Question:
Which observations are made when a sample of silicon chloride, \(SiC \imath_{4}\) is added to a beaker of water?
A No visible change is observed.
B Steamy fumes and a precipitate are both observed.
C The appearance of a precipitate is the only observation.
D The appearance of steamy fumes is the only observation
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:B
Question
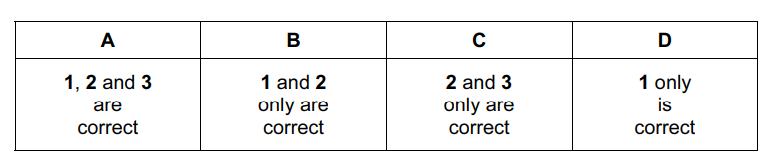
Which of these statements are always correct?
1 The sum of the oxidation numbers of all the atoms in a compound is zero.
2 The oxidation number of sodium in a salt is positive.
3 The oxidation number of chlorine in a compound is negative.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:B
Question
The table shows the melting points of \(SiO_2\) and \(P_4O_6\).
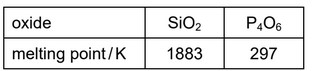
Which statement explains the difference between the melting points of \(SiO_2\) and \(P_4O_6\)?
A The bonding of the oxides changes from ionic to covalent.
B The metallic character of the elements decreases across Period 3.
C The oxidation number of the element increases from Si to P.
D The structure changes from giant molecular to simple molecular.
Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Question
The table describes two possible environmental consequences of adding too much ammonium nitrate fertiliser to the soil.
Which row is correct?

Answer/Explanation
Answer B
Question
The table shows some reactions of a white compound, G.
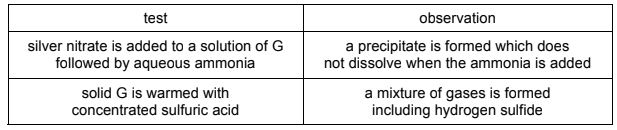
What could be the identity of G?
A caesium chloride
B lithium bromide
C potassium sulfate
D sodium iodide
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
D
Question
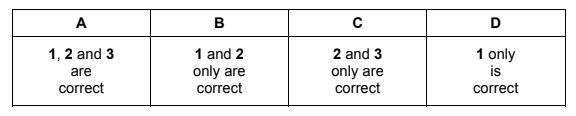
Which statements about ceramics are correct?
1 Ceramics are good electrical conductors.
2 Ceramics are strong materials.
3 Ceramics have high melting points.
The responses A to D should be selected on the basis of
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
C
Question
Sodium azide, NaN3, is dissolved in water. Acidified silver nitrate is added to the solution and a white precipitate forms. Aqueous ammonia is then added to the white precipitate.
The azide ion, N3–, has similar chemical properties to the Cl– ion.
Which row of the table can be predicted from this information?
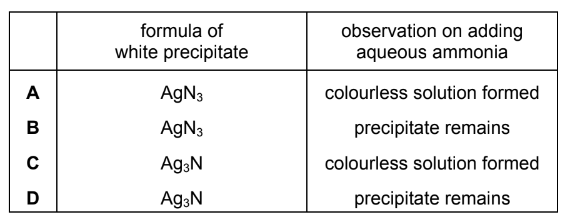
▶️Answer/Explanation
Answer A
Question
The relative melting points of four consecutive elements in the Periodic Table are shown in the graph.
The elements all have proton numbers less than 20.
Which element is in Group 16?
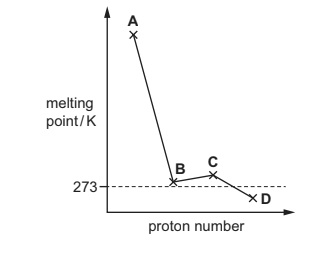
Answer/Explanation
Answer C
Question
Aqueous silver nitrate is added to a solution of potassium iodide.
Aqueous ammonia is then added.
What would be observed?
