Question
Substances can move into and out of cells through the cell membrane.
a. Outline the significance of surface area to volume ratio in the limitation of cell size.[4]
b. Describe transport across cell membranes by osmosis.[4]
c. Explain the adaptations of the small intestine to its function.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
a. a. surface area of the cell affects the rate of material exchange;
b. when the cell increases in size, so does its chemical activity/metabolism;
c. (when the cell increases in size/grows) more substances need to be taken in / more waste products need to be excreted;
d. as the volume of the cell increases, so does the surface area, however not to the same extent
OR
when the cell gets bigger, its surface area to volume ratio gets smaller;
e. substances will not be able enter the cell fast enough/cell volume will not be supplied
OR
metabolic rate will exceed the rate of exchange
OR
when the surface area: volume ratio is higher, the diffusion rate increases;
f. some cells have adaptations to increase their surface area/flatten/microvilli/shape of red blood cells;
g. cells in growth areas tend to divide and remain small
OR
cells divide when maximum size is reached;
b. a. form of diffusion;
b. osmosis is the movement of water molecules;
c. (movement) across a selectively/semi/partially_permeable membrane/cell membrane;
d. from a region of low solute concentration to a region of high solute concentration (until equilibrium is reached)
OR
movement of water molecules from a high concentration of water to a low concentration of water molecules;
e. it is a passive transport mechanism/does not use ATP;
f. channel proteins/aquaporins are used;
c. a. small intestine is where nutrients are absorbed into the bloodstream;
b. very long to maximize absorption;
c. (the small intestine) is lined with (smooth) muscle to allow for the mixing/ and moving of digested food;
d. muscles are circular and longitudinal;
e. that perform peristalsis;
f. the pancreas (and gall bladder) secretes substances into the small intestine to aid digestion;
g. contain villi, to increase surface area;
h. villi have microvilli to increase surface area even more;
i. villi absorb products of digestion/mineral ions/vitamins/glucose;
j. dense capillary network rapidly transports absorbed products;
k. lacteal absorbs lipids from the intestine (into the lymphatic system);
I. (most of the) chemical digestion (into monomers) occurs in small intestine/description of specific enzyme action;
Accept annotated diagrams as part of the explanation.
Question
a. Outline four types of membrane transport, including their use of energy.[4]
b. Draw the structure of a dipeptide.[3]
c. Explain the action of enzymes in digestion and the different roles of at least two named enzymes that are produced in the pancreas.[8]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
a. a. simple diffusion is passive movement of molecules/ions along a concentration gradient \(\sqrt{ }\)
b. facilitated diffusion is passive movement of molecules/ions along a concentration gradient through a protein channel «without use of energy» \(\checkmark\)
c. osmosis is the passage of water through a membrane from lower solute concentration to higher \(\checkmark\) OWTTE
d. active transport is movement of molecules/ions against the concentration gradient «through membrane pumps» with the use of ATP/energy
\(\checkmark\) Active transport requires mention of the use of energy.
e. endocytosis is the infolding of membrane/formation of vesicles to bring molecules into cell with use of energy
OR
exocytosis is the infolding of membrane/formation of vesicles to release molecules from cell with use of energy \(\checkmark\)
f. chemiosmosis occurs when protons diffuse through ATP synthase «in membrane» to produce ATP \(\checkmark\)
The description of each type of transport should include the name and brief description.
mpa, mpb and mpc require reference to concentration.
b. a. two amino acids, one with \(\mathrm{NH}_2 / \mathrm{NH}_3+\) end and one with \(\mathrm{COOH} / \mathrm{COO}-\mathrm{end} \checkmark\)
b. peptide bond between \(\mathrm{C}=0\) and \(\mathrm{N}-\mathrm{H}\) correctly drawn \(\checkmark\)
c. «chiral» \(\mathrm{C}\) with \(\mathrm{H}\) and \(\mathrm{R}\) group on each amino acid \(\checkmark\)
d. peptide bond labelled/clearly indicated between \(C\) terminal of one amino acid and \(\mathrm{N}\) terminal of the second amino acid \(\checkmark\)
c. a. enzymes catalyse/speed up chemical reactions/lower the energy needed \(\checkmark\) OWTTE
b. have specific active sites to which specific substrates bind \(\checkmark\)
c. enzyme catalysis involves molecular motion and the collision of substrates with the active site \(\checkmark\) OWTTE
d. enzymes break macromolecules into monomers/smaller molecules indigestion \(\checkmark\)
e. smaller molecules/monomers more readily absorbed \(\checkmark\)
f. <<pancreas > secretes enzymes into the «lumen of» small intestine \(\checkmark\)
g. the small intestine has an alkaline \(\mathrm{pH} \checkmark\)
h. enzymes have maximum action at specific \(\mathrm{pHs}\)
OR
enzymes can be denatured at other \(\mathrm{pHs} \checkmark\)
i. amylase breaks down starch into sugars/disaccharides \(\checkmark\)
j. lipase breaks lipids/triglycerides into monoglycerides/fatty acids and glycerol \(\checkmark\)
k. endopeptidase/protease breaks «peptide» bonds in proteins/polypeptides \(\checkmark\)
I. accept any other valid pancreatic enzyme, substrate and product \(\checkmark\)
Award [ 6 max] if there is no mention of two specific groups of enzymes.
Question
The image shows a phospholipid bilayer that is a component of the cell membrane.
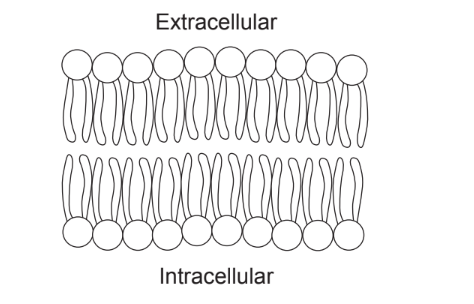
(a) Annotate the diagram to illustrate the amphipathic nature of phospholipids. [2]
(b) Outline a function of cholesterol in cell membranes. [1]
(c) Describe two pieces of evidence that show that eukaryotic cells originated by endosymbiosis. [2]
Answer/Explanation
a a. line to circle labelled phosphate (head) and (tail) labelled fatty acid/hydrocarbon/lipid (tail);
b. label hydrophilic/polar/attracted to water/ and hydrophobic/non polar/not attracted to water;
b reduces fluidity of membrane / reduces permeability of membrane (to some molecules);
c a. mitochondria/chloroplasts have their own DNA;
b. mitochondria can self-replicate/undergo a process like binary fission;
c. mitochondria/chloroplasts have double membranes;
d. mitochondria/chloroplasts have(70s) ribosomes;
e. mitochondria/chloroplasts are sensitive to antibiotics;
f. similar in size to bacteria