Question
(a) Compare the relative acidities of benzoic acid \((C_6H_5COOH)\), phenylmethanol \((C_6H_5CH_2OH)\), and phenol \((C_6H_5OH)\).
Explain your reasoning.
……………………………………. > ……………………………………. > …………………………………….
most acidic least acidic
(b) A series of nine separate experiments is carried out as shown in Table 5.1.
Complete the table by placing a tick (✓) in the relevant box if a reaction occurs. Place a cross (✗) in the box if no reaction occurs.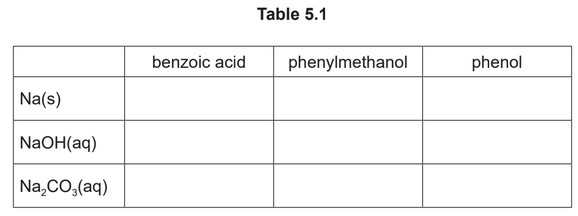
(c) (i) Benzoyl chloride, \(C_6H_5COCl\), can be synthesised by the reaction of benzoic acid with either \(PCl_5\) or \(SOCl_2\).
Complete the equations for these reactions.
reaction 1 \(C_6H_5COOH + PCl_5 → C_6H_5COCl\) + …………………… + ……………………
reaction 2 \(C_6H_5COOH + SOCl_2 → C_6H_5COCl\) + …………………… + ……………………
(ii) Use your answer to (c)(i) to suggest why it is easier to isolate, in a pure form, the \(C_6H_5COCl\) from reaction 2 compared to reaction 1.
(d) Benzoyl chloride is hydrolysed by water at room temperature to form benzoic acid.
(i) Complete the diagram to show the mechanism for the reaction between \(C_6H_5COCl\) and \(H_2O\).
Include charges, dipoles, lone pairs of electrons and curly arrows as appropriate.
(ii) Name the type of mechanism you showed in (d)(i).
(e) Acyl chlorides react with sodium carboxylates to form acid anhydrides as shown in Fig. 5.1.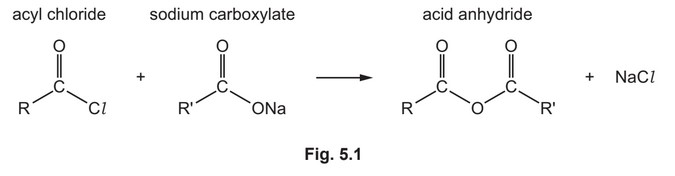
The condensation polymers, polyanhydride and polyester, are formed by similar methods.
The repeat unit for a polyanhydride is shown in Fig. 5.2.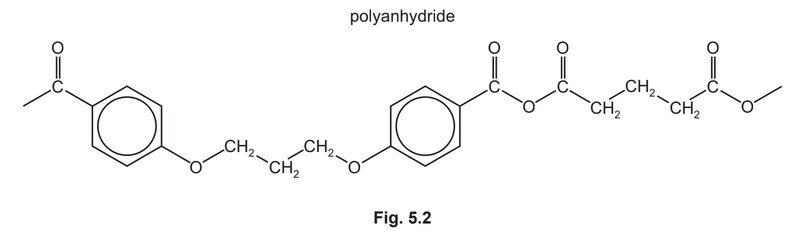
(i) Use Fig. 5.1 and Fig. 5.2 to suggest the structures of the two monomers used to make this polyanhydride.
(ii) Polyanhydrides are biodegradable polymers.