A a cream precipitate that dissolves on addition of aqueous ammonia
B a cream precipitate that does not dissolve on addition of aqueous ammonia
C a yellow precipitate that dissolves on addition of aqueous ammonia
D a yellow precipitate that does not dissolve on addition of aqueous ammonia
Answer/Explanation
Answer D
Question
The three minerals below are obtained from mines around the world. Each one behaves as a mixture of two carbonate compounds. They can be used as fire retardants because they decompose in the heat, producing\( CO_{2}\). This gas smothers the fire.
barytocite \(BaCa(CO_{3})_{2}\)
dolomite \( CaMg (CO_{3}{2}\)
huntite \( Mg_{3}Ca(CO_{3})_{4}\)
What is the order of effectiveness as fire retardant, from best to worst?
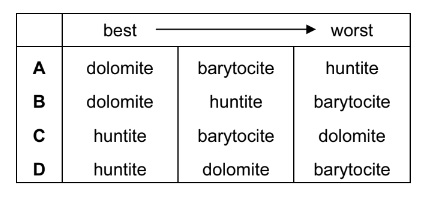
Answer/Explanation
Ans:D
Question
Which observations are made when a sample of silicon chloride, \(SiCl_{ 4}\), is added to a beaker of water?
A No visible changes are observed.
B Steamy fumes and a white precipitate are both observed.
C The appearance of a white precipitate is the only observation.
D The appearance of steamy fumes is the only observation.
Answer/Explanation
Ans:B
Question
Which statements about orbitals in a krypton atom are correct?
1 The 1s and 2s orbitals have the same energy as each other but different sizes.
2 The third energy level (n=3) has three subshells and nine orbitals.
3 The 3d subshell has five orbitals that have the same energy as each other in an isolated atom.
The responses A to D should be selected on the basis of
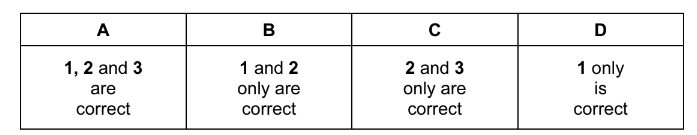
Answer/Explanation
Ans:C
Question
The Group IV elements carbon, silicon and germanium can all exist in the giant molecular structure which is also found in diamond. The bond lengths in these structures are given below.
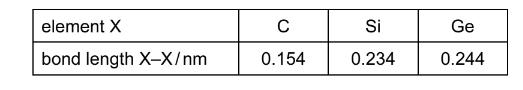
Why does the bond length increase down the group?
1 Orbital overlap decreases down the group.
2 Atomic radius increases down the group.
3 Nuclear charge increases down the group.
The responses A to D should be selected on the basis of
No other combination of statements is used as a correct response.
Answer/Explanation
Ans:B
Question
Which compound cannot be oxidised by acidified potassium dichromate(VI) solution but does react with sodium metal?
A \( (CH_{3})_{3}\)COH
B \(CH_{3}COCH_{2}CH_{3}\)
C \(CH_{3}CH_{2}CH_{2}CH_{2}\)OH
D \(CH_{3}CH_{2}CH(OH)CH_{3}\)
Answer/Explanation
Ans:A
Question
X is a particle with 18 electrons and 20 neutrons.
What could be the symbol of X?
1 \(\begin{matrix}
38\\18
\end{matrix}\) Ar
2 \(\begin{matrix}
40\\20
\end{matrix}\) \(Ca^{2+}\)
3 \(\begin{matrix}
39\\19
\end{matrix}\) \(K^+\)
Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Question
Use of the Data Booklet is relevant to this question. Carbon and nitrogen are adjacent in the Periodic Table.
Which properties do they both have?
1 There is an empty 2p orbital in one atom of the element.
2 The principal quantum number of the highest occupied orbital is 2.
3 They form compounds in which their atoms form bonds with four other atoms.

Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Question
Transition metals and their compounds are used as catalysts.
Which row is correct?
Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Question
Nitrogen and phosphorus are both in Group V of the Periodic Table. Phosphorus forms a chloride with the formula PCl5.
Why is it not possible for nitrogen to form NCl5?
- Nitrogen’s outer shell can only contain eight electrons.
- Nitrogen cannot have oxidation state +5.
- Nitrogen is almost inert.
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
D