Question
The table shows thermal properties of water and methane.
(a) Water molecules are polar and methane molecules are non-polar. Explain how this difference affects the thermal properties of these substances.
(b) Using the data in the table, deduce the reasons for methane being a gas on Earth.
(c) Water is used as a coolant in sweat. Using the data in the table, explain the reasons for methane not being as suitable as water for use as a coolant.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
(a)
a. water forms hydrogen bonds but methane does not/hydrogen bonds form between water molecules, but are absent in methane;
b. energy needed to break hydrogen bonds/intermolecular attractions;
c. hydrogen bonds raise the freezing point/boiling point/heat capacity/heat of vaporization
(b)
a. boiling point of methane is -160°C
OR
methane is in gaseous state when temperatures are above/higher than
-160°C;
b. temperatures on Earth are always above -160°C;
(c)
a. heat of vaporization is low/heat of vaporization is only 760 J g-1
OR
methane has a lower heat of vaporization compared to water;
b. no hydrogen bonds need to be broken;
c. not enough heat removed when methane evaporates;
d. methane boils at -160 °C so would already be a gas (in/on the human body);
Question
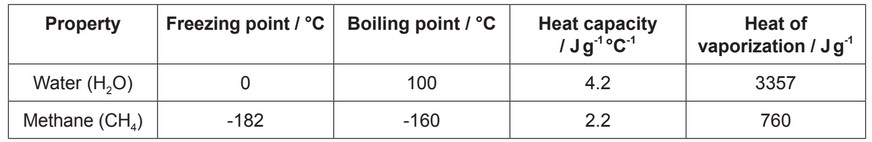
The diagram shows water molecules as they might be arranged in liquid water and the interactions between them.
(a) (i) State how many water molecules are shown in the diagram.
(ii) Identify the interactions that are shown between the water molecules.
(b) (i) With reference to the diagram, explain how water in sweat evaporates.
(ii) Outline the reasons for secretion of sweat in humans.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
(a) (i) 10;
(ii) hydrogen bonds/H bond;
(b)
(i)
a. heat increases molecular motion/vibration;
b. hydrogen bonds break/bonds between water molecules break;
c. water evaporation is separation of water molecules/water changes from liquid to gas/vapour;
d. heat removed from skin surface/body;
(ii)
a. cooling/removal of heat/lowering body temperature;
b. to prevent overheating
OR
to help maintain body temperature/temperature homeostasis/for
thermoregulation
OR
to keep temperature at 37 °C;
Question
(a) Describe anaerobic respiration in humans and in yeast.
(b) Methane can be the product of anaerobic respiration in some organisms.
(i) Distinguish between the thermal properties of water and methane.
(ii) Explain the role of methane in climate change.
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
a)
a. (in both) anaerobic respiration gives a small amount of ATP/2 ATP/energy from glucose;
b. anaerobic respiration occurs when there is no oxygen;
c. anaerobic respiration in yeast produces ethanol and carbon dioxide/alcoholic fermentation;
d. anaerobic respiration in humans (in muscle) produces lactate/lactic acid/lactic acid
fermentation;
e. both undergo glycolysis;
b) i. a. water has higher boiling/melting point;
b. water has a higher specific heat capacity;
c. water has a higher latent heat of vaporization;
d. differences due to water having many H-bonds/polarity between the molecules while methane
has no H-bonds/polarity;
ii.
a. methane is a greenhouse gas
OR
methane causes an increase in temperature of the atmosphere;
b. methane is one of the most powerful greenhouse gases / more powerful than CO2;
c. methane has a relatively short lifespan compared to CO2/decomposes to CO2;
Question
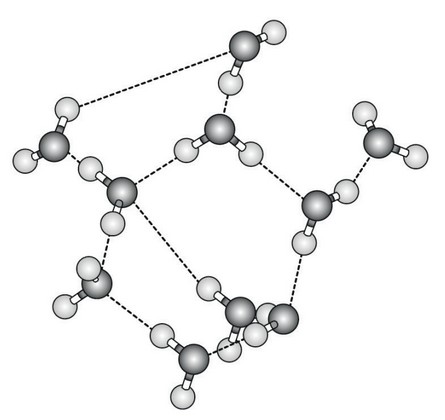
The figure represents a water molecule.
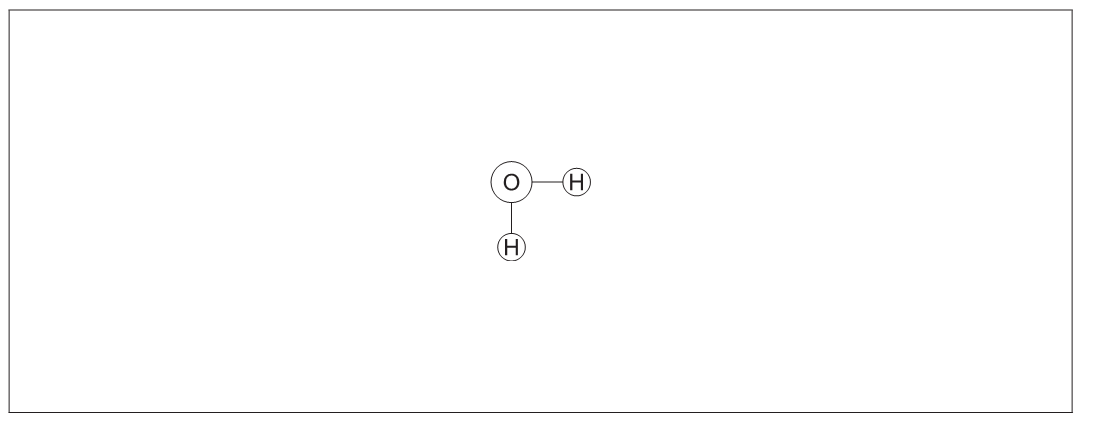
a. Draw a second water molecule to show how bonds can form between water molecules, including the name of the bond.[2]
b. Water has important solvent properties. Explain these properties using an example to illustrate your answer. [3]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a.
a. similar water molecule drawn with oxygen on one molecule facing hydrogen on the other water molecule
b. one hydrogen bond drawn as a dotted/dashed line between the two water molecules and labelled
O and H do not have to be labelled but must be positioned correctly
eg :
Can get this mark even if atoms incorrect
a. water molecule is polar
OR
water has «weak» positive and negative charges
c. water forms hydrogen bonds with polar substances
d. positive/hydrogen side/pole of water attracted to negative ions
OR
negative/oxygen side/pole attracted to positive ions
e. glucose/other example dissolves because it is polar
OR
sodium chloride/other example dissolves because ions are attracted to water