Question:
In which reaction is water behaving as a Brønsted–Lowry base?
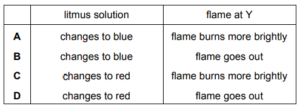
A \(H_{2}O~+~Na\rightarrow NaOH~+~\frac{1}{2}H_{2}\)
B \(H_{2}O~+~H_{3}PO_{4}\rightarrow H_{3}O^{+}~+~H_{2}PO_{4}~^{-}\)
C \(H_{2}O~+~CaO\rightarrow Ca(OH)_{2}\)
D \(NH_{3}~+~[Cu(H_{2}O)_{6}]^{2+}\rightarrow NH_{4}^{~+}~+~[Cu(H_{2}O)_{5}(OH)]^{+}\)
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:B
Question
Three test-tubes, $\mathrm{X}, \mathrm{Y}$ and $\mathrm{Z}$, each contain water.
- A small amount of $\mathrm{NaC} l$ is added to test-tube $\mathrm{X}$.
- A small amount of $\mathrm{SiCl}_4$ is added to test-tube $\mathrm{Y}$.
- $\mathrm{A}$ small amount of $\mathrm{AlC} \mathrm{Cl}_3$ is added to test-tube $Z$.
After a short time, two drops of universal indicator solution are added to each test-tube.
Which statements can be correct?
1 The $\mathrm{pH}$ in test-tube $\mathrm{X}$ is 7 .
2 The $\mathrm{pH}$ in test-tube $Y$ is 2 .
3 The $\mathrm{pH}$ in test-tube $\mathrm{Z}$ is 2 .
The responses A to D should be selected on the basis of
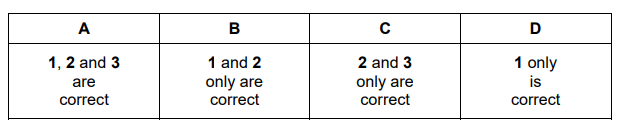
No other combination of statements is used as a correct response.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:A
Question:
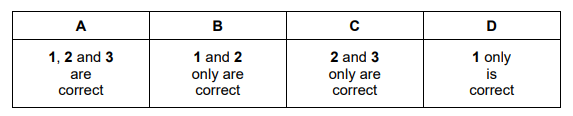
A sample containing x mol of \(A \imath C \imath_{6}\) is dissolved in water to give solution W. In order to precipitate all of the aluminium as its hydroxide, y mol of sodium hydroxide are required. More of the alkali is added to re-dissolve the precipitate, giving solution Z. Which statements are correct?
1 the initial pH of solution W is below 7
2 y = 3x
3 Z contains x mol of aluminium
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:D
Question
With which compound does concentrated sulfuric acid react both as a strong acid and as an oxidising agent?
A magnesium carbonate
B potassium chloride
C sodium bromide
D sulfur trioxide
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:C
Question:
How does concentrated sulfuric acid behave when it reacts with sodium chloride?
A as an acid only
B as an acid and oxidising agent
C as an oxidising agent only
D as a reducing agent only
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:A
Question:
A student investigates calcium nitrate crystals by heating them in the apparatus shown. A colourless gas leaves the apparatus at Y. A flame is held to this gas.
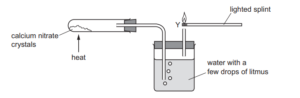
Which observations would the student make?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:D
Question:
Solid ammonium nitrate is put into a test-tube and solution X is added to it. The resulting mixture
is warmed and the gas given off is tested with damp red litmus paper. The litmus paper changes
colour from red to blue. What could be the identity of X and its role in the reaction?
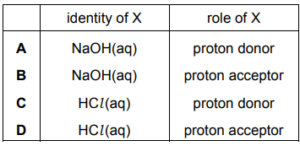
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:B
Question:
Compound Z is insoluble in water but soluble at low pH. What could be compound Z?
A barium carbonate
B barium chloride
C barium hydroxide
D barium sulfate
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:A
Question
Diethylzinc, \((C_2H_5)_2Zn\), is added to NaOH(aq). Two reactions occur.
reaction 1 \((C_2H_5)_2Zn + H_2O \rightarrow ZnO + 2C_2H_6\)
reaction 2 \(H_2O + ZnO + 2OH^– \rightarrow Zn(OH)_4^{2–}\)
In these reactions, which compounds act as Brønsted–Lowry acids?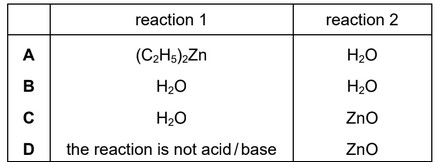
Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question
Which reaction mixture produces an acidic gas?
A aqueous ammonium nitrate and solid calcium oxide
B calcium and aqueous hydrochloric acid
C potassium chloride and concentrated sulfuric acid
D sodium oxide and water
Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Question
A 5 cm³ sample of 0.05moldm-3 sodium chloride is mixed with a 5 cm3 sample of 0.05moldm-3 potassium iodide. 10 cm3 of acidified 0.05moldm–3 silver nitrate is then added, followed by concentrated ammonia solution.
What is seen after the addition of an excess of concentrated ammonia solution?
