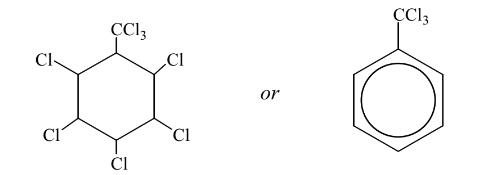Question
Procaine is used as an anaesthetic in medicine. It can be synthesised from methylbenzene in five steps as shown in Fig. 7.1.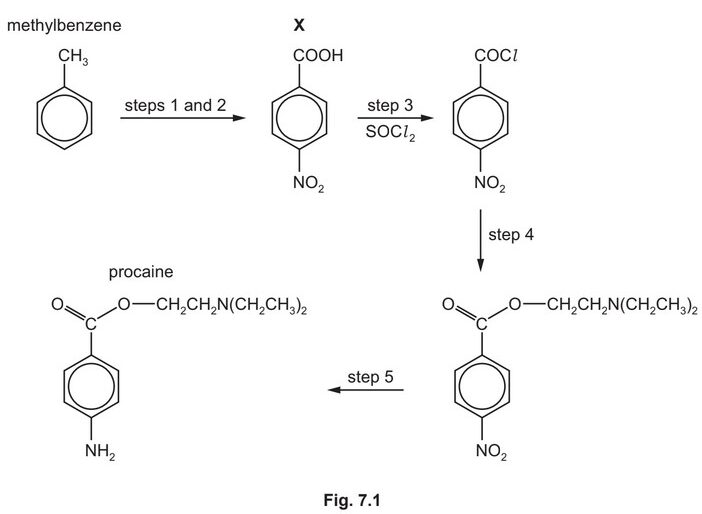
(a) (i) Name all the functional groups present in procaine.
(ii) A molecule of procaine has 13 carbon atoms.
State the number of carbon atoms that are sp, \(sp^2\) and \(sp^3\) hybridised in procaine.
sp carbons = ………………… \(sp^2\) carbons = ………………… \(sp^3\) carbons = …………………
(b) The proton (\(^1H\)) NMR spectrum of procaine dissolved in \(D_2O\) is recorded.
Predict the number of peaks observed.
(c) State why procaine can act as a base.
(d) Compound X can be synthesised in two steps from methylbenzene.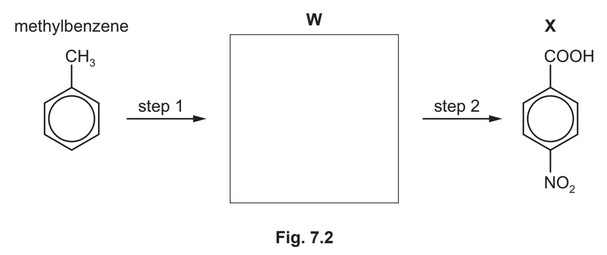
(i) Draw the structure of compound W in the box provided. [1]
(ii) State the reagents and conditions for step 1 and step 2.
step 1 ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
step 2 ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(e) Procaine is synthesised in three steps from X.
Suggest the reagents and conditions for step 4 and for step 5 in Fig. 7.1.
step 4 ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
step 5 ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
(f) (i) Explain what is meant by partition coefficient, \(K_{pc}\).
(ii) The partition coefficient of procaine between octan-1-ol and water is 1.77.
Octan-1-ol and water are immiscible. A solution containing 0.500g of procaine in 75.0cm3 of water is shaken with 50.0\(cm^3\) of octan-1-ol.
Calculate the mass of procaine that is extracted into the octan-1-ol.
mass of procaine extracted = ………………………… g
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
(a) (i) phenylamine AND amine AND ester
(ii) sp carbons = 0, \(sp^2\) carbons = 7, \(sp^3\) carbons = 6
(b) 6
(c) lone pair on the N can accept a proton
(d) (i) 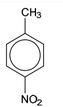
(ii) step 1 M1 concentrated \(HNO_3\) and \(H_2SO_4\)
step 2 M2 hot (alkaline) KMnO4 (followed by addition of \(H^+\))
(e) step 4 M1 \(HOCH_2CH_2N(CH_2CH_3)_2\)
step 5 \(M_2\) Sn AND HCl
M3 concentrated (HCl) AND heat / reflux
(f) (i) M1 ratio of the concentration of a solute in two solvents
M2 at equilibrium
(ii) M1 \(K_{pc} = [procaine]_{oct} / [procaine]_{water}\)
1.77 = (x / 50)/(0.5 – x / 75)
M2 1.77 = 1.5x / 0.5 – x
0.885 –1.77x = 1.5x
x = 0.271 g min 2sf
Question
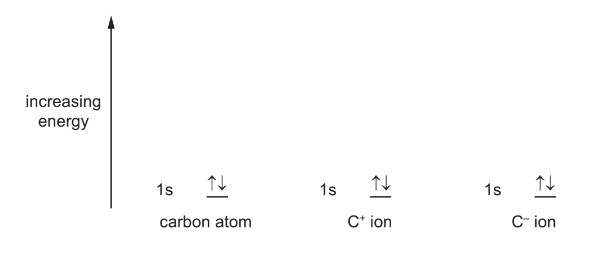
(a) Complete the diagrams to show the energies of the electrons in a carbon atom, a C+ ion and a C– ion.
(b) One of the simple molecular allotropes of carbon is buckminsterfullerene, C60.
(i) What is the hybridisation of the carbon atoms in C60?
(ii) C60 reacts with an excess of hydrogen to form a single product, C60Hx.
Using your answer to (i), suggest a suitable value for x.
(c) Methylbenzene can undergo different reactions to form the products shown below.
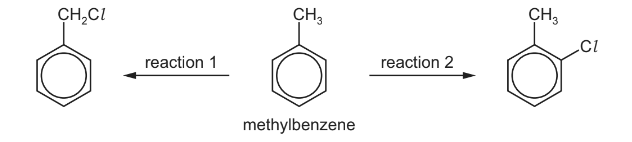
(i) Give the reagents and conditions for these two reactions.
(ii) Name the mechanism of reaction 1.
(iii) Draw the structure of the product obtained if reaction 1 is carried out using an excess of
chlorine.
Answer/Explanation
Answer: (a) 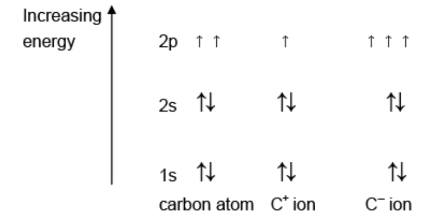
(b) (i) sp2
(b) (ii) x = 60/C60H60
(c) (i) reaction 1: Cl2 and UV light;
reaction 2: AlCl3, Cl2 (NOT aqueous);
c(ii) (free) radical substitution
c(iii)