Question
Describe the genetic code and its relationship to polypeptides and proteins.
Outline the role of proteins in active and passive transport of molecules through membranes.
Many cell functions, like synthesis of macromolecules and transport, require energy in the form of ATP. Explain how ATP is generated in animal cells.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
Remember, up to TWO “quality of construction” marks per essay.
a. (the genetic code is based on) sets of three nucleotides/triplets of bases called codons;
b. bases include adenine, guanine, cytosine and thymine in DNA / adenine, guanine, cytosine and uracil in RNA; (do not accept ATCG)
c. each codon is code for one amino acid;
d. some codons are (start or) stop codons;
e. DNA is transcribed into mRNA by base-pair matching/complementary base pairing;
f. mRNA is translated into a sequence of amino acids/polypeptide;
g. each gene codes for a polypeptide;
h. polypeptides may be joined/modified to form proteins;
Remember, up to TWO “quality of construction” marks per essay.
a. channel proteins allow diffusion/osmosis/passive transport;
b. large/polar molecules cannot cross the (hydrophobic) membrane freely;
c. facilitated diffusion involves moving molecules through proteins down their concentration gradient/without requiring ATP;
d. aquaporins (specific integral membrane proteins) facilitate the movement of water molecules/osmosis;
e. some proteins (for facilitated diffusion) are specific to molecule/ions;
f. active transport involves moving molecules through proteins against their concentration gradient/requiring ATP;
g. (some) proteins in the membrane are pumps / pumps perform active transport / sodium potassium pump;
Remember, up to TWO “quality of construction” marks per essay.
a. ATP is a form of energy currency/immediately available for use;
b. ATP is generated in cells by cell respiration (from organic compounds);
c. aerobic (cell respiration) requires oxygen;
d. anaerobic (cell respiration) does not require oxygen;
e. glycolysis breaks down glucose into pyruvate;
f. glycolysis occurs in cytoplasm;
g. (by glycolysis) a small amount of ATP is released;
h. ADP changes into ATP with the addition of a phosphate group/phosphoric acid / accept as chemical equation;
i. in mitochondria/aerobic respiration produces large amount of ATP / 38 mols (for the cell, per glucose molecule);
j. oxygen/aerobic respiration is required for mitochondrial production of ATP;
k. in mitochondria/aerobic respiration pyruvate is broken down into carbon dioxide and water;
Question
The diagram shows some of the structures in an animal cell.
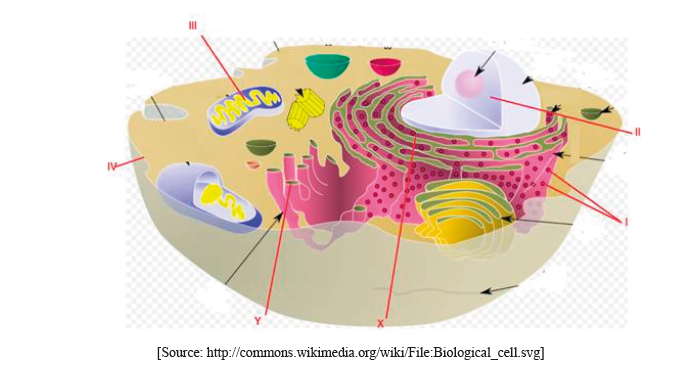
(i) Label structures I, II, III and IV.
I.
II.
III.
IV.
(ii) State one function of structure III.
Explain how materials are transported within a cell between structures X and Y.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
(i) Award [1] for any two of the following correctly labeled.
I. ribosomes
II. nucleus (do not accept nuclear membrane)
III. mitochondrion
IV. plasma/cell membrane
(ii) ATP production/site of aerobic respiration (do not accept energy production)
(protein) material transported by vesicles;
from rER to Golgi apparatus/complex/body/membrane;
vesicles bud off from rER/fuse with Golgi membrane (due to membrane fluidity);
Do not accept vacuole(s).
Question
State two differences in structure between plant and animal cells.
Outline how molecules move across a membrane by simple diffusion.
Explain the role of protein pumps in active transport.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
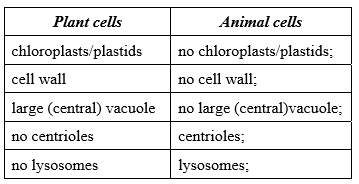
Answers do not need to be shown in a table format.
membranes are porous/permeable allowing diffusion;
diffusion is (passive) movement (of particles) from high to low concentration;
due to random motion/kinetic energy of molecules / no ATP involved;
diffusion continues until concentrations are equal (across the membrane);
(can) move solutes against a concentration gradient;
using energy/ATP;
specific for the solute/molecule transported;
protein pumps change shape (as they transport molecules);
Question
The diagram (not to scale) shows a cell which contains water and sodium ions. This cell is immersed in a salt solution of water and sodium ions.
State the mode of transport if water moves into the cell.
State the mode of transport if sodium ions move into the cell.
Explain facilitated diffusion.
State the name of the structures formed within a cell by endocytosis.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a (i)iosmosis
a (ii)ąctive transport
movement down the concentration gradient / from high to low concentration;
through channel proteins/ion channels;
passive transport / it requires no energy from the cell / no ATP;
for molecules that cannot pass through the phospholipid bilayer;
channel is specific/selective to the ion/molecule being transported;
vesicles / vacuoles / endosome
