Question
The anti-inflammatory drug ketoprofen can be synthesised from benzene via the following five steps.
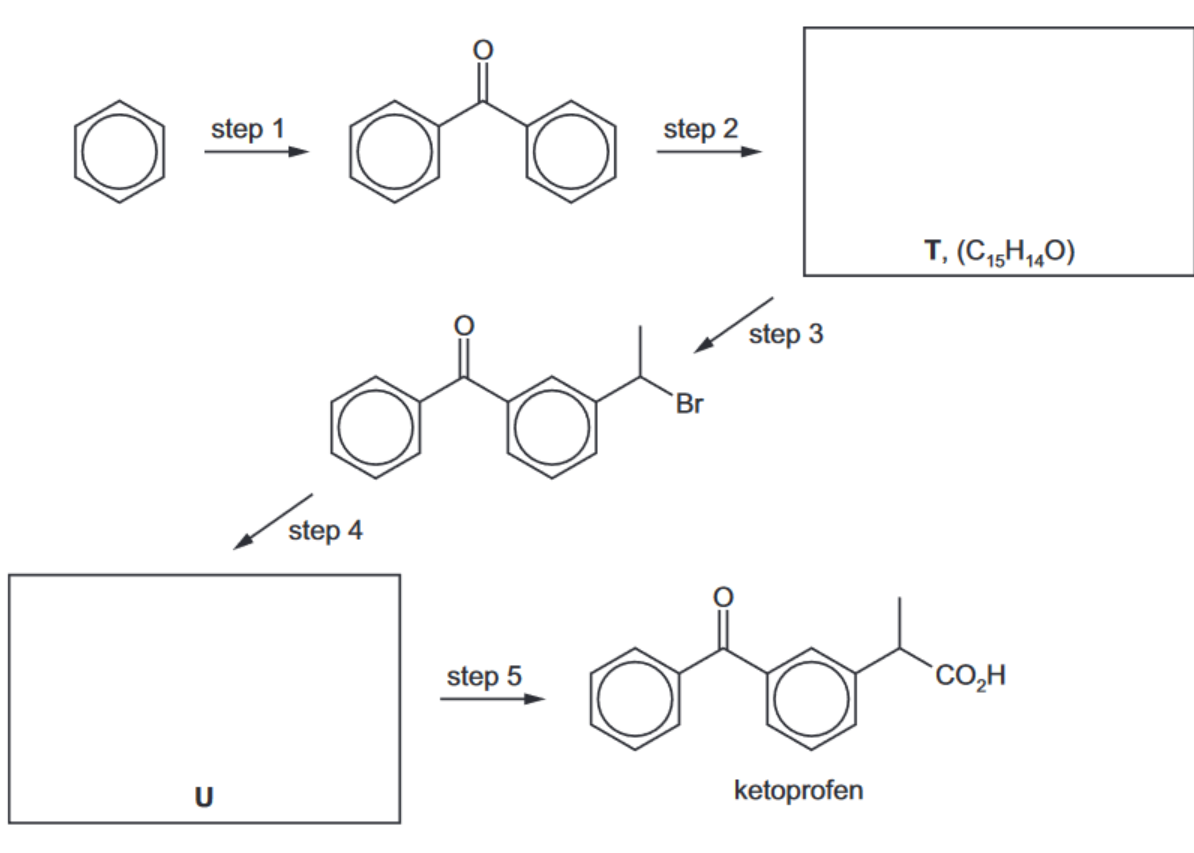
a) Suggest the structures of compounds T and U and draw them in the boxes above.
[2]
(b) Suggest reagents and conditions for steps 1-5.
step 1 ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
step 2 ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
step 3 ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
step 4 ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
step 5 ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. [5]
(c) What types of reaction are steps 1 and 5?
