Question
By which process do potassium ions move through potassium channels in axons?
Active transport
Exocytosis
Facilitated diffusion
Simple diffusion
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
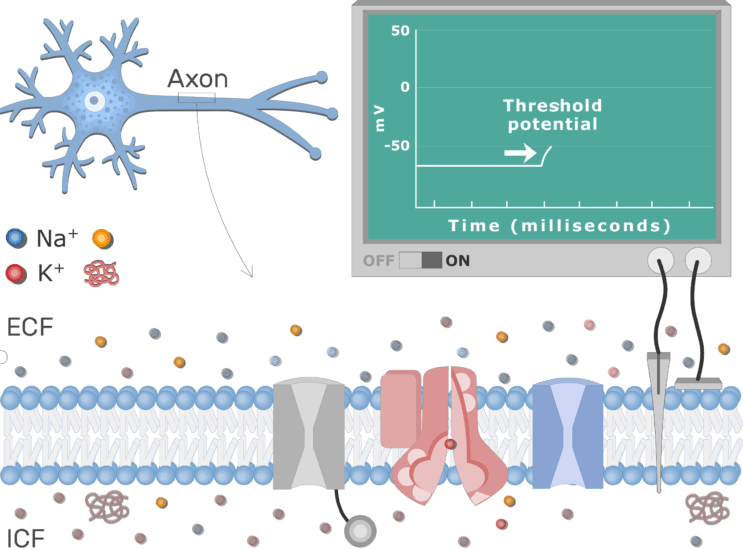
Facilitated diffusion of potassium is a process by which potassium ions move through potassium channels in axons. Potassium channels are integral proteins with a hydrophilic inner pore that allow potassium ions to pass through. This process does not require energy and is driven by the concentration gradient of potassium ions across the membrane. Facilitated diffusion of potassium is important for the transmission of electrical impulses by nerve cells.
The diagram is a model of one type of movement across a membrane.
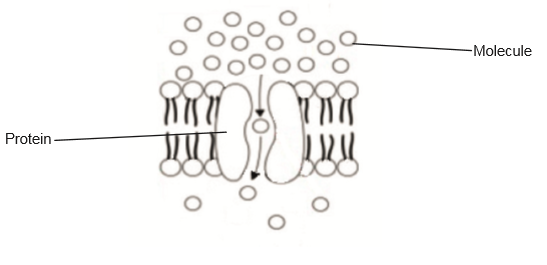
What is this type of movement?
A. Simple diffusion
B. Facilitated diffusion
C. Osmosis
D. Active transport
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
B
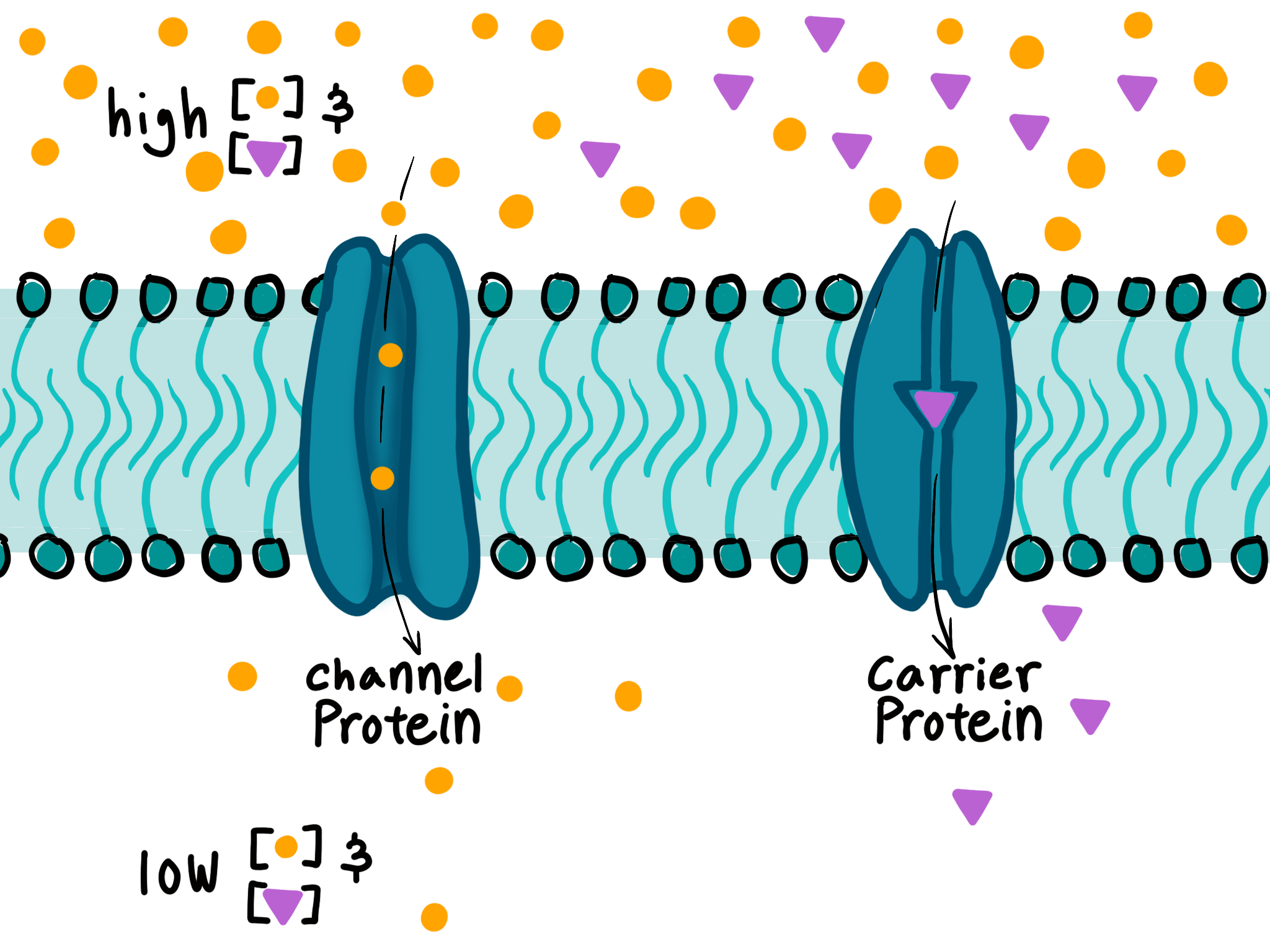
Facilitated diffusion is a type of passive transport that allows substances to move across a cell membrane with the help of transport proteins. It is a selective process, meaning that only certain molecules and ions can pass through the membrane. This process does not require energy from ATP hydrolysis.
What features of a cell favour efficient removal of waste products?
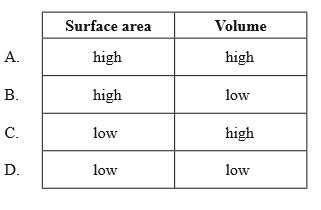
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
B
The surface area to volume ratio (SA:V) of a cell affects how efficiently it can remove waste products.