Suggest how this polyanhydride can be degraded.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
(a) M1 benzoic acid > phenol > phenylmethanol
M2 / M3 Any two of:
in benzoic acid negative inductive effect of C=O AND O-H bond is weakened
OR due to delocalisation of minus charge by C=O / 2O carboxylate ion is stabilised
in phenol lone pair on oxygen is delocalised into the ring AND O-H bond is weakened
in phenyl methanol positive inductive effect of \(CH_2\) group AND O-H bond is strengthened
(b) 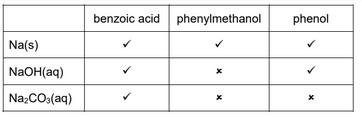
Three correct for one mark, six correct for two marks, nine correct for three marks
(c) (i) \(POCl_3\) and HCl AND \(SO_2\) and HCl
(ii) all the by-products / SO2 and HCl are gaseous OR no liquid by-products formed
(d) (i) 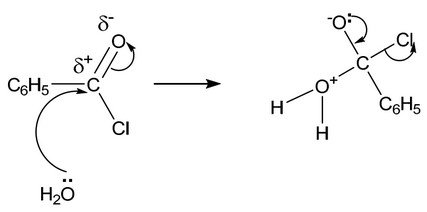
On the left-hand side:
lone pair on O
correct arrow from O to C (of C=O)
dipole on C=O
correct arrow on C=O
M1 / M2 Two correct for one mark, four correct for two marks
On the right-hand side:
M3 correct intermediate
M4 arrow from lone pair on O– to C-O bond AND arrow from C-Cl to Cl
(ii) addition-elimination
(e) (i) 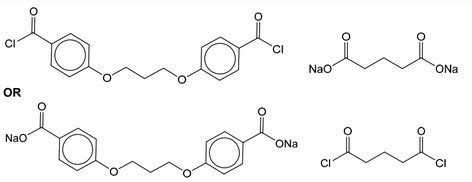
(ii) hydrolysis OR heating in dilute acid / alkali
Question
Fumaric acid is a naturally occurring dicarboxylic acid.
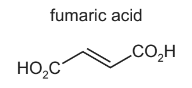
(a) Identify the products of the reaction between fumaric acid and an excess of hot, concentrated, acidified manganate(VII).
(b) Fumaric acid can form addition and condensation polymers.
(i) Draw the repeat unit of the addition polymer poly(fumaric acid).
(ii) Draw the repeat unit of the polyester formed when fumaric acid reacts with ethane-1,2-diol,
(CH2OH)2.
The ester bond should be shown fully displayed.
(iii) Explain why polyesters normally biodegrade more readily than polyalkenes.
(c) Fumaric acid reacts with cold, dilute, acidified manganate(VII) to form compound P.
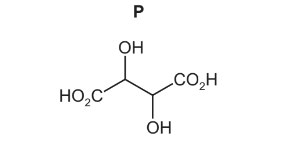
Only three stereoisomers of P exist. One of the stereoisomers is shown.
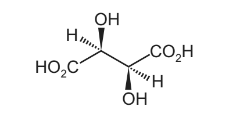
Complete the three-dimensional diagrams in the boxes to show the other two stereoisomers of P.
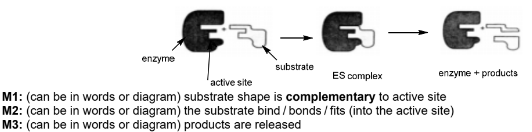
(d) The enzyme fumarase catalyses the reaction of fumarate ions, C4H2O42-, with water to form malate ions, C4H4O52-.
\(C_{4}H_{2}O_{4}^{2-} + H_{2}O \rightleftharpoons C_{4}H_{4}O_{5}^{2-}\)
Describe, with the aid of a suitably labelled diagram, how an enzyme such as fumarase can catalyse a reaction.
Answer/Explanation
Answer: (a) CO2 and H2O / in words
(b)(i) 
(b)(ii) 
(b)(iii) C—C bonds are non-polar / polyalkenes cannot be hydrolysed
OR polyesters / they can be broken down by hydrolysis
(c) 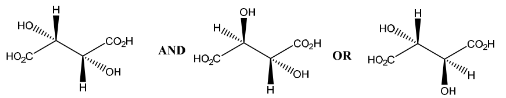
(d)