Question
The electron micrograph shows the surface membrane of an animal cell.

(a) State the technique used to obtain this electron micrograph.
(b) Using the scale, calculate the magnification of the image.
(c) Identify the type of molecule that can be seen at region X.
(d) Outline the reason that images such as this falsified the Davson-Danielli model.
(e) Explain the reason that animal cells and tissues under investigation must be maintained in solutions with the same osmolarity.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
(a) freeze fracture/etching
OR
involves freezing and fracturing cells;
(b) 140000 to 150 000 (X);
(c) protein/named membrane protein;
(d) the phospholipid bilayer was not coated by/sandwiched between two protein layers
OR
(transmembrane/integral) proteins are found within the phospholipid bilayer;
(e)
a. to prevent osmosis;
b. cells placed in the in the incorrect osmolarity might swell/burst/shrink;
c. hypotonic solution would cause water to enter cells/tissues;
d. hypertonic solutions would cause water to leave cells/tissues;
e. water loss would hinder (metabolic) reactions in cell cytoplasm
OR
distort appearance of the cells (for the investigation);
Question
Draw the ultrastructure of a prokaryotic cell based on electron micrographs. [3]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans
a.cell wall;
b.plasma membrane; Clearly shown as a separate line under the cell wall or theinner line
c.cytoplasm AND 70S ribosomes; Do not allow (small) circles
d.nucleoid/naked DNA;
e.plasmid
OR
pili
OR
flagella/flagellum;

Question
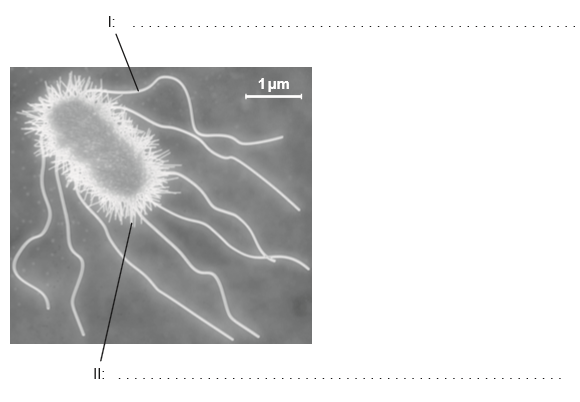
a. Outline the cell theory[2]
b (i) Annotate the electron micrograph of the Escherichia coli cell with the function of the structures labelled I and II.[2]
b (ii) falculate the magnification of the electron micrograph.[4]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. living things are composed of cells;
b. cells are the basic/smallest unit of life;
c. cells come from pre-existing cells;
Do not accept cells are the “smallest organisms”.
Do not accept “cells are the building blocks” of life on its own.
a. I: locomotion;
b. II: attachment to surfaces / holds bacteria together / conjugation;
Do not accept “exchange material” on its own.
If more than one function is given, mark the first answer only.
×15 000 (accept answers in the range of × 14 000 to × 16 000)
Examiners report
Most gained both marks for their knowledge of cell theory in part a.
Students who read the rubric correctly in b scored well. However approximately half of the students read “label” instead of “function”.
A disappointing number had no idea how to calculate the magnification (15000X) and some answers showed no concept of scale, with answers such as 0.15 X or 5×10-7 X.
Question
Draw a labelled diagram of a prokaryotic cell.
Bacteria are prokaryotes that sometimes act as pathogens. Describe how the body can defend itself against pathogens.
Explain the evolution of antibiotic resistance in bacteria.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. cell wall – uniformly thick and drawn outside the plasma membrane;
b. plasma membrane – a continuous single line;
c. cytoplasm/cytosol;
d. nucleoid/(naked) DNA – shown as a tangle of thread or irregular shape without a nuclear membrane;
e. (70S) ribosomes – drawn as a small circle or dark dot;
f. pili – hair like structures / flagellum – shown to be longer than any pili;
g. plasmid – circular ring of DNA;
h. capsule – drawn outside the cell wall;
Award [1] for each structure clearly drawn and labelled which conforms to the italicized guidelines given above.
Remember, up to TWO “quality of construction” marks per essay.
a. skin/mucus membranes act as barrier (to pathogens);
b. sebaceous glands secrete lactic acid/fatty acids/sebum / make surface of skin acidic;
c. (skin/stomach) acid prevents growth of many pathogens;
d. lysozyme in mucus can kill bacteria;
e. pathogens caught in sticky mucus and removed from body;
f. inflammatory response/inflammation can cause swelling/redness/fever (to inhibit the pathogen);
g. phagocytes/macrophages/leucocytes/white blood cells (non-specifically) identify (pathogens/bacteria/fungi/viruses) as foreign;
h. (phagocytes macrophages/leucocytes/white blood cells) ingest pathogens;
i. specific lymphocytes recognize one specific antigen;
j. (antigen-specific) lymphocytes clone themselves;
k. lymphocytes/leucocytes produce antibodies;
l. antigen-antibody complex formed and stimulates destruction of pathogen;
a. antibiotics (are chemicals) used to treat bacterial diseases;
b. within populations, bacteria vary in their (genetic) resistance to antibiotics/fitness;
c. resistance arises by (random) gene mutation;
d. when antibiotics are used antibiotic-sensitive bacteria are killed;
e. (natural) selection favours those with resistance;
f. resistant bacteria survive, reproduce and spread the gene / increase allele frequency of resistant bacteria;
g. the more an antibiotic is used, the more bacterial resistance/the larger the population of antibiotic-resistant bacteria;
h. genes can be transferred to other bacteria by plasmids;
i. doctors/vets use different antibiotics but resistance develops to these as well;
j. multiple-antibiotic resistant bacteria evolve/it becomes difficult to treat some infections;
(Plus up to [2] for quality)
Question
The diagram shows some of the structures in an animal cell.
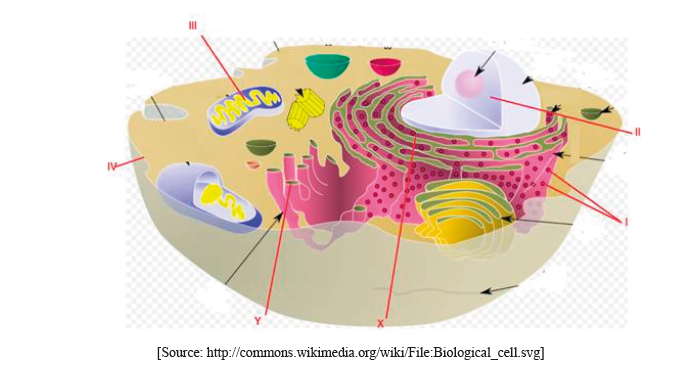
(i) Label structures I, II, III and IV.
I.
II.
III.
IV.
(ii) State one function of structure III.
Explain how materials are transported within a cell between structures X and Y.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
(i) Award [1] for any two of the following correctly labeled.
I. ribosomes
II. nucleus (do not accept nuclear membrane)
III. mitochondrion
IV. plasma/cell membrane
(ii) ATP production/site of aerobic respiration (do not accept energy production)
(protein) material transported by vesicles;
from rER to Golgi apparatus/complex/body/membrane;
vesicles bud off from rER/fuse with Golgi membrane (due to membrane fluidity);
Do not accept vacuole(s).