Question:
The Boltzmann distribution curve for a gaseous mixture of ethene and hydrogen is shown. Nickel is an effective catalyst for the reaction that occurs
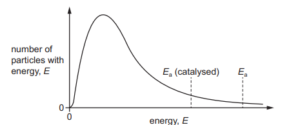
How does the diagram appear if the same reaction mixture is at a higher temperature?
A The curve is unchanged.
B The values of both \(E^{a}\) (catalysed) and \(E^{a}\) decrease.
C The values of both \(E^{a}\) (catalysed) and \(E^{a}\) increase.
D The values of both \(E^{a}\) (catalysed) and \(E^{a}\) remain the same.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:D
Question
Nitric oxide, NO, and bromine vapour react together according to the following equation.
$
2 \mathrm{NO}(\mathrm{g})+\mathrm{Br}_2(\mathrm{~g}) \rightarrow 2 \mathrm{NOBr}(\mathrm{g}) \quad \Delta H^{\ominus}=-23 \mathrm{~kJ} \mathrm{~mol}^{-1}
$
The reaction has an activation energy of $+5.4 \mathrm{~kJ} \mathrm{~mol}^{-1}$.
What is the correct reaction pathway diagram for this reaction?
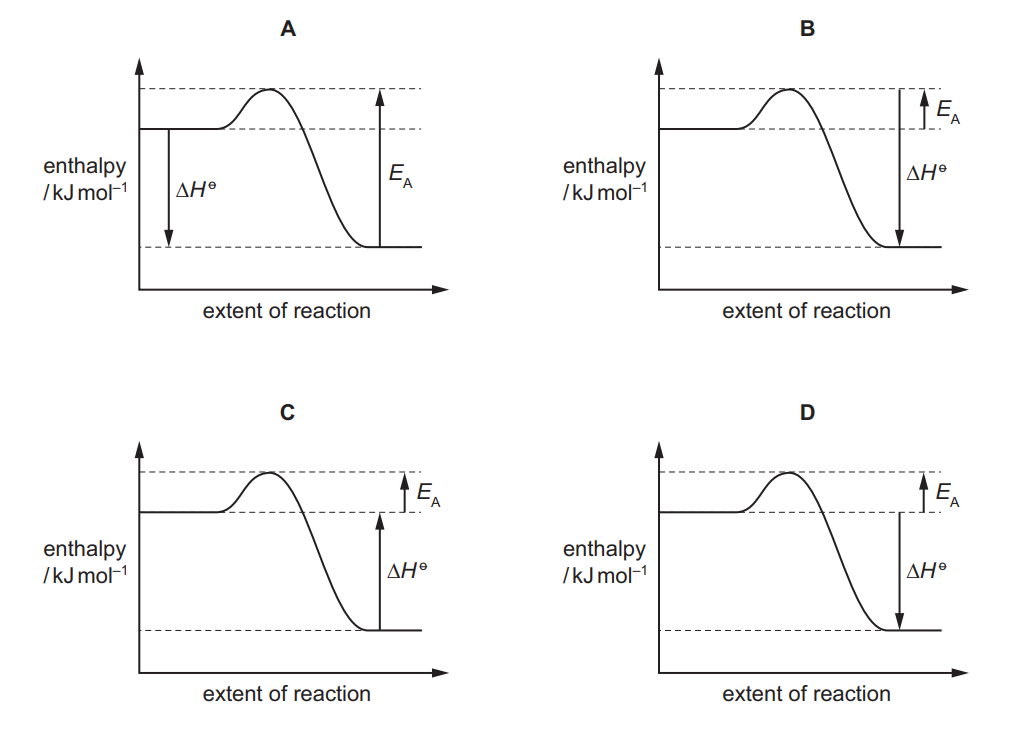
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:D
Question
\(SO_3\) is manufactured from \(SO_2\) and \(O_2\) in the Contact process.
The reaction is exothermic.
