Question
Which rows correctly show the relative electrical conductivities of the sets of three Period 3 elements?
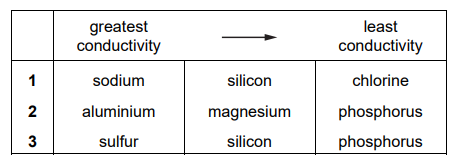
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:B
Question
$\mathrm{X}$ and $\mathrm{Y}$ are two elements in Period 3 of the Periodic Table. They combine to form compound $Z$.
$X$ forms a soluble acidic oxide. The oxidation number of $X$ in this oxide is +4 .
$Y$ forms an amphoteric oxide.
What is the formula of compound $Z$ ?
A AlP
B $\mathrm{Al}_2 \mathrm{~S}_3$
C $\mathrm{Si}_2 \mathrm{P}_5$
D $\mathrm{SiS}_2$
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:B
Question
Element Z has a giant structure.
The chloride of Z reacts with water to give a solution with a pH less than 5.
Which pair shows two elements which could be Z?
A aluminium, magnesium
B aluminium, silicon
C phosphorus, magnesium
D phosphorus, silicon
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:B
Question:
Sodium, magnesium and aluminium are three elements in Period 3 of the Periodic Table. Each element forms an oxide. Which row is correct?
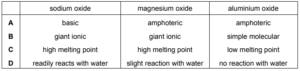
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:D
Question
The magnitude of property X of five elements from the third period of the Periodic Table, P, Q, R, S and T is shown. P, Q, R, S and T have consecutive atomic numbers. The letters do not represent the symbols of the elements
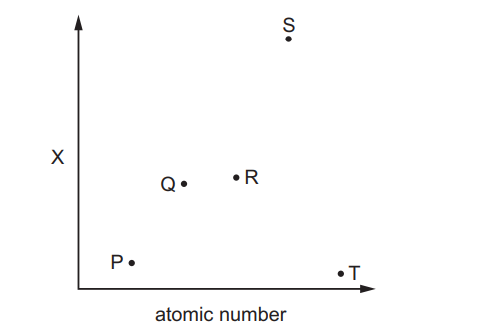
Which row correctly identifies property X and element R?
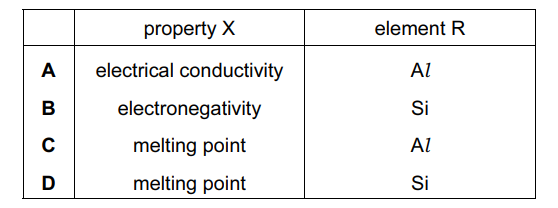
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:C
Question
The electrical conductivities of two compounds, Y and Z, are shown in the table.
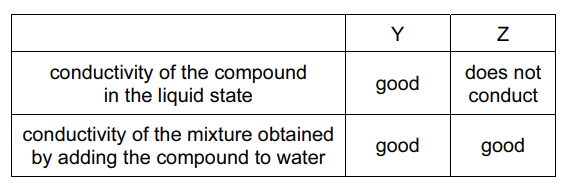
What could compounds Y and Z be?
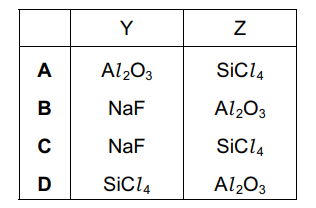
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:C
Question
Which reagents, when used in an excess, can be used to make sodium lactate, $\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{CH}(\mathrm{OH}) \mathrm{CO}_2 \mathrm{Na}$, from lactic acid, $\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{CH}(\mathrm{OH}) \mathrm{CO}_2 \mathrm{H}$ ?
$1 \mathrm{Na}$
$2 \mathrm{NaHCO}_3$
$3 \mathrm{NaOH}$
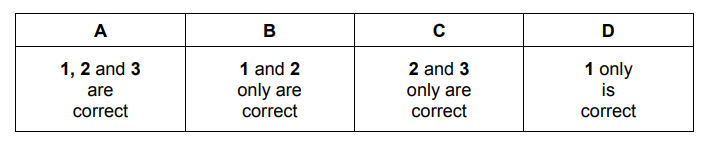
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:C
Question
Which statement for the element in Period 3 and Group 13 of the Periodic Table is correct?
A It has the highest melting point of the elements in its period.
B It has exactly one electron in its shell with principal quantum number 3.
C It forms an oxide that reacts with aqueous sodium hydroxide.
D It forms a chloride that dissolves in water to give a neutral solution.
Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Question
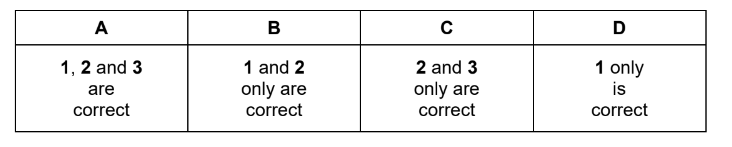
Which statements are correct going across Period 3 from sodium to chlorine?
