Question:
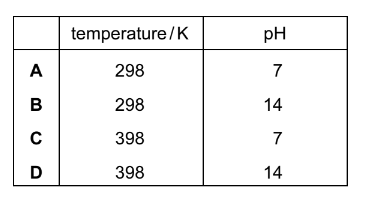
A large excess of marble chips is reacted with \(25cm^{3}~of~1.0moldm^{-3}\) 3 hydrochloric acid at \(40^{\circ}C\). How is the result different when the reaction is repeated with \(60cm^{-3}~of~0.5~moldm^{-3}~hydrochloric~acid~at~40 ^{\circ}C\)
A The reaction is faster and more of the products are made when the reaction is complete.
B The reaction is faster and less of the products are made when the reaction is complete.
C The reaction is slower and more of the products are made when the reaction is complete.
D The reaction is slower and less of the products are made when the reaction is complete.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:C
Question
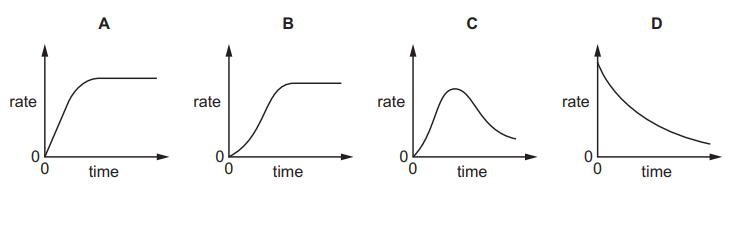
An autocatalytic reaction is a reaction in which one of the products catalyses the reaction.
Which curve would be obtained if the rate of an autocatalytic reaction is plotted against time?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:C
Question
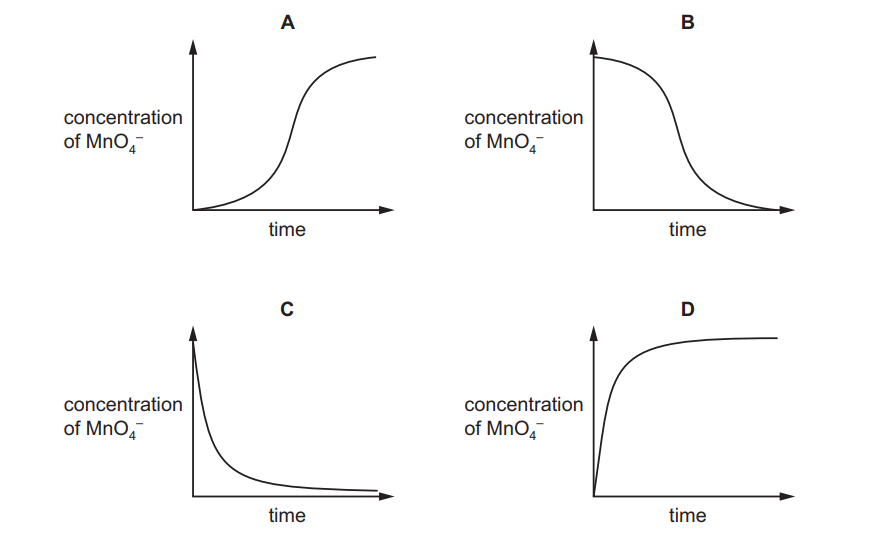
Oxidation of ethanedioate ions by acidified manganate(VII) ions is very slow at room temperature.
$
2 \mathrm{MnO}_4^{-}+5 \mathrm{C}_2 \mathrm{O}_4{ }^{2-}+16 \mathrm{H}^{+} \rightarrow 2 \mathrm{Mn}^{2+}+10 \mathrm{CO}_2+8 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}
$
$\mathrm{Mn}^{2+}$ ions catalyse this reaction.
Which graph shows how the concentration of acidified manganate(VII) ions varies after ethanedioate ions are added?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:B
Question
A chemist puts a sample of dilute aqueous hydrochloric acid into beaker 1. She adds a sample of zinc and measures the rate of production of hydrogen gas.
She then puts a different sample of dilute aqueous hydrochloric acid into beaker 2. She adds a different sample of zinc and measures the rate of production of hydrogen gas.
