Question
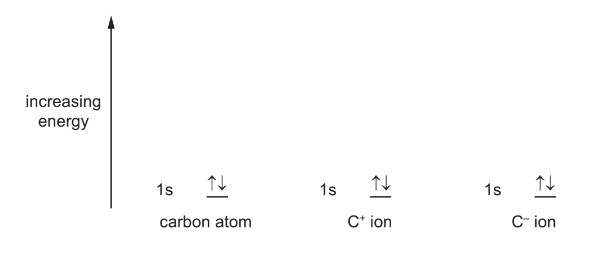
(a) Complete the diagrams to show the energies of the electrons in a carbon atom, a C+ ion and a C– ion.
(b) One of the simple molecular allotropes of carbon is buckminsterfullerene, C60.
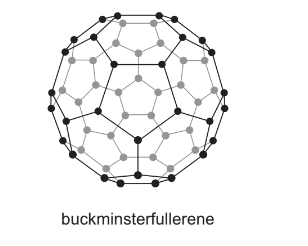
(i) What is the hybridisation of the carbon atoms in C60?
(ii) C60 reacts with an excess of hydrogen to form a single product, C60Hx.
Using your answer to (i), suggest a suitable value for x.
(c) Methylbenzene can undergo different reactions to form the products shown below.
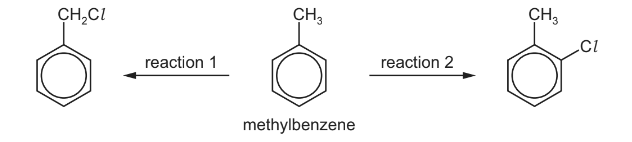
(i) Give the reagents and conditions for these two reactions.
(ii) Name the mechanism of reaction 1.
(iii) Draw the structure of the product obtained if reaction 1 is carried out using an excess of
chlorine.
Answer/Explanation
Answer: (a) 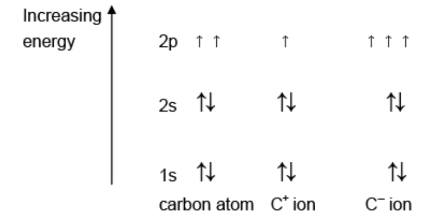
(b) (i) sp2
(b) (ii) x = 60/C60H60
(c) (i) reaction 1: Cl2 and UV light;
reaction 2: AlCl3, Cl2 (NOT aqueous);
c(ii) (free) radical substitution
c(iii)
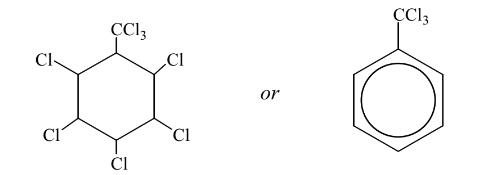
Question
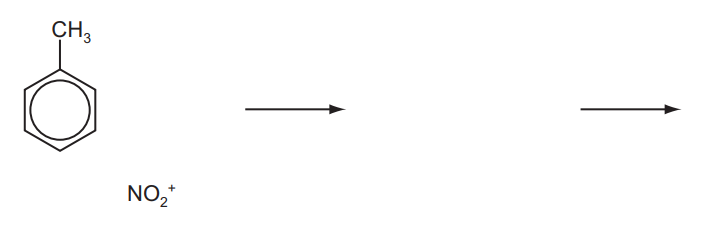
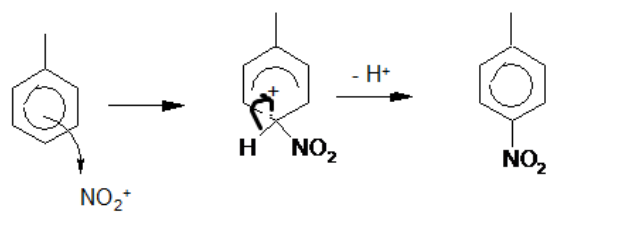
(a) Methylbenzene undergoes electrophilic substitution with nitronium ions, $\mathrm{NO}_2^{+}$. Nitronium ions are generated by the reaction between concentrated sulfuric acid and concentrated nitric acid.
(i) Construct an equation for the formation of nitronium ions, $\mathrm{NO}_2^{+}$, by this method.
(ii) Complete the scheme to show the mechanism for this reaction. Use curly arrows to show the movement of electron pairs.[4]
(b) (i) Describe and explain the relative acidities of chloroethanoic acid and ethanoic acid.
