Question
The catalytic converters fitted to cars remove pollutants from the exhaust gases. Some of the
reactions that occur involve oxygen, which comes from the air.
Which pollutants in the exhaust gases will react with oxygen on the surface of the catalytic
converter?
A NO_{2}
B unburnt fuel
C CO
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:C
Question:
Hydrochloric acid reacts with zinc
\(1HC \imath(aq)~+~Zn(s)\rightarrow ZnC\imath_{2}(aq)~+~H_{2}g\)
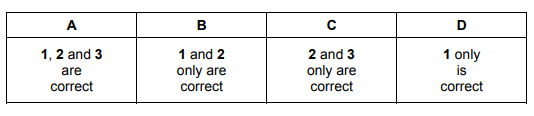
What will increase the rate of this reaction but will not change the Boltzmann distribution of molecular energies?
1 addition of a suitable catalyst
2 an increase in concentration of hydrochloric acid
3 an increase in temperature of hydrochloric acid

▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:B
Question
Hydrogen peroxide, \(H_2O_2\), decomposes to form water and oxygen. The reaction is catalysed by bromide ions.
step 1 \(2Br^– (aq) + H_2O_2(aq) + 2H^+ (aq) \rightarrow 2H_2O(l) + Br_2(aq)\)
step 2 \(H_2O_2(aq) + Br_2(aq) \rightarrow 2Br^– (aq) + 2H^+ (aq) + O_2(g)\)
Which row is correct?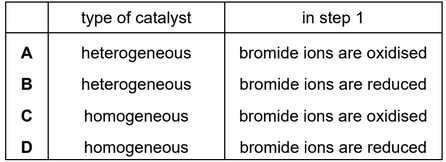
Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Question
Which statement about catalysts is correct?
A They change the reaction pathway by increasing the activation energy.
B They increase the rate of reaction by lowering the enthalpy change of the reaction.
C They increase the number of particles that have sufficient energy to react.
D Heterogeneous catalysts are in the same state as the reactant.
Answer/Explanation
Answer: C
Question
A diketo acid is a compound with two ketone groups and one carboxylic acid group.
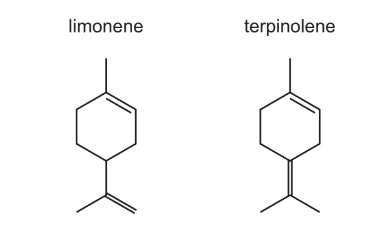
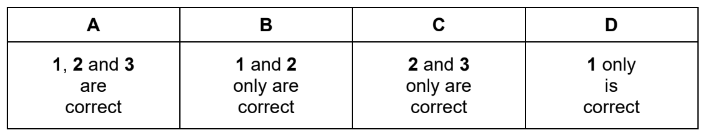
Which statements about the reactions of limonene and terpinolene are correct?
1 When reacted with an excess of hydrogen and a nickel catalyst, limonene and terpinolene produce the same compound.
2 An excess of hot concentrated acidified KMnO4 reacts with limonene and with terpinolene to form different diketo acids.
3 The reactions of limonene and terpinolene with an excess of Br2 produce positional isomers with the same number of chiral carbon atoms.
Answer/Explanation
Answer B
Question
Some polluting gases are removed from car exhaust fumes using a catalytic converter.
Platinum or palladium can be used as the catalyst. The reactions are faster when platinum is the catalyst than they are when palladium is the catalyst.
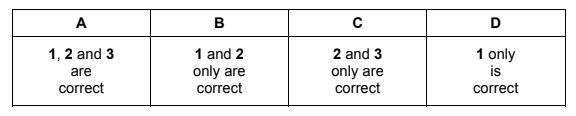
Which statements are correct?
1 Platinum acts as a heterogeneous catalyst in these reactions.
2 The palladium-catalysed reactions have higher activation energies than the platinum-catalysed reactions.
3 The platinum-catalysed reactions are more exothermic than the palladium-catalysed reactions.
The responses A to D should be selected on the basis of
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
B
Question
The stoichiometry of a catalysed reaction is shown by the equation below.
\(P(g) + Q(g) \rightleftharpoons R(g) + S(l)\)
Two experiments are carried out in which the amount of R is measured. The results are shown in the diagram.
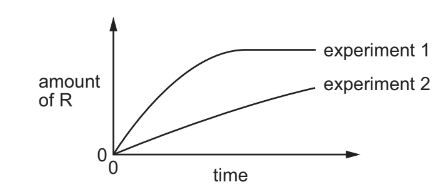
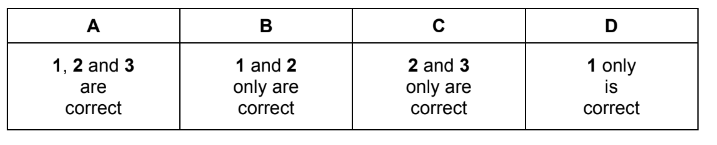
Which changes in the conditions could explain the results shown?
1 A lower pressure was used in experiment 2.
2 A different catalyst was used in experiment 2.
3 Product S was continuously removed from the reaction vessel in experiment 2.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Answer B
Question
Catalytic converters are fitted in the exhaust systems of many cars.
Which gas:
● causes acid rain if it is released into the air
● is removed from car exhaust fumes by a catalytic converter?
A carbon dioxide
B carbon monoxide
C hydrocarbon vapour
D nitrogen dioxide
Answer/Explanation
Answer D
Question
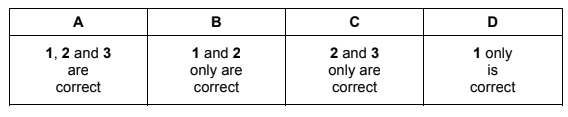
Vanadium and pepsin can both act as catalysts. Vanadium is a metal. Pepsin is an enzyme. Which statements are correct for both vanadium and pepsin?