Which row shows the effect on the equilibrium yield obtained in the Contact process of increasing the temperature and of adding a vanadium(V) oxide catalyst?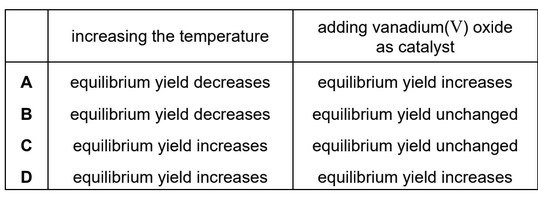
Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question
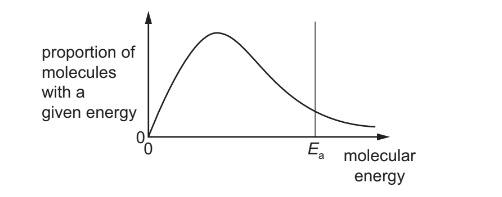
The diagram shows the Boltzmann distribution of energies for a reactant gas. For a particular reaction, the activation energy is X.
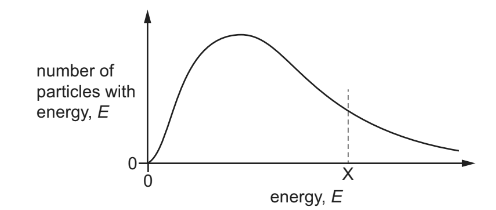
Which change to the diagram occurs if an effective catalyst is added at the same temperature?
A More particles will possess higher values of E.
B The peak will move to the left.
C The peak will move to the right.
D The value of the activation energy decreases.
Answer/Explanation
Answer D
Question
The diagram shows the Boltzmann distribution of energies in a gas. The gas undergoes a reaction with an activation energy, Ea. The peak of the distribution is labelled P.
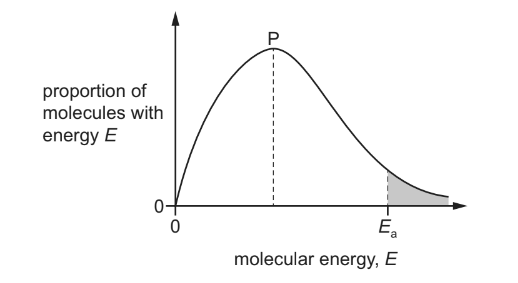
If the same reaction is carried out in the presence of a catalyst, which statement is correct?
A The peak P is at a lower height and the position of Ea moves to the left.
B The peak P is at a lower height and the position of Ea moves to the right.
C The peak P remains at the same height and the position of Ea moves to the left.
D The peak P remains at the same height and the position of Ea moves to the right.
Answer/Explanation
Answer C
Question
Which statement about the effect of a catalyst on a reversible reaction is correct?
A The activation energy of the forward reaction stays the same.
B The composition of the equilibrium mixture stays the same.
C The rate of the backward reaction stays the same.
D The value of the equilibrium constant changes.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
B
Question
The diagram shows the distribution of molecular energies in a sample of gas at a temperature \(T_1\).
The activation energy for an uncatalysed reaction of this gas, \(E_{a(uncat)}\), is shown.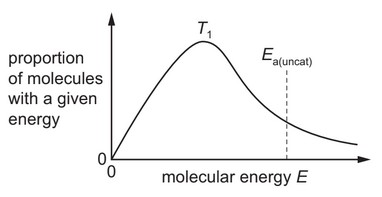
Which diagram correctly shows the new distribution and new activation energy, \(E_{a(cat)}\), when the
temperature is increased to \(T_2\), and a catalyst is used that increases the rate of the reaction?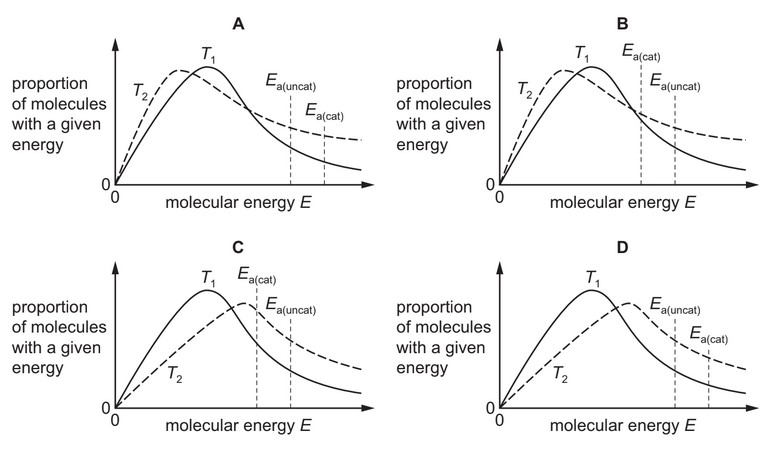
Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Question
The diagram represents, for a given temperature, the Boltzmann distribution of the kinetic energies of the molecules in a mixture of two gases that react together. The activation energy for the reaction, Ea , is marked.
