper has a high melting point.
What is the reason for the high melting point of copper?
A strong attractive forces between copper atoms only
B strong attractive forces between copper ions and delocalised electrons
C strong attractive forces between copper ions only
D strong attractive forces between copper atoms and delocalised electrons
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:B
Question:
The strong hydrogen bonding present in liquid water causes an increase in which properties?
1 viscosity
2 boiling point
3 surface tension

▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:A
Question
The boiling points of methane, ethane, propane and butane are given.
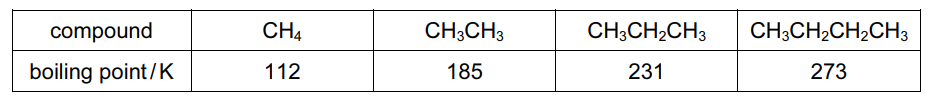
Which statement explains the increase in boiling point from methane to butane?
A Closer packing of molecules results in stronger van der Waals’ forces.
B More covalent bonds are present and therefore more energy is required to break the bonds.
C More electrons in the molecules results in stronger van der Waals’ forces.
D More hydrogen atoms in the molecules results in stronger hydrogen bonding.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:C
Question
Which molecules have an overall dipole moment?
1 carbon monoxide, $\mathrm{CO}$
2 phosphine, $\mathrm{PH}_3$
3 carbon dioxide, $\mathrm{CO}_2$
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:B
Question
Elements X, Y and Z are all in the first two periods of the Periodic Table.
Their Pauling electronegativity values, \(E_N\), are shown.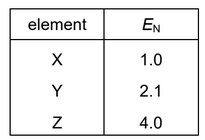
Substances exist with formulae XZ, YZ and \(Z_2\).
Which row puts these substances in order of increasing melting point?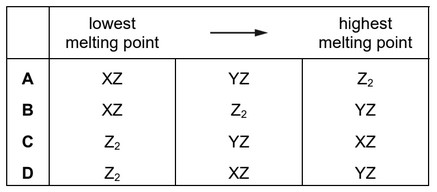
Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Question
The boiling points of some hydrogen halides are shown.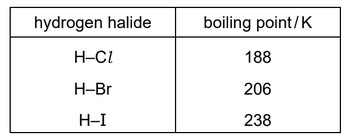
What is the explanation for the trend in boiling point for the hydrogen halides from HCl to HI?
A The bond energies of the hydrogen halides increase from HCl to HI.
B There is an increase in the strength of the intermolecular forces of attraction from HCl to HI.
C The intermolecular hydrogen bonds become stronger from HCl to HI.
D There is an increase in the bond polarity from HCl to HI.
Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question
For which pair is the boiling point of the first compound higher than the boiling point of the second compound?
A \(CH_3CH_2OH\) and \(CH_3CH_2SH\)
B \(CH_3CO_2CH_3\) and \(CH_3CH_2CO_2H\)
C \(CH_3OCH_3\) and \(CH_3CH_2OH\)
D \(CH_3CH_2CHO\) and \(CH_3CH_2CO_2H\)
Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Question
Which type of interaction exists between water molecules and metal cations in aqueous solution?
A dipole-dipole interactions
B hydrogen bonds
C ion-dipole interactions
D ionic bonds
Answer/Explanation
Answer C
Question
Liquids X and Y do not react with one another. They have identical boiling points.
When a particular volume of X is shaken with a similar volume of Y, they form a liquid mixture Z. The average intermolecular forces in liquid Z are stronger than the average of the forces in X and the forces in Y.
Which deductions from this information are correct?
1 The mixing of X and Y is exothermic.
2 The vapour pressure of liquid Z will be less than that of either liquid X or liquid Y at the same temperature.
3 The boiling point of liquid Z will be lower than that of either liquid X or liquid Y at the same pressure.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Answer B
Question
Liquids X and Y do not react with one another. They have identical boiling points.
When a particular volume of X is shaken with a similar volume of Y, they form a liquid mixture Z. The average intermolecular forces in liquid Z are stronger than the average of the forces in X and the forces in Y.
Which deductions from this information are correct?
1 The mixing of X and Y is exothermic.
2 The vapour pressure of liquid Z will be less than that of either liquid X or liquid Y at the same temperature.
3 The boiling point of liquid Z will be lower than that of either liquid X or liquid Y at the same pressure.

