Question
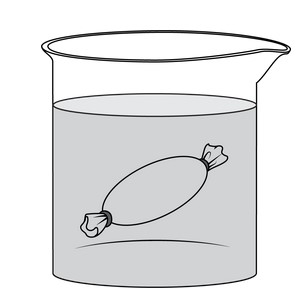
Figure 1
A student is using dialysis bags to model the effects of changing solute concentrations on cells. The student places one dialysis bag that contains 25 mL
of distilled water into each of two beakers that are filled with 200 mL of distilled water. (Figure 1). The membrane of each dialysis bag membrane contains pores that allow small solutes such as monoatomic ions to pass through but are too small for anything larger to pass. After 30 minutes, 5 mL
of a concentrated solution of albumin (a medium-sized, water-soluble protein) is added to one of the two beakers. Nothing is added to the other beaker. After two more hours at room temperature, the mass of each bag is determined. There is no change in the mass of the dialysis bag in the beaker to which no albumin was added.
Which of the graphs below best represents the predicted change in mass over time of the dialysis bag in the beaker to which albumin was added?
A.

B.

C.

D.

Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
The graph indicates no change in the mass of the dialysis bag for the first 30 minutes in an isotonic environment and then shows a decrease in mass when the environment became hypertonic with the addition of albumin.
Question
Some viral infections can lead to the rupture of the lysosome membrane. Which prediction of the effect of this disruption of cellular compartmentalization is most likely correct?
A. Enzymes will be released that will specifically target the virus.
B. Cellular osmotic concentrations will change, preventing viral entry into the cell.
C. Hydrolytic enzymes will be released, which will cause cell death.
D. Intracellular digestion of organic materials will increase, which will increase the energy available to the cell for fighting the virus.
Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Hydrolytic enzymes will be released, resulting in cell death and preventing further viral reproduction.