Question
Nitrobenzene, $\mathrm{C}_6 \mathrm{H}_5 \mathrm{NO}_2$, can be reduced to phenylamine, $\mathrm{C}_6 \mathrm{H}_5 \mathrm{NH}_2$, in acid solution in a two step process.
(a) (i) Balance the half-equation for this reaction to work out how many moles of electrons are needed to reduce one mole of nitrobenzene.
$\mathrm{C}_6 \mathrm{H}_5 \mathrm{NO}_2+\ldots \ldots \ldots \mathrm{e}^{-}+\ldots \ldots \ldots . . \mathrm{H}^{+} \rightarrow \mathrm{C}_6 \mathrm{H}_5 \mathrm{NH}_2+\ldots \ldots \ldots \ldots \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}$
(ii) The reducing agent normally used is granulated tin and concentrated hydrochloric acid. In the first step, the reduction of nitrobenzene to phenylammonium chloride can be represented by the equation shown.
Use oxidation numbers or electrons transferred to balance this equation. You might find your answer to (i) useful.
$
. \mathrm{C}_6 \mathrm{H}_5 \mathrm{NO}_2+\ldots . . \mathrm{HCl}+\ldots \ldots . \mathrm{Sn} \rightarrow \ldots \ldots \mathrm{C}_6 \mathrm{H}_5 \mathrm{NH}_3 \mathrm{Cl}+\ldots \ldots . \mathrm{SnCl}_4+\ldots \ldots . \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}
$
(b) When $5.0 \mathrm{~g}$ of nitrobenzene was reduced in this reaction, $4.2 \mathrm{~g}$ of phenylammonium chloride, $\mathrm{C}_6 \mathrm{H}_5 \mathrm{NH}_3 \mathrm{Cl}$, was produced.
Calculate the percentage yield.
percentage yield of phenylammonium chloride = ……………………….. % [2]
(c) Following the reaction in (b), an excess of $\mathrm{NaOH}(\mathrm{aq})$ was added to liberate phenylamine from phenylammonium chloride.
(i) Calculate the mass of phenylamine, $\mathrm{C}_6 \mathrm{H}_5 \mathrm{NH}_2$, produced when $4.20 \mathrm{~g}$ of phenylammonium chloride reacts with an excess of $\mathrm{NaOH}(\mathrm{aq})$.
mass of phenylamine = ……………………….. g [1]
The final volume of the alkaline solution of phenylamine in (i) was $25.0 \mathrm{~cm}^3$. The phenylamine was extracted by addition of $50 \mathrm{~cm}^3$ of dichloromethane. After the extraction, the dichloromethane layer contained $2.68 \mathrm{~g}$ of phenylamine.
(ii) Use the data to calculate the partition coefficient, $K_{\text {partition }}$, of phenylamine between dichloromethane and water.
$
K_{\text {partition }}=
$
d) How does the basicity of phenylamine compare to that of ethylamine? Explain your answer.
(e) Phenol can be synthesised from phenylamine in two steps
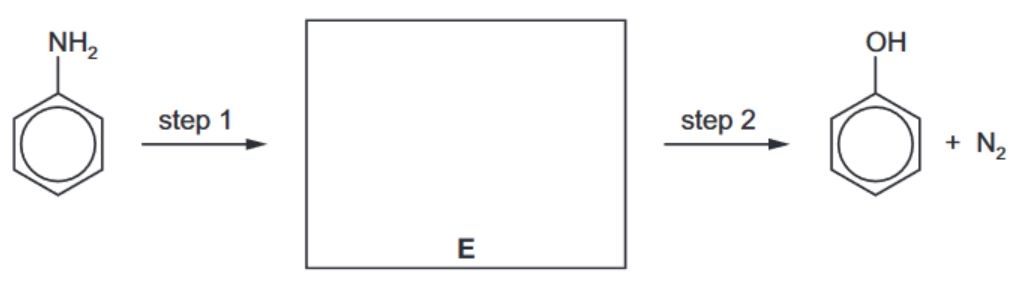
i) State the reagents and conditions for steps 1 and 2.
step 1 ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
step 2 …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. [2]
(ii) Draw the structure of the intermediate compound E in the box above. [1] [Total: 13]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a) (i) $\mathrm{C}_6 \mathrm{H}_5 \mathrm{NO}_2+6 \mathrm{e}^{-}+6 \mathrm{H}^{+} \longrightarrow \mathrm{C}_6 \mathrm{H}_5 \mathrm{NH}_2+2 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}$
(b) $\quad\left(\mathrm{M}_{\mathrm{r}}\right.$ values: $\left.\mathrm{C}_6 \mathrm{H}_5 \mathrm{NO}_2=123 \mathrm{C}_6 \mathrm{H}_5 \mathrm{NH}_3 \mathrm{Cl}=129.5\right)$ theoretical yield $=5.0 \times 129.5 / 123=5.26 \mathrm{~g}$ percentage yield $=100 \times 4.2 / 5.26=79.8 \%(80 \%)$
(c) (i) $\mathrm{C}_6 \mathrm{H}_5 \mathrm{NH}_2=93$
yield of phenylamine $=4.2 \times 93 / 129.5=3.016 \mathrm{~g}$
(ii) mass left in water $=3.016-2.68=0.336 \mathrm{~g}$ $K_{\text {part }}=(2.68 / 50) /(0.336 / 25)=3.99$
(d) phenylamine is less basic that ethylamine the lone pair on $\mathrm{N}$ is delocalised over the ring…
…making it less available for reaction with a proton $/ \delta+\mathrm{H}$
(e) (i) step 1: $\mathrm{HNO}_2 \mathrm{OR}\left(\mathrm{NaNO}_2+\mathrm{HCl}\right)$ at $T \leqslant 10^{\circ} \mathrm{C}$ step 2: boil/heat in water
(ii)
Question
Phenylamine, C6H5NH2, and ethylamine, C2H5NH2, can be distinguished by adding aqueous bromine.
(a) State what is seen when aqueous bromine is added to phenylamine.
(b) Suggest what is seen when aqueous bromine is added to ethylamine.
(c) Draw the structure of the organic product formed when an excess of aqueous bromine is added to phenylamine.
(d) Name the product you have drawn in (c).
Answer/Explanation
Answer (a) bromine decolourised OR orange / brown to colourless
white precipitate
(b) no change
(c)
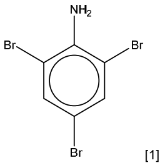
(d) 2,4,6-tribromophenylamine ECF 8(c) for a bromophenylamine