Question
(a) (i) Use the Data Booklet to draw the structure of the tripeptide Ala-Ser-Gly showing its peptide bonds in full. Ala-Ser-Gly [2]
(ii) Calculate the relative molecular mass, $M_{\Gamma}$, of Ala-Ser-Gly.
$M_{\mathrm{r}}=$[1]
(b) Electrophoresis can be used to separate mixtures of amino acids and peptides.
A mixture of the tripeptide Ala-Ser-Gly and its three constituent amino acids was subjected to electrophoresis in a buffer at pH 11.
(i) Draw the structure of serine at pH 11. [1]
At the end of the experiment the following results were seen
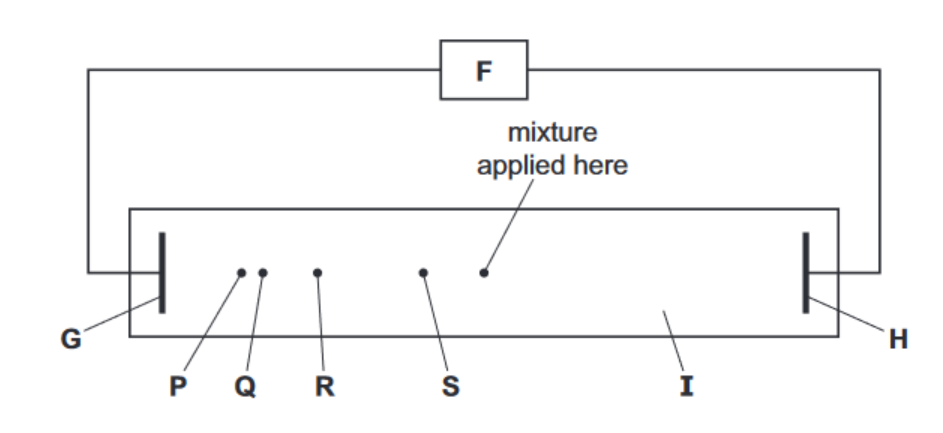
(ii) Identify the components labelled F–I in the above diagram.
F ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
G ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
H ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
I …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
[4]
(iii) Suggest the identities of the species responsible for
spot P, ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
spot S. ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Explain your answers.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… [3]
(c) (i) State the reagents and conditions needed for converting the tripeptide into its three constituent amino acids
ii) Name the type of reaction in (i).
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… [1] [Total: 13]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a) (i)
(ii) $M_{\mathrm{r}}=233$
(b) (i) $\mathrm{NH}_2 \mathrm{CH}\left(\mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{OH}\right) \mathrm{CO}_2^{-}$
(ii) F is a DC power supply
$\mathbf{G}$ is the anode OR positive electrode
$I$ is the cathode OR negative electrode
$\mathbf{H}$ is filter paper (OR gel) soaked in buffer solution
(iii) $\mathbf{P}$ is $\mathrm{NH}_2 \mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{CO}_2^{-}$or $\mathrm{NH}_2 \mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{CO}_2 \mathrm{H}$ or glycine $\mathbf{S}$ is [ala-ser-gly] ${ }^{(-)}$ glycine is the smallest, so travels fastest; tripeptide is the largest, so travels slowest
(c) (i) heat with $\mathrm{H}_3 \mathrm{O}^{+} \mathrm{OR}$ heat with $\mathrm{OH}^{-}$(aq)
(ii) hydrolysis
Question
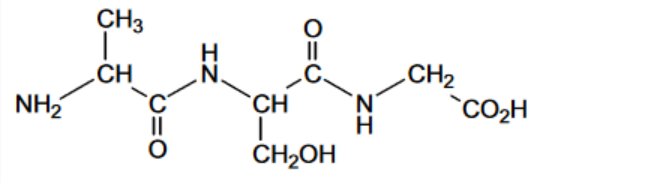
Valine (Val) and lysine (Lys) are amino acids. The structures of these amino acids can be found in the Data Booklet.
The isoelectric point of an amino acid is the pH at which it exists as a zwitterion. The isoelectric
point of valine is 6.0. The isoelectric point of lysine is 9.7.
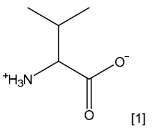
(a) Draw the structure of valine at pH 6.0.
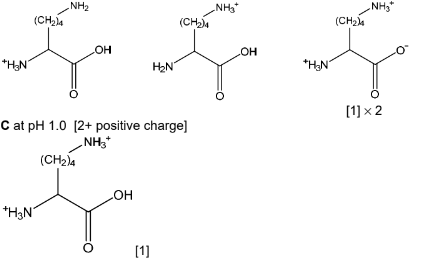
(b) A solution of lysine is produced with pH 9.7. Dilute sulfuric acid is added slowly until the pH of
the solution is 1.0. The sulfuric acid reacts with lysine to produce different organic ions that are
not present in significant concentrations at pH 9.7.
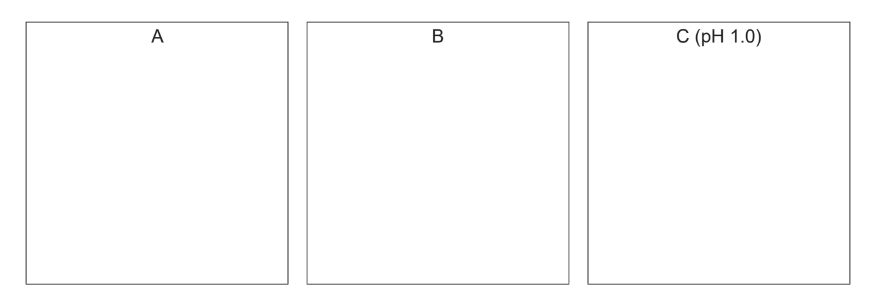
Draw the structures of three of the organic ions that form during the addition of sulfuric acid in
the boxes. Draw the organic ion present at pH 1.0 in box C.
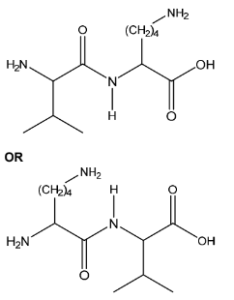
(c) Draw the structure of the dipeptide Val-Lys. The peptide bond should be shown fully displayed.
Answer/Explanation
Answer (a)
(b) A and B any two from: [all net single positive charge]
(c) M1: peptide link correct and displayed unit including C=O M2: everything else correct