Question
Sodium oxide, Na2O, is a white crystalline solid with a high melting point.
(a) Write an equation for the reaction of sodium with oxygen, forming sodium oxide.
Include state symbols.
(b) Explain why sodium oxide has a high melting point.
(c) When sodium oxide reacts with water an alkaline solution is obtained.
(i) Explain why the solution obtained is alkaline. You should use the Brønsted-Lowry theory
of acids and bases in your answer.
(ii) Calculate the pH of the solution obtained when 3.10g of sodium oxide are added to 400cm3
of water.
(d) Use the data below, and other suitable data from the Data Booklet, to calculate the lattice
energy of sodium oxide, ΔHθlatt Na2O(s).

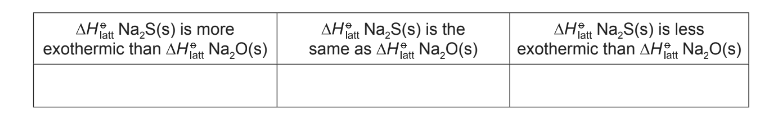
(e) State how ΔHθlatt Na2S(s) differs from ΔHθlatt Na2O(s).
Indicate this by placing a tick (✓) in the appropriate box in the table.
Answer/Explanation
Answer: (a) 4Na(s) + O2(g) → 2Na2O(s)
balanced with all formulae correct
state symbols
(b) giant ionic
strong bond / attraction between
AND
positive and negative ions / anions and cations / Na+ and O2– / oppositely charged ions
(c)(i) the reaction produces sodium hydroxide / hydroxide ions / OH– ions
the hydroxide ions can receive / accept H+ ions / protons
(c)(ii) Calculation of Na2O moles 3.10g / 62 OR 0.05
Calculation of [OH–] 0.05 × (2 / 0.400) = 0.25 mol dm–3
Calculation of pH –log 0.25 = 0.60
14 – 0.60 = 13.40
(d) use of (2 × 109) or 218 and (2 × 494) or 988
use of (0.5 × 496) or 248
use of 416, 142, 844
evaluation of expression correctly
∆Hlat = –416 – (2 × 109) – (0.5 × 496) – (2× 494) – (–142 + 844) = –2572
(e) the lattice energy of Na2S is less exothermic
the sulfide ion is larger than the oxide ion / S2– larger than O2 / ionic radii quoted 0.184 nm and 0.140 nm
AND less attraction (between the ions)/bonds are weaker
Question
This question is about Period 3 elements and their compounds.
(a) Give an explanation for each of the following statements.
(i) The atomic radius decreases across Period 3 ( $\mathrm{Na}$ to $\mathrm{Ar}$ ).[2]
(ii) The first ionisation energy of sulfur is lower than that of phosphorus.[2]
(iii) Sodium is a better electrical conductor than phosphorus.[2]
(iv) Magnesium is a better electrical conductor than sodium.[1]
(b) The flow chart below shows a series of reactions
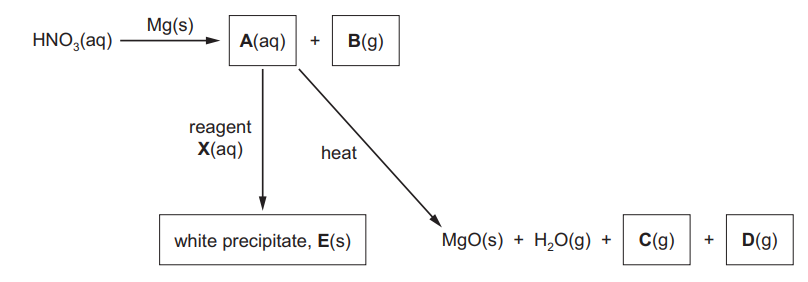
(i) Give the formula of each of the compounds A to D.
A ……………………………………… B ………………………………………
C ……………………………………… D ………………………………………[4]
(ii) E reacts with dilute aqueous acid to produce a gas that turns lime-water cloudy.
Suggest the identity of reagent X………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. [1][Total: 12]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a) (i) greater attractive force
OR
greater force between nucleus and (outer) electrons
proton number/ atomic number/ nuclear charge increases across period AND electrons occupy same
shell/ shielding roughly constant
(ii) sulfur’s electron removed from full (3p) orbital
OR
sulfur has two electrons in the same orbital
electron–electron repulsion (reduces energy required)
(iii) sodium has mobile/ free electrons / electrons free (to move throughout the structure)
phosphorus is simple/ covalent/molecular
(iv) magnesium has two free/delocalised/ outer/ valence electrons per atom
OR
more free/delocalised/ outer electrons than sodium
(b) (i)
$
\begin{aligned}
& \mathbf{A}=\mathrm{Mg}\left(\mathrm{NO}_3\right)_2 \\
& \mathbf{B}=\mathrm{H}_2 \\
& \mathbf{C}=\mathrm{NO}_2 \mathrm{OR} \mathrm{O}_2 \\
& \mathbf{D}=\mathrm{O}_2 \text { OR NOO }
\end{aligned}
$
(ii) any Group I carbonate OR ammonium carbonate