Question
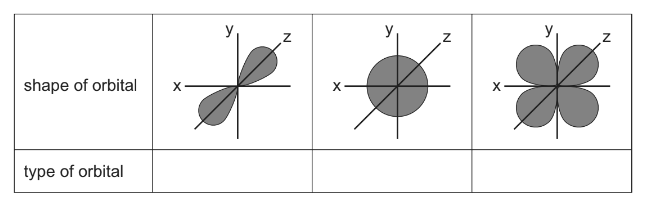
(b) Cadmium forms the two ions, Cd22+ and Cd2+. The electronic configuration of cadmium in these ions is shown.
● [Kr] 4d105s1
● [Kr] 4d10
Use this information to explain why cadmium is not a transition element.
octahedral complexes.
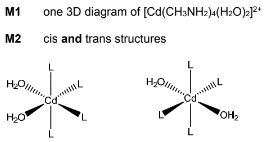
equilibrium 1 \([Cd(H_{2}O)_{6}]^{2+} + 4CH_{3}NH_{2} \rightleftharpoons [Cd(CH_{3}NH_{2})_{4}(H_{2}O)_{2}]^{2+} + 4H_{2}O\)ΔHθr = –57kJmol–1
(ii) Complete the three-dimensional diagrams to show the isomers of [Cd(CH3NH2)4(H2O)2]2+.
Use L to represent CH3NH2 in your diagrams.

(d) (i) State what is meant by the term stability constant.
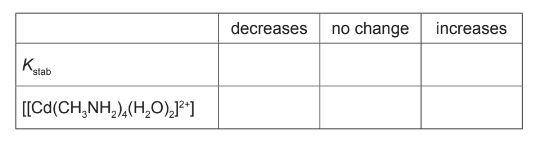
EDTA4– is a polydentate ligand. When a solution of EDTA4– is added to [Cd(H2O)6]2+ a new complex [CdEDTA]2– is formed.
The values for the stability constants for two Cd2+ complexes are shown.

(iii) A solution containing equal numbers of moles of CH3NH2 and EDTA is added to [Cd(H2O)6]2+.
Predict which complex is formed in the larger amount. Explain your answer.
(e) Methylamine is a Brønsted-Lowry base.
Write an equation showing how methylamine dissolves in water to give an alkaline solution.
(f) Methylamine is a useful reagent in organic chemistry.
(i) Write an equation for the reaction of ethanoyl chloride with methylamine.
(ii) Methylamine also reacts with propanone to form compound P as shown.
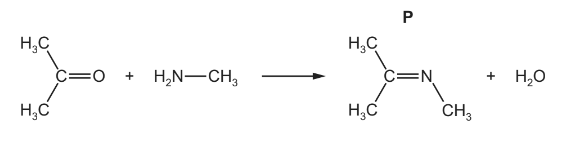
Deduce the type of reaction shown here.
Answer/Explanation
Answer: (a) 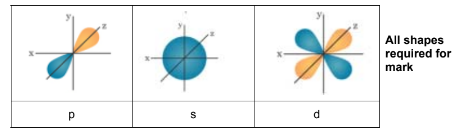
(b) both cadmium ions have full d subshells
(c)(i) donates one lone pair to the central metal ion
(c)(ii)
(d)(i) equilibrium constant for the formation of a complex ion in solution / solvent
(d)(ii)
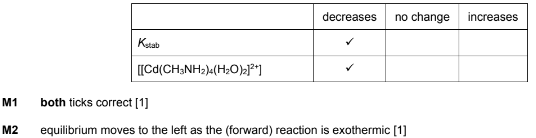
(d)(iii) [CdEDTA]2– and larger Kstab value
(e) CH3NH2 + H2O ⇌ CH3NH3+ + OH–
(f)(i) CH3COCl + CH3NH2 → CH3CONHCH3 + HCl
M1 Correct formulae of CH3COCl or CH3CONHCH3
M2 rest of the equation
(f)(ii) condensation or addition-elimination
Question
Noradrenaline is a hormone found in humans.
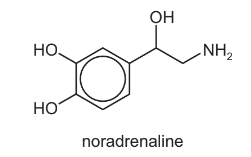
(a) Give the molecular formula of noradrenaline.
(b) State whether or not noradrenaline shows stereoisomerism. Explain your answer.
(c) HNO2(aq) is reacted at 5°C with separate samples of noradrenaline and phenylamine.
The reaction with phenylamine produces a stable diazonium ion.
The reaction with noradrenaline produces an unstable diazonium ion.
(i) Suggest why the diazonium ion produced with phenylamine is stable.
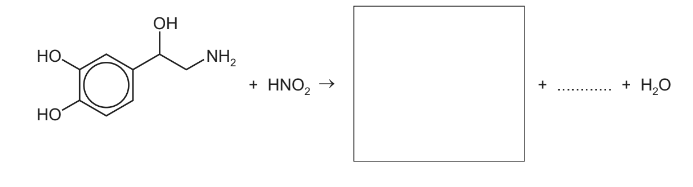
(ii) When one noradrenaline molecule reacts with one HNO2 molecule, the products are
one water molecule, one molecule of an unreactive gas, and one molecule of an organic compound made up of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen only.
Complete the chemical equation for this reaction.
Answer/Explanation
Answer: (a) C8H11O3N
(b) Yes, as it has a chiral C atom
(c) (phenyldiazonium ion is stabilised because) positive charge is delocalised by ring / positive charge is spread over ring
(c)(ii) 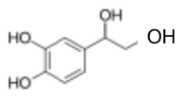
N2