1 They will speed up any chemical reaction.
2 They can lower the activation energy for a reaction.
3 They are not used up when they act as catalysts.
Answer/Explanation
Answer C
Question
Two reactions are shown.
reaction 1 N2(g) + 3H2(g) \(\rightleftharpoons \)2NH3(g)
reaction 2 2O3(g) \(\rightleftharpoons \)3O2(g)
In reaction 1, a finely powdered iron catalyst is used.
In reaction 2, a vaporised tetrachloromethane catalyst in ultraviolet light is used.
Which statement about the catalysts used is correct?
A Both reaction 1 and reaction 2 use a heterogeneous catalyst.
B Both reaction 1 and reaction 2 use a homogeneous catalyst.
C Reaction 1 uses a heterogeneous catalyst and reaction 2 uses a homogeneous catalyst.
D Reaction 1 uses a homogeneous catalyst and reaction 2 uses a heterogeneous catalyst.
Answer/Explanation
Answer C
Question
Which statement about the effect of a catalyst on a reversible reaction is correct?
A The activation energy of the forward reaction stays the same.
B The composition of the equilibrium mixture stays the same.
C The rate of the backward reaction stays the same.
D The value of the equilibrium constant changes.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
B
Question
The diagram shows the Boltzmann distribution of energies in a gas. The gas can take part in a
reaction with an activation energy, Ea. The gas is maintained at a constant temperature.
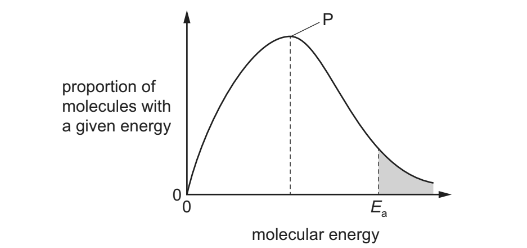
Which statement is correct?
A If a catalyst is added, peak P will be lower and Eawill move to the left.
B If a catalyst is added, peak P will be lower and Eawill move to the right.
C If a catalyst is added, peak P will be the same and Ea will move to the left.
D If a catalyst is added, peak P will be the same and Ea will move to the right.
Answer/Explanation
Answer C
Question
3 \(NO + SO_{3} \rightarrow NO_{2} + SO_{2}\)
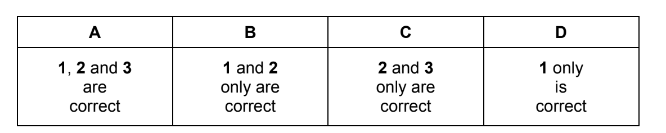
Answer/Explanation
Answer: B
Question
An autocatalytic reaction is a reaction in which one of the products catalyses the reaction.
Which curve would be obtained if the rate of an autocatalytic reaction is plotted against time?
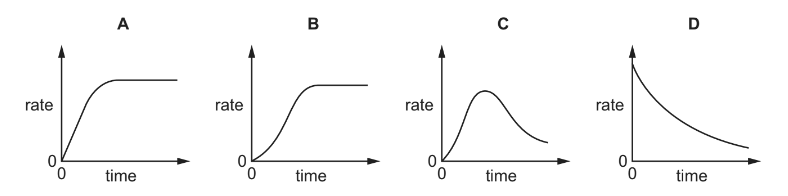
Answer/Explanation
Answer: C
Question
Enzymes are biological catalysts. Many enzymes show specificity. An example of an enzyme which shows specificity is glucokinase. Glucokinase is involved in the metabolism of glucose.
What does specificity mean in this context?
A Glucokinase is most effective as a catalyst over a narrow pH range.
B Glucokinase is most effective as a catalyst over a narrow range of temperatures.
C Glucokinase only operates on a narrow range of substrate molecules.
D Glucokinase provides an alternative route for the reactions it catalyses.
Answer/Explanation
Answer: C
Question
Ammonia is made by the Haber process. The reactants are nitrogen and hydrogen.
\(N_{2}(g) + 3H_{2}(g) \rightleftharpoons 2NH_{3}\)(g) ∆H –ve
What will increase the rate of the forward reaction?
A adding argon to the mixture but keeping the total volume constant
B decreasing the temperature
C increasing the total pressure by reducing the total volume at constant temperature
D removing ammonia as it is made but keeping the total volume of the mixture the same.
Answer/Explanation
Ans:C
Question
A reversible reaction is catalysed. Which statements about the effects of the catalyst on this system are correct?
1 The catalyst alters the mechanism of the reaction.
2 The catalyst reduces the activation energy for both the forward and the backward reaction.
3 The catalyst alters the composition of the equilibrium mixture.
The responses A to D should be selected on the basis of

No other combination of statements is used as a correct response.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:B
Question
One of the reactions taking place in a catalytic converter in a car exhaust system is between nitrogen oxide and octane (unburned petrol). The products of this reaction are non-toxic.
Which is the correct equation for the reaction?
- \(C_{8}H_{16}+16NO\rightarrow8CO_{2}+8H_{2}+8H_{2}O\)
- \(C_{8}H_{16}+24NO\rightarrow8CO_{2}+12H_{2}+8H_{2}O\)
- \(C_{8}H_{18}+17NO\rightarrow8CO+8\frac{1}{2}N_{2}+9H_{2}O\)
- \(C_{8}H_{18}+25NO\rightarrow8CO_{2}+12\frac{1}{2}N_{2}+9H_{2}O\)
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
D