Question
This question is about Period 3 elements and their compounds.
(a) Give an explanation for each of the following statements.
(i) The atomic radius decreases across Period 3 ( $\mathrm{Na}$ to $\mathrm{Ar}$ ).[2]
(ii) The first ionisation energy of sulfur is lower than that of phosphorus.[2]
(iii) Sodium is a better electrical conductor than phosphorus.[2]
(iv) Magnesium is a better electrical conductor than sodium.[1]
(b) The flow chart below shows a series of reactions
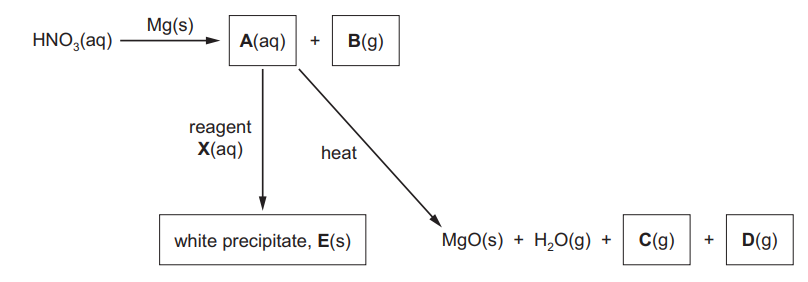
(i) Give the formula of each of the compounds A to D.
A ……………………………………… B ………………………………………
C ……………………………………… D ………………………………………[4]
(ii) E reacts with dilute aqueous acid to produce a gas that turns lime-water cloudy.
Suggest the identity of reagent X………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. [1][Total: 12]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a) (i) greater attractive force
OR
greater force between nucleus and (outer) electrons
proton number/ atomic number/ nuclear charge increases across period AND electrons occupy same
shell/ shielding roughly constant
(ii) sulfur’s electron removed from full (3p) orbital
OR
sulfur has two electrons in the same orbital
electron–electron repulsion (reduces energy required)
(iii) sodium has mobile/ free electrons / electrons free (to move throughout the structure)
phosphorus is simple/ covalent/molecular
(iv) magnesium has two free/delocalised/ outer/ valence electrons per atom
OR
more free/delocalised/ outer electrons than sodium
(b) (i)
$
\begin{aligned}
& \mathbf{A}=\mathrm{Mg}\left(\mathrm{NO}_3\right)_2 \\
& \mathbf{B}=\mathrm{H}_2 \\
& \mathbf{C}=\mathrm{NO}_2 \mathrm{OR} \mathrm{O}_2 \\
& \mathbf{D}=\mathrm{O}_2 \text { OR NOO }
\end{aligned}
$
(ii) any Group I carbonate OR ammonium carbonate
Question
(a) The graph shows a sketch of the first ionisation energies of six successive elements in the Periodic Table.The letters are not the symbols of the elements.
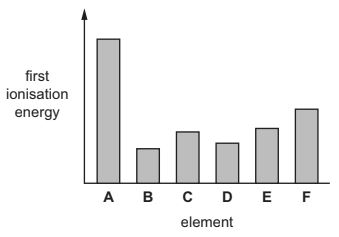
(I) Explain what is meant by the term first ionisation energy.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… [3]
(ii) Suggest why the first ionisation energy of B is much less than that of A.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… [3]
(b) P–T are successive elements in Period 3 of the Periodic Table.The letters are not the symbols of the elements.
On the axes, sketch a graph to show the trend in the atomic radius of the elements P–T. Explain your answer.
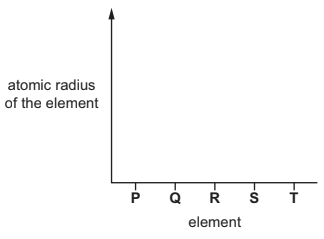
explanation ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
[3]
[Total: 9]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Answer:
(a)(i) • energy required / energy change
• when one electron is removed
• from each atom in one mole of
• gaseous atoms
(a)(ii) for element B
(outer electron is removed) from a higher energy level
more shielding
less attraction to nucleus
(b) line on graph decreases P—T
increasing nuclear charge AND electrons in same shell
greater attraction between nucleus (and electrons)