step 1 ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
step 5 ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. [2] [Total: 9]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a)

(b) $\quad$ step 1: $\mathrm{C}_6 \mathrm{H}_5 \mathrm{COCl}+\mathrm{AlCl}_3$ (+ heat)
step 2: $\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{Cl}+\mathrm{AlCl}_3$ (+ heat)
step 3: $\mathrm{Br}_2$ + light (or heat)
step 4: $\mathrm{KCN}$ + heat (in ethanol)
step 5: $\mathrm{H}_3 \mathrm{O}^{+} \mathrm{OR} \mathrm{H}^{+}$in $\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}$ OR $\mathrm{HCl}(\mathrm{aq})$ etc AND heat/boil/ reflux
(c) step 1: electrophilic substitution OR nucleophilic substitution
step 5: hydrolysis OR nucleophilic substitution
Question
Procaine is used as an anaesthetic in medicine. It can be synthesised from methylbenzene in five steps as shown in Fig. 7.1.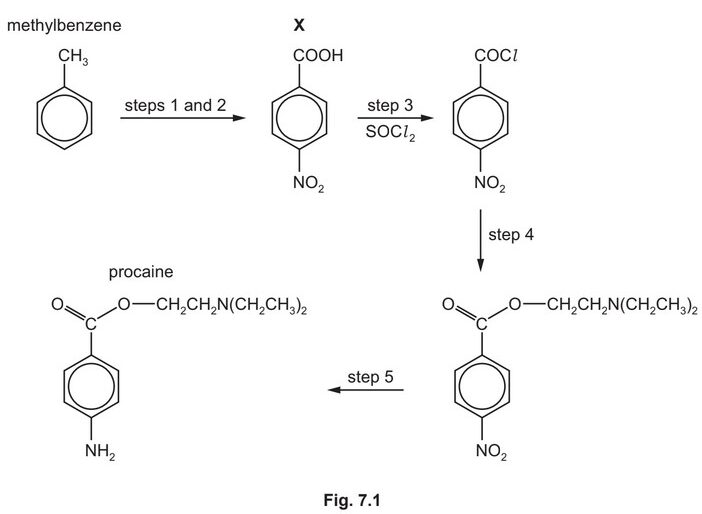
(a) (i) Name all the functional groups present in procaine.
(ii) A molecule of procaine has 13 carbon atoms.
State the number of carbon atoms that are sp, \(sp^2\) and \(sp^3\) hybridised in procaine.
sp carbons = ………………… \(sp^2\) carbons = ………………… \(sp^3\) carbons = …………………
(b) The proton (\(^1H\)) NMR spectrum of procaine dissolved in \(D_2O\) is recorded.
Predict the number of peaks observed.
(c) State why procaine can act as a base.
(d) Compound X can be synthesised in two steps from methylbenzene.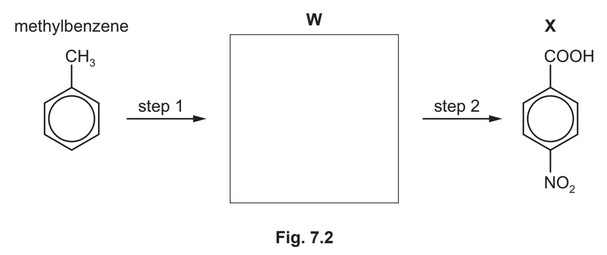
(i) Draw the structure of compound W in the box provided. [1]
(ii) State the reagents and conditions for step 1 and step 2.
step 1 ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
step 2 ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(e) Procaine is synthesised in three steps from X.
Suggest the reagents and conditions for step 4 and for step 5 in Fig. 7.1.
step 4 ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
step 5 ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
(f) (i) Explain what is meant by partition coefficient, \(K_{pc}\).
(ii) The partition coefficient of procaine between octan-1-ol and water is 1.77.
Octan-1-ol and water are immiscible. A solution containing 0.500g of procaine in 75.0cm3 of water is shaken with 50.0\(cm^3\) of octan-1-ol.
Calculate the mass of procaine that is extracted into the octan-1-ol.
mass of procaine extracted = ………………………… g
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
(a) (i) phenylamine AND amine AND ester
(ii) sp carbons = 0, \(sp^2\) carbons = 7, \(sp^3\) carbons = 6
(b) 6
(c) lone pair on the N can accept a proton
(d) (i) 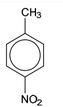
(ii) step 1 M1 concentrated \(HNO_3\) and \(H_2SO_4\)
step 2 M2 hot (alkaline) KMnO4 (followed by addition of \(H^+\))
(e) step 4 M1 \(HOCH_2CH_2N(CH_2CH_3)_2\)
step 5 \(M_2\) Sn AND HCl
M3 concentrated (HCl) AND heat / reflux
(f) (i) M1 ratio of the concentration of a solute in two solvents
M2 at equilibrium
(ii) M1 \(K_{pc} = [procaine]_{oct} / [procaine]_{water}\)
1.77 = (x / 50)/(0.5 – x / 75)
M2 1.77 = 1.5x / 0.5 – x
0.885 –1.77x = 1.5x
x = 0.271 g min 2sf