The higher the SA:V, the easier it is for the cell to exchange substances with its environment. This is because a high SA:V means that the cell has more surface area relative to its volume, so it can diffuse more substances across its membrane per unit of time.
A low SA:V means that the cell has less surface area relative to its volume, so it can diffuse fewer substances across its membrane per unit of time. This can limit the cell size, because if the cell grows too large, its metabolic rate may exceed the rate of exchange of vital materials and wastes. The cell may not be able to get enough nutrients and oxygen, or get rid of carbon dioxide and waste materials fast enough.
Therefore, a high SA:V can favor efficient removal of waste products by allowing faster diffusion across the cell membrane. A low SA:V can hinder efficient removal of waste products by slowing down diffusion across the cell membrane.

The salt concentration inside the Paramecium is 1.8 %. The salt concentration in the surrounding medium suddenly drops to 0.2 %. What will be the likely response?
A. The cell will lose salt to the medium.
B. The contractile vacuole will expel more water.
C. The cell will swell and eventually burst.
D. The membrane will become more permeable to salt.
▶️Answer/Explanation
is the correct answer.
When the salt concentration outside the cell suddenly drops, water will move into the cell by osmosis, causing the cell to swell. To prevent the cell from bursting, the contractile vacuole will expel more water from the cell.
This process of expelling excess water from the cell is known as osmoregulation, and it is the correct response to a sudden drop in salt concentration in the surrounding medium.