▶️Answer/Explanation
Answer B
Question
What is the oxidation number of sulfur in each species?
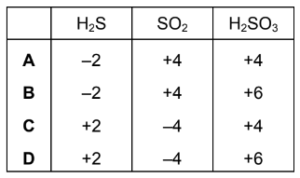
Answer/Explanation
Answer A
Question
Ethanal, CH3CHO, ethanol, C2H5OH, and methoxymethane, CH3OCH3, are three organic compounds.
Which compound has the highest boiling point and what is the interaction that causes this boiling point to be the highest?
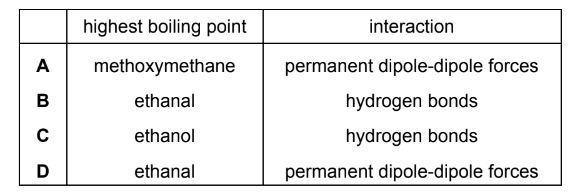
▶️Answer/Explanation
Answer C
Question
Which statements are correct?
1 The hydrogen bonds in ice are more regularly arranged than in water.
2 The solidification of water to form ice is exothermic.
3 Pure water is less dense than ice.
Answer/Explanation
Answer B
Question
Which molecule has no overall dipole?
A CH3Cl B CH2Cl2 C CHCl3 D CCl
Answer/Explanation
Answer D
Question
Which compound has a boiling point that is influenced by hydrogen bonding?
A CH3CHO B CH3OCH3 C HCO2CH3 D HCO2H
Answer/Explanation
Answer D
Question
Which molecule has the largest overall dipole?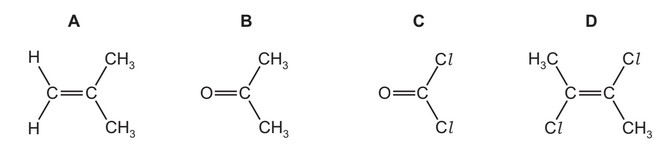
Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question
At room temperature and pressure, H2O is a liquid and H2S is a gas.
What is the reason for this difference?
A O has higher first and second ionisation energies than S.
B The covalent bond between O and H is stronger than the covalent bond between S and H.
C There is significant hydrogen bonding between H2O molecules but not between H2 molecules.
D The instantaneous dipole-induced dipole forces between H2O molecules are stronger than the instantaneous dipole-induced dipole forces between H2S molecules.
Answer/Explanation
Answer: C
Question
Nitrogen, \(N_{2}\), and carbon monoxide, CO, both have\( M_{r}\) = 28.
The boiling point of \(N_{2}\) is 77K. The boiling point of CO is 82K.
What could be responsible for this difference in boiling points?
A CO molecules have a permanent dipole, the \(N_{2}\) molecules are not polar.
B \(N_{2}\) has σ and π bonding, CO has σ bonding only.
C \( N_{2}\) has a strong N≡N bond, CO has a C=O bond.
D The CO molecule has more electrons than the \(N_{2}\) molecule.
Answer/Explanation
Ans:A
Question
P and Q are two liquid compounds with similar Mr values. Molecules of P attract each other by
hydrogen bonds. Molecules of Q attract each other by van der Waals’ forces only.
How do the properties of P and Q differ?
1 P has a higher surface tension than Q.
2 P is less soluble in water than Q.
3 P has a lower melting point than Q
The responses A to D should be selected on the basis of

Answer/Explanation
.Ans:D
Question
Pollutant oxide Y, which contains non-metallic element X, is formed in a car engine. Further oxidation of Y to Z occurs in the atmosphere. In this further oxidation, 1mol of Y reacts with 0.5mol of gaseous oxygen molecules. X could be either nitrogen or sulfur. Which statements about X, Y and Z can be correct?
1 The oxidation number of X increases by two from Y to Z.
2 Y has an unpaired electron in its molecule.
3 Y is a polar molecule.
The responses A to D should be selected on the basis of

Answer/Explanation
Ans:A
Question
Which molecular structure will have the smallest overall dipole?
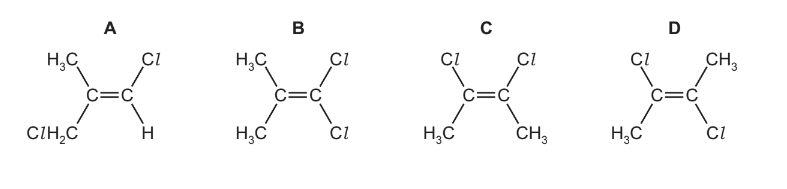
Answer/Explanation
Ans:D