A a cream precipitate
B a white precipitate
C a yellow precipitate
D no precipitate
Answer/Explanation
Answer: C
Question
Which type of reaction occurs when solid ammonium sulfate is heated with an excess of sodium hydroxide solution?
A acid-base
B precipitation
C redox
D thermal decomposition
Answer/Explanation
Answer A
Question
In which reaction does ammonia behave as a Brønsted-Lowry base?
A NH3 + CH3CH2Br → CH3CH2NH2 + HBr
B NH3 + H2O + CO2→ (NH4)HCO3
C 2NH3 + 2Na → 2NaNH2 + H2
D 4NH3 + 3O2 → 2N2 + 6H2O
Answer/Explanation
Answer B
Question
In which reactions does NH3 behave as a Brønsted-Lowry acid?
1 2NH3 → NH2–+ NH4+
2 HSO4–+ NH3 → SO42– + NH4+
3 Ag++ 2NH3 → [Ag(NH3)2]
The responses A to D should be selected on the basis of
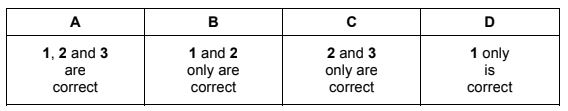
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
D
Question
The following reaction takes place in a suitable solvent.
\(Na^+NH_2^– + NH^{4+}Cl^– → Na^+Cl^– + 2NH_3\)
Which statements explain why this reaction should be classified as a Brønsted-Lowry acid-base reaction?
1 The ammonium ion acts as a proton donor.
2 \(Na^+Cl^–\) is a salt.
3 Ammonia is a nucleophile.
The responses A to D should be selected on the basis of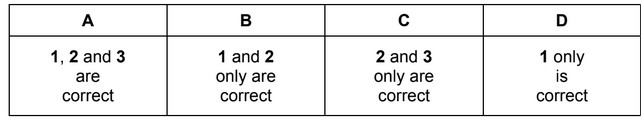
Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Question
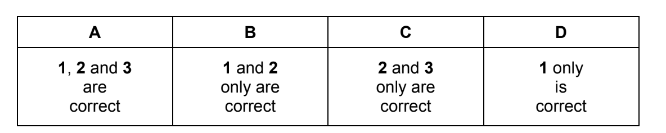
Answer/Explanation
Answer: C
Question
A little water is added to each of the following compounds and the mixture warmed.
For which compounds will an acidic gas be evolved?
1 aluminium chloride
2 silicon tetrachloride
3 phosphorous pentachloride
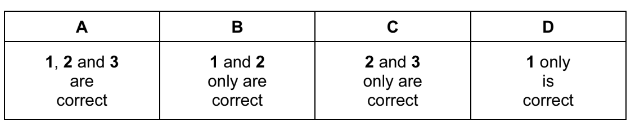
Answer/Explanation
Answer: A
Question
Which statement about the ammonia molecule and/or the ammonium ion is correct?
A Ammonia molecules are basic because they can donate H+ ions. B Ammonium ions are basic because they can accept H+ ions. C If ammonium ions are heated with NaOH(aq), ammonia molecules are formed. D The bond angle in NH4+ is 2.5° less than the bond angle in NH3.
Answer/Explanation
Answer: C
Question
In which reaction is the underlined substance acting as a base?
A \( HNO_{3} + H_{2}SO_{4} → H_{2}NO_{3} ^{+} + HSO4^{–}\)
B \(HSiO_{3}^{–}+ HCN → CN^{–} + H_{2}O + SiO_{2}\)
C \(HNO_{2} + HCO_{3}^{–} → H_{2}O + CO_{2} + NO_{2}^{–}\)
D \(C_{6}H_{5}O^{–} + CH_{2}ClCO_{2}H → C_{6}H_{5}OH + CH2ClCO_{2}\)
Answer/Explanation
Ans:C
Question
Use of the Data Booklet is relevant to this question. A sample of potassium oxide, K$_2$O, is dissolved in\ (250cm^{3}\) of distilled water. \(25.0cm^{3}\)0
of this solution is titrated against sulfuric acid of concentration\ (2.00moldm^{3-}\). 15.0 cm^{3}\) of this sulfuric acid is needed for complete neutralisation. Which mass of potassium oxide was originally dissolved in \(250cm^{3}\) of distilled water?
A 2.83g B 28.3g C 47.1g D 56.6g
Answer/Explanation
Ans:B
Question
The Brønsted-Lowry theory describes acid and base character.
When concentrated sulfuric acid and concentrated nitric acid are mixed, the following reactions occur.
\(H_{2}SO_{4}+HNO_{3}\rightleftharpoons HSO_{4}^-+H_{2}NO_{3}^+\)
\(HNO_{3}\rightleftharpoons H_{2}O+NO_{2}^+\)
\(H_{2}O+H_{2}SO_{4}\rightleftharpoons HSO_{4}^-+H_{3}O^+\)
Which species are bases in these reactions?
1 \( HSO_{4}^–\)
2 \( HNO_{3}\)
3 \( NO_{2}\)
The responses A to D should be selected on the basis of

Answer/Explanation
Ans:B