Question
Lipids are more efficient energy stores than carbohydrates. What is a reason for this?
A. Lipids are bigger molecules than carbohydrates.
B. Lipids release more energy per gram than carbohydrates.
C. Lipids can be more easily mobilized than carbohydrates when needed.
D. Lipids can be used in aerobic and anaerobic respiration when needed.
Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question
The table shows the range and classification of body mass index (BMI) values, as shown in the nomogram.
BMI value | Less than 18.5 | 18.5 to 24.9 | 25.0 to 29.9 | 30.0 or more |
Classification | underweight | normal weight | overweight | obese |
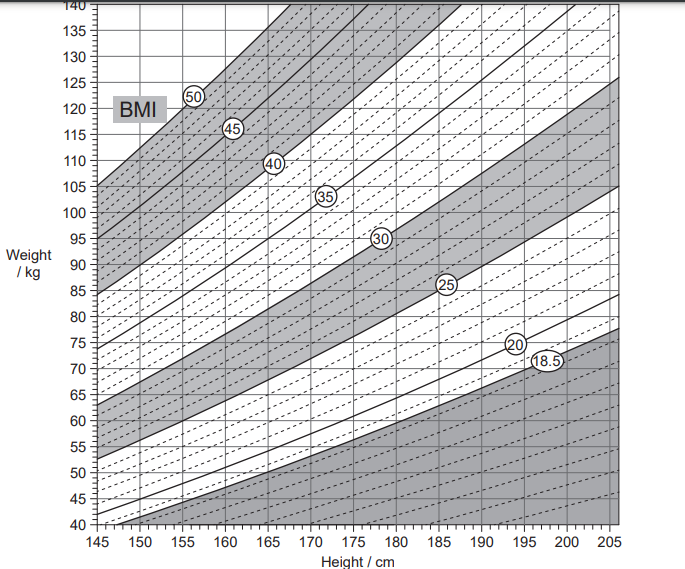
What is the approximate reduction in body mass that a person of height 155 cm and mass 95 kg
would have to lose to reach normal body mass?
10 kg
22 kg
36 kg
54 kg
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: C