1 The charge on the nucleus increases, pulling the electrons closer to it.
2 The radius of the most common ion of each element decreases.
3 The shielding caused by inner electrons decreases, so the outer electrons are pulled closer
to the nucleus.
Answer/Explanation
Answer: D
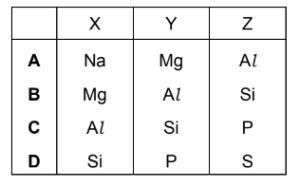
Question
X, Y and Z are consecutive elements in Period 3 of the Periodic Table. Element Y has the highest first ionisation energy and the lowest melting point of these three elements.
What are the identities of X, Y and Z?
Answer/Explanation
Answer D
Question
The elements Cl , Mg, Si and S are all in Period 3.
What is the correct sequence of the melting points of these elements, from lowest to highest?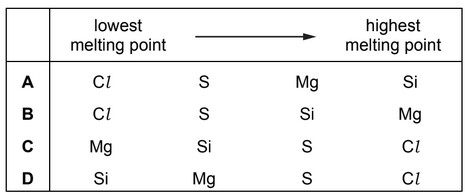
Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Question
Which statements describe a trend in Period 3 between every pair of adjacent elements from sodium to chlorine?
1 The atomic radius decreases.
2 The 1st ionisation energy decreases.
3 The melting point decreases.
The responses A to D should be selected on the basis of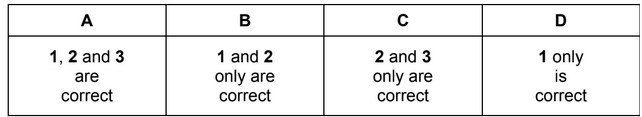
Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Question
Which graph correctly shows the relative melting points of the elements Mg, Al, Si and P plotted against their relative electronegativities?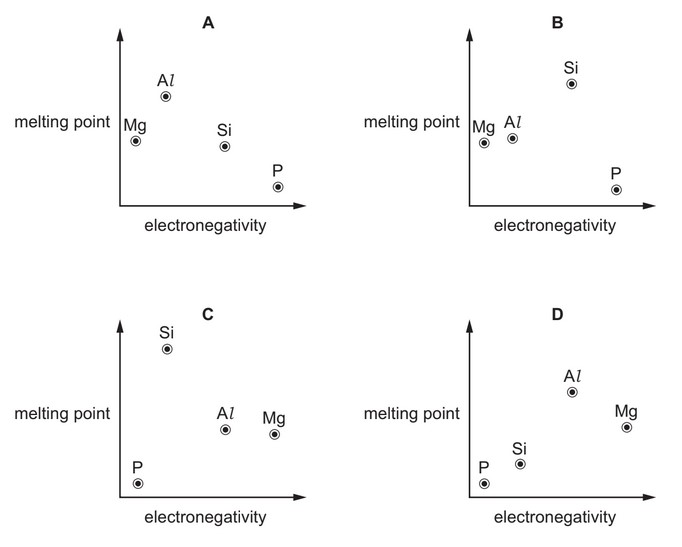
Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question
The diagram shows the melting points of eight elements with consecutive atomic numbers.
Which element could be sodium?
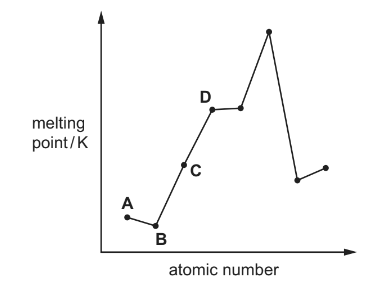
Answer/Explanation
Answer: C
Question
Elements D and E are both in Period 3. Element D has the smallest atomic radius in Period 3.
There are only two elements in Period 3 which have a lower melting point than element E.
Elements D and E react together to form compound L.
Which compound could be L?
A MgCl2 B MgS C Na2S D PCl3
Answer/Explanation
Answer: D
Question
Use of the Data Booklet is relevant to this question.
Which diagram correctly shows the atomic radii of the elements Mg, Al, Si and P plotted against their melting points?