The rate of the reaction in beaker 2 is greater than the rate of the reaction in beaker 1.
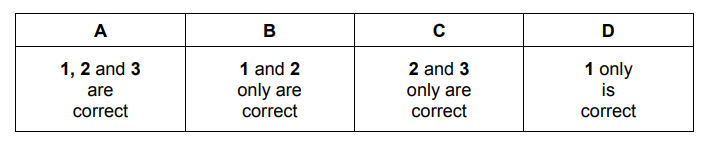
Which factors could help to explain this observation?
1 The reaction in beaker 1 has a higher activation energy than the reaction in beaker 2.
2 The zinc in beaker 1 is in larger pieces than the zinc in beaker 2.
3 The acid in beaker 1 is at a lower concentration than the acid in beaker 2.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:C
Question
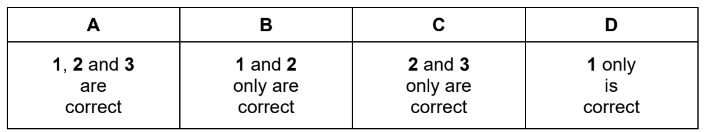
Which changes can be used to measure the rates of chemical reactions?
1 the decrease in concentration of a reactant per unit time
2 the rate of appearance of a product
3 the increase in total volume of gas per unit time at constant pressure
▶️Answer/Explanation
Answer A
Question
Two compounds X and Y react to produce compound Z. The reaction is reversible.
\(X + Y \rightleftharpoons Z\)
When X and Y are mixed together in a closed system a dynamic equilibrium is gradually
established.
Which graph could represent the change in the rates of the forward and reverse reactions over
time?
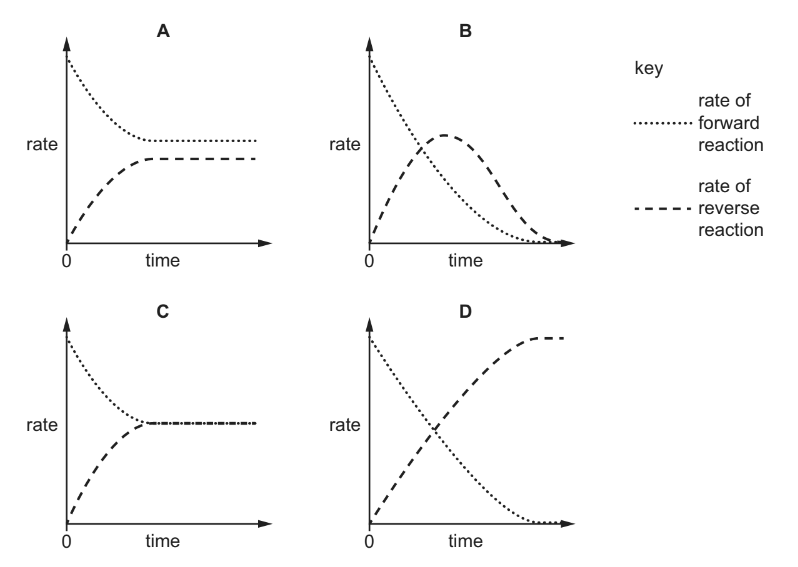
▶️Answer/Explanation
Answer C
Question
The factors affecting the rate of reaction between aqueous sodium thiosulfate and hydrochloric acid can be investigated. The ionic equation for the reaction is shown.
\(S_{2}O_{3}^{2-}(aq) + 2H^{+} \rightarrow H_{2}O(l) + S(s) + SO_{2}(aq)\)
Which of the following can be used to investigate the rate of this reaction?