The dotted curves below show the Boltzmann distribution for the same reaction at a higher temperature. On these diagrams, H represents the activation energy at the higher temperature.
Which diagram is correct?
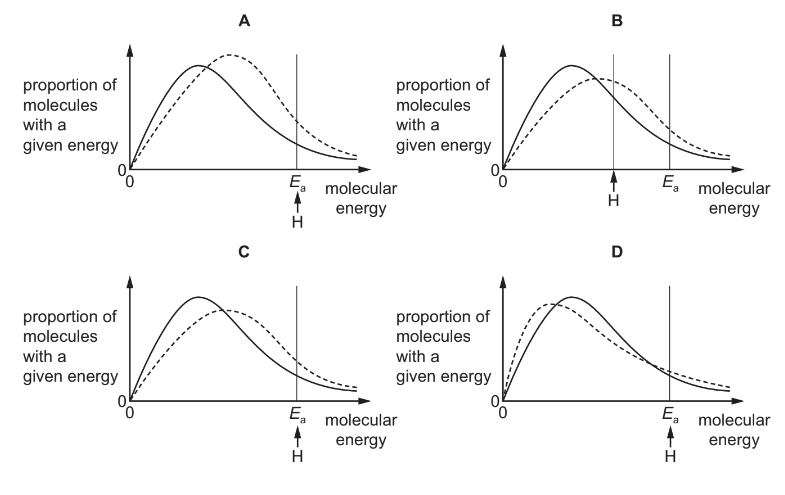
Answer/Explanation
Answer: C
Question
Why does raising the pressure of a fixed mass of gaseous reactants at a constant temperature cause an increase in the rate of reaction?
1 More collisions occur per second when the pressure is increased.
2 More molecules have energy greater than the activation energy at the higher pressure.
3 Raising the pressure lowers the activation energy.
The responses A to D should be selected on the basis of
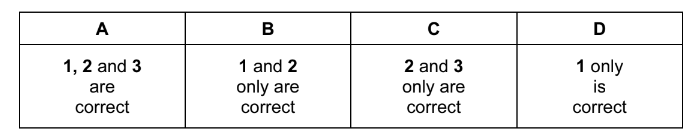
Answer/Explanation
Ans:D
Question
The diagram shows a reaction pathway for an endothermic reaction. Which arrow represents the activation energy for the forward reaction?
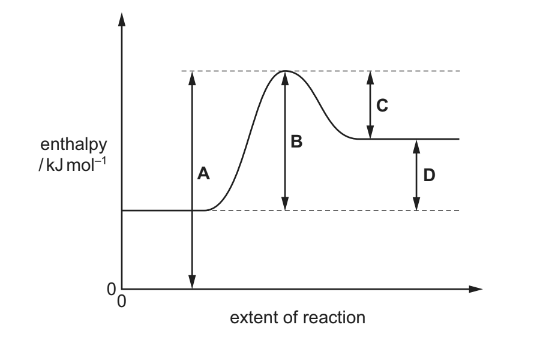
Answer/Explanation
Ans:B
Question
Which statements correctly describe an effect of a rise in temperature on a gas-phase reaction?
1 More particles now have energies greater than the activation energy.
2 The energy distribution profile changes with more particles having the most probable energy.
3 The activation energy of the reaction is decreased.
The responses A to D should be selected on the basis of
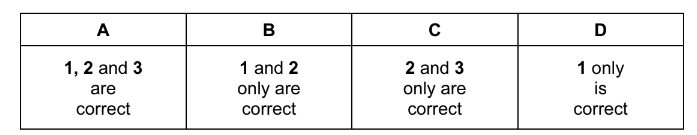
Answer/Explanation
Ans:D
Question
Ammonia is made by the Haber process. The reactants are nitrogen and hydrogen.