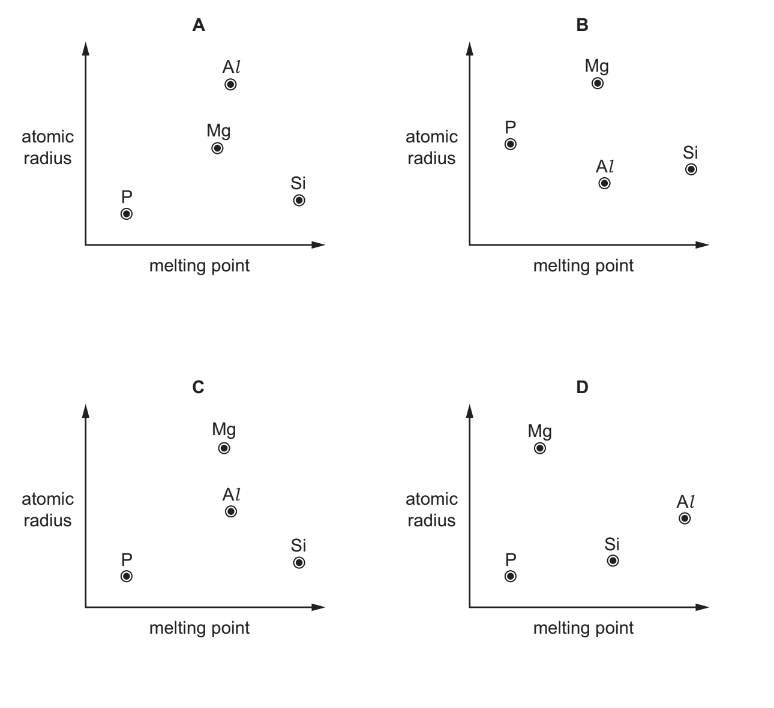
Answer/Explanation
Ans:C
Question
Use of the Data Booklet is relevant to this question. Which of the elements sodium, magnesium, aluminium, silicon, phosphorus, sulfur and chlorine
• has a lower first ionisation energy than the preceding element in the Periodic Table,
• conducts electricity and
• has a lower atomic radius than the preceding element in the Periodic Table?
A aluminium
B magnesium
C phosphorus
D sulfur
Answer/Explanation
Ans:A
Question
The melting points of the Period 3 elements sodium to aluminium are shown in the table.
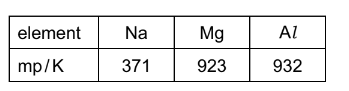
Which factor explains the increase in melting points from sodium to aluminium?
A the changes in first ionisation energy from sodium to aluminium
B the increase in electronegativity from sodium to aluminium
C the increase in the Ar of the elements from sodium to aluminium
D the increase in the number of outer electrons in each atom from sodium to aluminium
Answer/Explanation
Ans:D
Question
Element X, in Period 3, has the following properties.
● Its oxide has a giant structure.
● It forms covalent bonds with chlorine.
● Its oxide will neutralise HCl(aq).
What is element X?
A Mg B Al C Si D P
Answer/Explanation
Ans:B
Question
Use of the Data Booklet is relevant to this question. Which graph correctly shows relative electronegativity plotted against relative atomic radius for the elements Na, Mg, Al and Si?
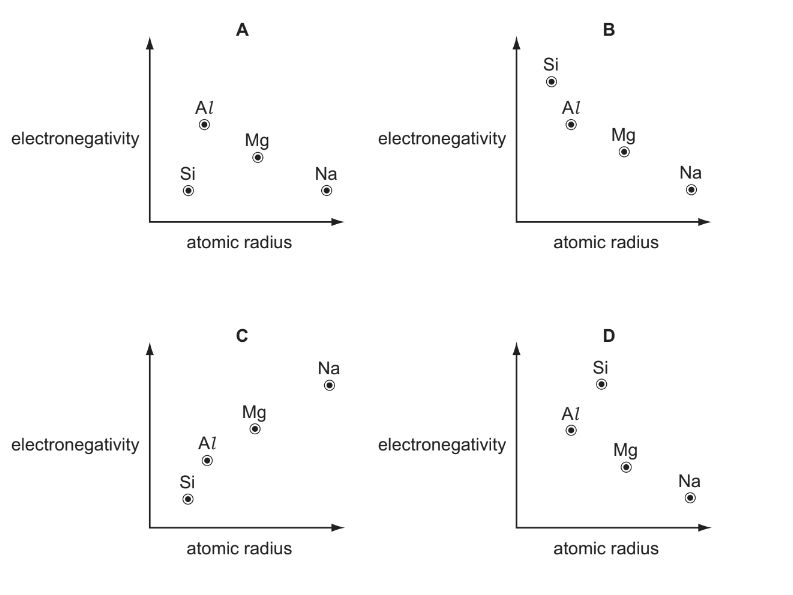
Answer/Explanation
Ans:B
Question
Consecutive elements X, Y and Z are in the third period of the Periodic Table. Element Y has the
highest first ionisation energy and the lowest melting point of these three elements.
What could be the identities of X, Y and Z?
A sodium, magnesium, aluminium
B magnesium, aluminium, silicon
C aluminium, silicon, phosphorus
D silicon, phosphorus, sulfur
Answer/Explanation
Ans: D