Question
A corridor is 13.2 m long and has closed doors that reflect sound at both ends. The speed of sound in the air in the corridor is \(330 m s^{–1}.
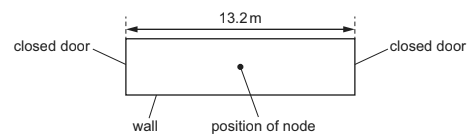
What is the lowest frequency of sound that could create a stationary wave in the corridor with a node halfway along it?
A \(0.040\) Hz B \(13\) Hz C \(25\) Hz D \(50\) Hz
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
Question
A string is fixed between point P and an oscillator M. Another string is fixed between M and point Q. M is midway between P and Q.
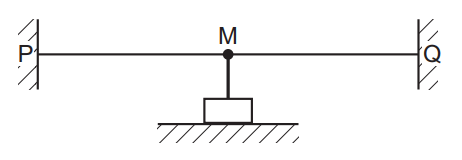
The frequency of the oscillator is adjusted until a stationary wave is formed on both strings. The
speed of the wave between P and M is twice the speed of the wave between M and Q.
Which diagram could represent the stationary wave pattern?
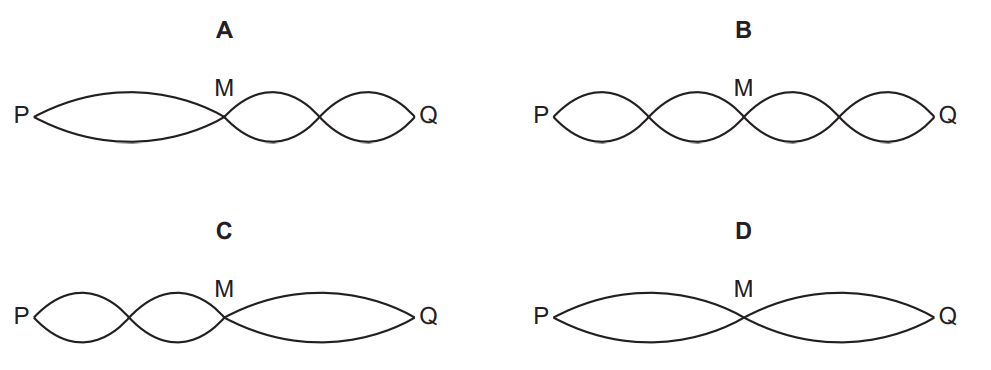
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
Question
The diagram shows part of a stationary wave on a string.
X and Y are points on the string. The vibrations at X and Y are 180° out of phase.
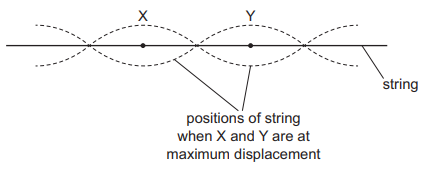
What is the distance between X and Y?
A one-quarter of a wavelength
B half a wavelength
C one wavelength
D two wavelengths
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
Question
Which statement concerning a stationary wave is correct?
A All the particles between two adjacent nodes oscillate in phase.
B The amplitude of the stationary wave is equal to the amplitude of one of the waves creating it.
C The wavelength of the stationary wave is equal to the separation of two adjacent nodes.
D There is no displacement of a particle at an antinode at any time.
Answer/Explanation
Question
Two waves, P and Q, meet at a point X and superpose.
Initially, the two waves meet at X in phase (zero phase difference) so that the resultant wave has
an amplitude of 14.0 cm at that point.
The phase difference between the two waves is then changed so that they meet at X with a
phase difference of 180°. The resultant wave now has an amplitude of 4.0 cm at X.
What is the amplitude of one of the waves at point X?
A 2.0 cm B 5.0 cm C 10 cm D 18 cm
Answer/Explanation
Ans