\(N_{2}(g) + 3H_{2}(g) \rightleftharpoons 2NH_{3}\)(g) ∆H –ve
What will increase the rate of the forward reaction?
A adding argon to the mixture but keeping the total volume constant
B decreasing the temperature
C increasing the total pressure by reducing the total volume at constant temperature
D removing ammonia as it is made but keeping the total volume of the mixture the same.
Answer/Explanation
Ans:C
Question
The reaction pathway diagram below illustrates the energies of the reactants, the products and the transition state of a reaction.
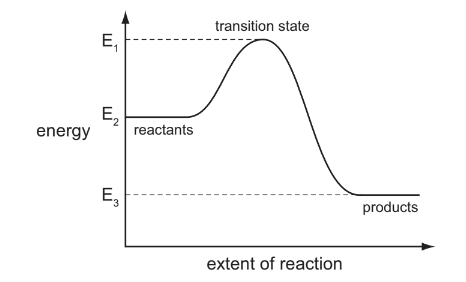
Which expression represents the activation energy of the forward reaction?
A E1 – E2 B E2 – E1 C E2 – E3 D E3 – E2
Answer/Explanation
Ans:A
Question
R and S react together.
\(R+ S\rightleftharpoons T\)
Which factors affect the rate of the forward reaction?
1 the activation energy of the reaction
2 the enthalpy change of the reaction
3 the equilibrium constant of the reaction
The responses A to D should be selected on the basis of

Answer/Explanation
Ans:D
Question
Sulfur trioxide is manufactured from sulfur dioxide and oxygen, using the Contact process.
Which condition affects the value of the equilibrium constant, \(K_c\)?
A adjusting the temperature
B increasing the pressure
C removing \(SO_3\) from the equilibrium mixture
D using a catalyst
Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Question
The reaction pathway for a reversible reaction is shown below.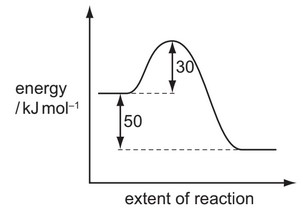
Which statement is correct?
A The activation energy of the reverse reaction is \(+80kJmol^{–1}\).
B The enthalpy change for the forward reaction is \(+30kJ mol^{–1}\).
C The enthalpy change for the forward reaction is \(+50kJ mol^{–1}\).
D The enthalpy change for the reverse reaction is \(+30kJ mol^{–1}\).
Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Question
If \(N_2O_4\) gas is placed in a sealed vessel the following equilibrium is established.
\(N_2O_4(g) \leftrightarrow 2NO_2(g)\)
The forward reaction is endothermic.
What happens when the temperature is increased?
1 The equilibrium constant increases.
2 The partial pressure of \(NO_2\) increases.
3 The activation energy is unchanged.
Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Question
Which stage in the free radical substitution of methane by chlorine will have the lowest activation
energy?
A \(CH_3• + Cl_2 → CH_3Cl + Cl•\)
B \(Cl • + Cl • → Cl_2\)
C \(Cl • + CH_4 → CH_3• + HCl\)
D \(Cl_2 → Cl • + Cl •\)
Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question
In the manufacture of sulfuric acid the reaction \(2SO_{2}\left ( g \right )+O_{2}\left ( g \right )\rightleftharpoons 2SO_{3}\left ( g \right )\) usually takes place at 400 °C and 1 atm pressure. In one industrial plant, it is decided to change the pressure to 20atm.
- What will be the consequences of this change?
- increased running costs
- an increased percentage of sulfur trioxide in the equilibrium mixture
- the rate of the backward reaction increases
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
A
Question
Ammonia is manufactured by the Haber Process, in an exothermic reaction.
Assuming that the amount of catalyst remains constant, which change will not bring about an increase in the rate of the forward reaction?
- decreasing the size of the catalyst pieces
- increasing the pressure
- increasing the temperature
- removing the ammonia as it is formed
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
D