1 change of mass
2 change of appearance caused by formation of a precipitate
3 change of electrical conductivity
Answer/Explanation
Answer C
Question
When 4 g of powdered calcium carbonate, \(M_r\) = 100, were added to 100 \(cm^3\) of 0.10 mol \(dm^{–3}\) hydrochloric acid the volume of carbon dioxide produced was recorded.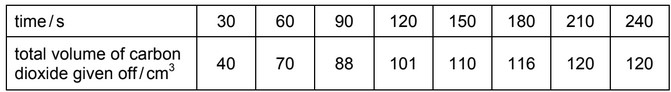
Which row gives the correct explanations about these results?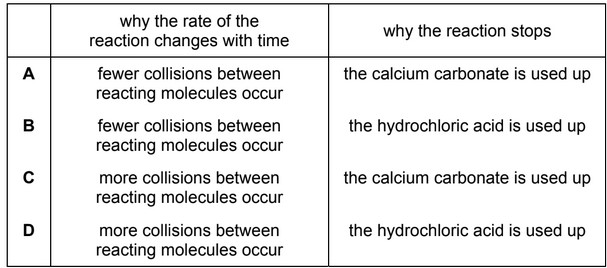
Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question
Ammonia is made by the Haber process. The reactants are nitrogen and hydrogen.
\(N_{2}(g) + 3H_{2}(g) \rightleftharpoons 2NH_{3}\)(g) ∆H –ve
What will increase the rate of the forward reaction?
A adding argon to the mixture but keeping the total volume constant
B decreasing the temperature
C increasing the total pressure by reducing the total volume at constant temperature
D removing ammonia as it is made but keeping the total volume of the mixture the same.
Answer/Explanation
Ans:C
Question
The equilibrium constant, Kc, for the reaction H_{2}(g) + I_{2}(g) \(\rightleftharpoons \)2HI(g), is 60 at 450 °C.
What is the number of moles of hydrogen iodide in equilibrium with 2mol of hydrogen and 0.3mol of iodine at 450°C?
A \( \frac{1}{100} \) B \( \frac{1}{10} \)
C 6 D 36
Answer/Explanation
Ans:C
Question
When making sparkler fireworks, a mixture of barium nitrate powder with aluminium powder, water and glue is coated onto wires and allowed to dry. At this stage, the following exothermic reaction may occur.
![]()
Which conditions would be best to reduce the rate of this reaction during the drying process, and would also keep the aluminium and barium nitrate unchanged?
Answer/Explanation
Ans:A
Question
Why does the rate of a gaseous reaction increase when the pressure is increased at a constant temperature?
A More particles have energy that exceeds the activation energy.
B The particles have more space in which to move.
C The particles move faster.
D There are more frequent collisions between particles.
Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Question
Nitrogen reacts with hydrogen to produce ammonia.
\(N_2(g) + 3H_2(g) \rightleftarrow 2NH_3(g)\)
A mixture of 2.00 mol of nitrogen, 6.00mol of hydrogen, and 2.40mol of ammonia is allowed to
reach equilibrium in a sealed vessel of volume 1 \(dm^3\) under certain conditions. It was found that 2.32 mol of nitrogen were present in the equilibrium mixture.
What is the value of Kc under these conditions?
A \(\frac{(1.76)^2}{(2.32)(6.96)^3}\)
B \(\frac{(1.76)^2}{(2.32)(6.32)^3}
C \(\frac{(2.08)^2}{(2.32)(6.32)^3}\)
D \(\frac{(2.40)^2}{(2.32)(6.00)^3}\)
Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Question
An autocatalytic reaction is a reaction in which one of the products catalyses the reaction.
Which curve was obtained if the rate of reaction was plotted against time for an autocatalytic
reaction?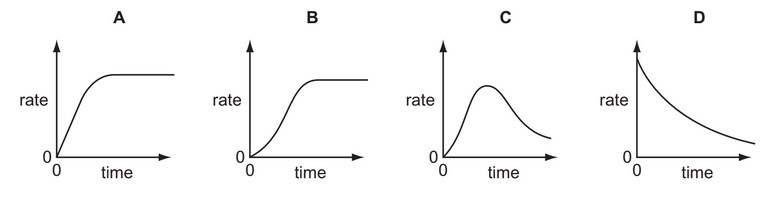
Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Question
Ammonia is manufactured by the Haber Process, in an exothermic reaction.
Assuming that the amount of catalyst remains constant, which change will not bring about an increase in the rate of the forward reaction?
- decreasing the size of the catalyst pieces
- increasing the pressure
- increasing the temperature
- removing the ammonia as it is formed
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
D