(ii) Describe and explain the relative acidities of phenol and ethanol. [3]
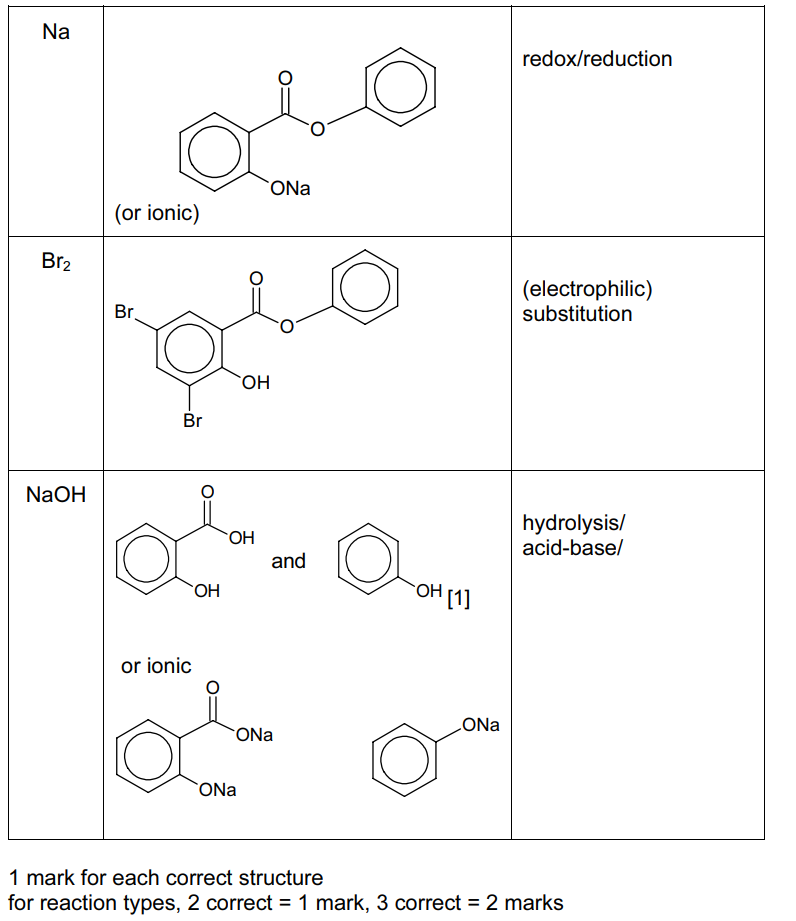
(c) Phenyl 2-hydroxybenzoate is an antiseptic.
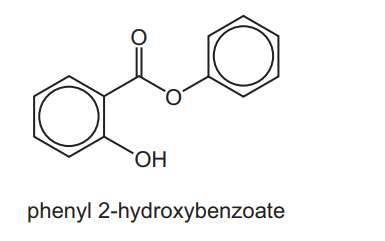
Complete the following table about the reactions of phenyl 2-hydroxybenzoate with the three reagents
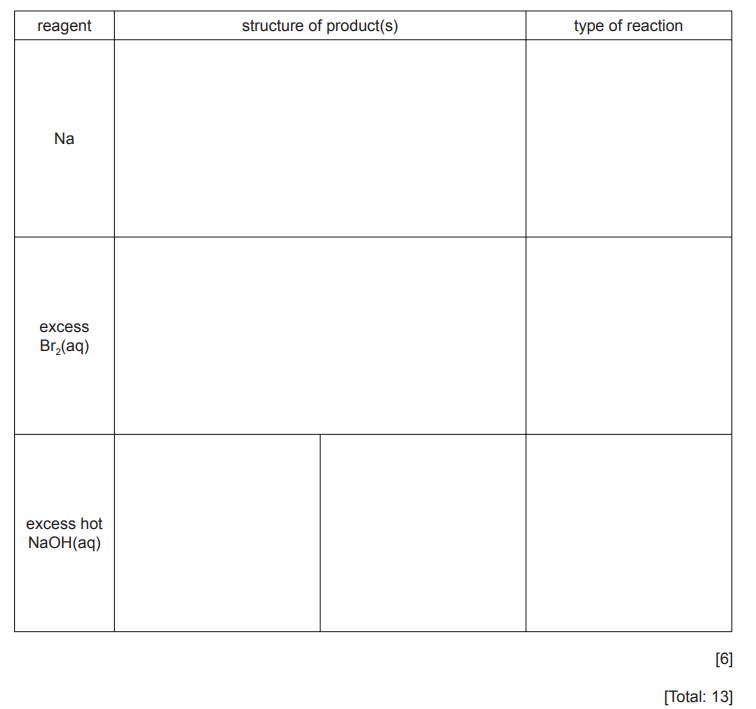
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a) (i) $\begin{aligned} & 2 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{SO}_4+\mathrm{HNO}_3 \rightarrow 2 \mathrm{HSO}_4^{-}+\mathrm{NO}_2^{+}+\mathrm{H}_3 \mathrm{O}^{+} \\ & \text {OR } \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{SO}_4+\mathrm{HNO}_3 \rightarrow \mathrm{HSO}_4^{-}+\mathrm{NO}_2^{+}+\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}\end{aligned}$
(ii) any three of
- curly arrow from inside the benzene ring to $\mathrm{NO}_2^{+}$group
- intermediate – penalise $\mathrm{NO}_2$ connectivity or missing methyl group (once)
- curly arrow from $\mathrm{C}-\mathrm{H}$ bond into ring
- product $+\mathrm{H}^{+}$(or as diagram $-\mathrm{H}^{+}$)
allow 2- and 3-substituted nitromethylbenzene)
(b) (i) acidity of $\mathrm{ClCH}_2 \mathrm{CO}_2 \mathrm{H}>\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{CO}_2 \mathrm{H}$ AND $\left(\mathrm{ClCH}_2 \mathrm{CO}_2 \mathrm{H}\right)$ as an electronegative/electron withdrawing $\mathrm{Cl}$
(ii) acidity of phenol $>\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{OH}$ AND electrons on oxygen (on phenol) delocalised into ring OR benzene ring withdraws electrons from oxygen stronger acid linked to weakening $\mathrm{O}-\mathrm{H}$ bond/anion being stabilised
c